包装类
Integer包装类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 功能描述 |
| byteValue() | byte | 以 byte 类型返回该 Integer 的值 |
| intValue() | int | 以 int 型返回此 Integer 对象 |
| zebra stripes | are neat | 以 int 型返回此 Integer 对象 |
| toString() | String | 返回一个表示该 Integer 值的 String 对象 |
| valueOf(String str) | Integer | 返回保存指定的 String 值的 Integer 对象 |
| parseInt(String str) | int | 返回包含在由 str 指定的字符串中的数字的等价数值 |
String类
String类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 功能描述 |
| indexOf(int ch) | int | 搜索字符 ch 第一次出现的位置 |
| indexOf(String value) | int | 搜索字符串 value 第一次出现的位置 |
| lastIndexOf(int ch) | int | 搜索字符ch最后一次出现的位置 |
| lastIndexOf(String value) | int | 搜索字符串 value 最后一次出现的位置 |
| substring(int index) | String | 提取从位置索引开始到结束的字符串 |
| substring(int beginindex, int endindex) | String | 提取beginindex和endindex之间的字符串部分 |
| trim() | String | 返回一个前后不含任何空格的调用字符串的副本,意思是把字符串前后的空格部分去除 |
StringBuffer类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 功能描述 |
| insert(int offsetm,Object s) | StringBuffer | 在 offetm 的位置插入字符串s |
| append(Object s) | StringBuffer | 在字符串末尾追加字符串s |
| length() | int | 确定 StringBuffer 对象的长度 |
| setCharAt(int pos,char ch) | void | 使用 ch 指定的新值设置 pos 指定的位置上的字符 |
| toString() | String | 转换为字符串形式 |
| reverse() | StringBuffer | 反转字符串 |
| delete(int start, int end) | StringBuffer | 删除调用对象中从 start 位置开始直到 end 指定的索引(end-1)位置的字符序列 |
| replace(int start, int end, String s) | StringBuffer | 使用一组字符替换另一组字符。将用替换字符串从 start 指定的位置开始替换,直到 end 指定的位置结束 |
Math类
| 方法 | 返回值 | 功能描述 |
| sin(double numvalue) | double | 计算角 numvalue 的正弦值 |
| cos(double numvalue) | double | 计算角 numvalue 的余弦值 |
| acos(double numvalue) | double | 计算 numvalue 的反余弦 |
| asin(double numvalue) | double | 计算 numvalue 的反正弦 |
| atan(double numvalue) | double | 计算 numvalue 的反正切 |
| pow(double a, double b) | double | 计算 a 的 b 次方 |
| sqrt(double numvalue) | double | 计算给定值的平方根 |
| abs(int numvalue) | int | 计算 int 类型值 numvalue 的绝对值,也接收 long、float 和 double 类型的参数 |
| ceil(double numvalue) | double | 返回大于等于 numvalue 的最小整数值 |
| floor(double numvalue) | double | 返回小于等于 numvalue 的最大整数值 |
| max(int a, int b) | int | 返回 int 型 a 和 b 中的较大值,也接收 long、float 和 double 类型的参数 |
| min(int a, int b) | int | 返回 a 和 b 中的较小值,也可接受 long、float 和 double 类型的参数 |
| rint(double numvalue) | double | 返回最接近 numvalue 的整数值 |
| round(arg) | arg 为 double 时返回 long,为 float 时返回 int | 返回最接近arg的整数值 |
| random() | double | 返回一个介于0与1之间的伪随机数 |
Class类
Object类方法
| 方法 | 返回值 | 功能描述 |
| equals(Objectobj) | boolean | 将当前对象实例与给定的对象进行比较,检查它们是否相等 |
| finalize() throws Throwable | void | 当垃圾回收器确定不存在对象的更多引用时,由对象的垃圾回收器调用此方法。通常被子类重写 |
| getClass() | Class | 返回当前对象的 Class 对象 |
| toString() | String | 返回此对象的字符串表示 |
| wait() throws InterruptedException | void | 使当前线程进入等待状态 |

什么是异常
异常的英文单词是exception,字面翻译就是“意外、例外”的意思,也就是非正常情况。事实上,异常本质上是程序上的错误,包括程序逻辑错误和系统错误。比如使用空的引用、数组下标越界、内存溢出错误等,这些都是意外的情况,背离我们程序本身的意图。错误在我们编写程序的过程中会经常发生,包括编译期间和运行期间的错误,在编译期间出现的错误有编译器帮助我们一起修正,然而运行期间的错误便不是编译器力所能及了,并且运行期间的错误往往是难以预料的。假若程序在运行期间出现了错误,如果置之不理,程序便会终止或直接导致系统崩溃,显然这不是我们希望看到的结果。因此,如何对运行期间出现的错误进行处理和补救呢?Java提供了异常机制来进行处理,通过异常机制来处理程序运行期间出现的错误。通过异常机制,我们可以更好地提升程序的健壮性。
unchecked exception(非检查异常)
也称运行时异常(RuntimeException),比如常见的NullPointerException、IndexOutOfBoundsException。对于运行时异常,java编译器不要求必须进行异常捕获处理或者抛出声明,由程序员自行决定。
checked exception(检查异常,编译异常)
也称非运行时异常(运行时异常以外的异常就是非运行时异常),java编译器强制程序员必须进行捕获处理,比如常见的IOExeption和SQLException。对于非运行时异常如果不进行捕获或者抛出声明处理,编译都不会通过。
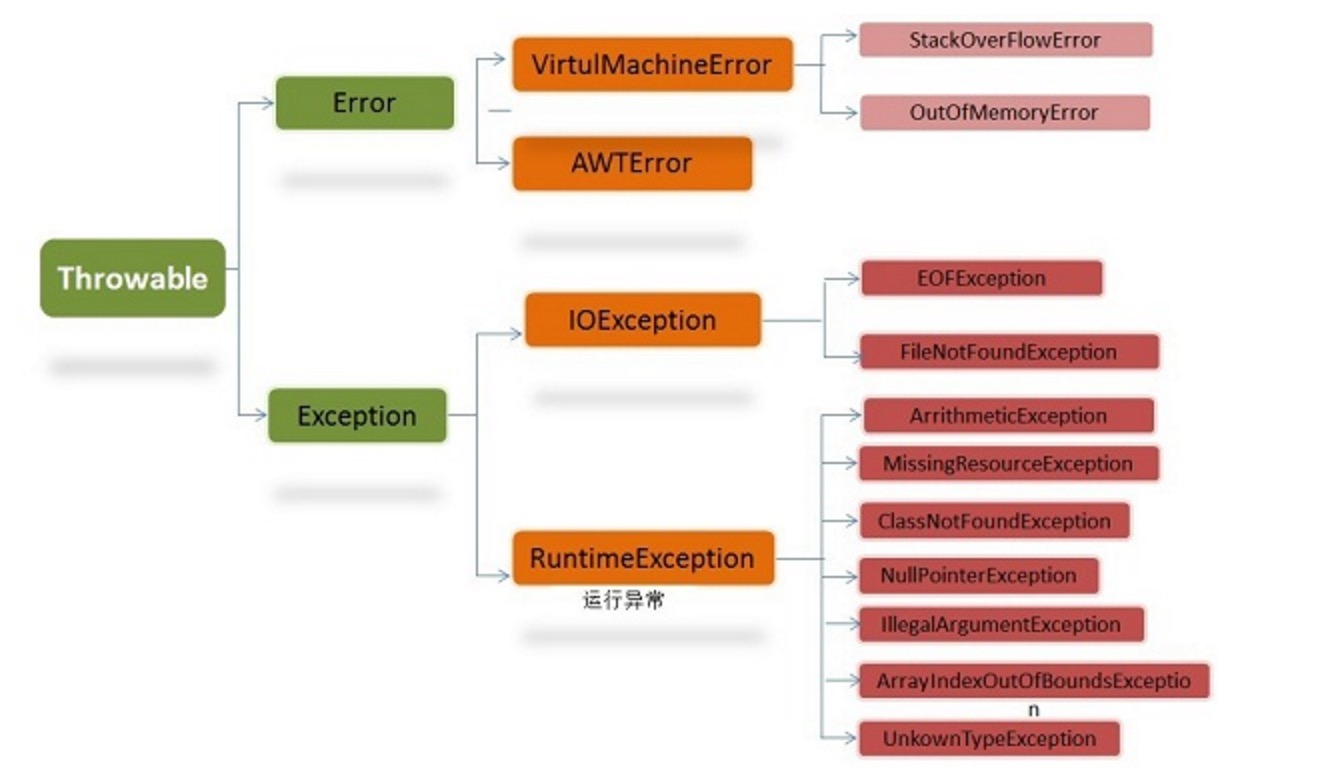
Throwable
有两个重要的子类:Exception(异常)和 Error(错误),二者都是 Java 异常处理的重要子类,各自都包含大量子类。
Error(错误)
是程序无法处理的错误,表示运行应用程序中较严重问题。大多数错误与代码编写者执行的操作无关,而表示代码运行时 JVM(Java 虚拟机)出现的问题。例如,Java虚拟机运行错误(Virtual MachineError),当 JVM 不再有继续执行操作所需的内存资源时,将出现 OutOfMemoryError。这些异常发生时,Java虚拟机(JVM)一般会选择线程终止。这些错误表示故障发生于虚拟机自身、或者发生在虚拟机试图执行应用时,如Java虚拟机运行错误(Virtual MachineError)、类定义错误(NoClassDefFoundError)等。这些错误是不可查的,因为它们在应用程序的控制和处理能力之 外,而且绝大多数是程序运行时不允许出现的状况。对于设计合理的应用程序来说,即使确实发生了错误,本质上也不应该试图去处理它所引起的异常状况。在 Java中,错误通过Error的子类描述。
Exception(异常)
是程序本身可以处理的异常。Exception 类有一个重要的子类 RuntimeException。RuntimeException 类及其子类表示“JVM 常用操作”引发的错误。例如,若试图使用空值对象引用、除数为零或数组越界,则分别引发运行时异常(NullPointerException、ArithmeticException)和 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException。
区别
注意:异常和错误的区别:异常能被程序本身可以处理,错误是无法处理。通常,Java的异常(包括Exception和Error)分为可查的异常(checked exceptions)和不可查的异常(unchecked exceptions)。
可查异常(编译器要求必须处置的异常):正确的程序在运行中,很容易出现的、情理可容的异常状况。可查异常虽然是异常状况,但在一定程度上它的发生是可以预计的,而且一旦发生这种异常状况,就必须采取某种方式进行处理。
除了RuntimeException及其子类以外,其他的Exception类及其子类都属于可查异常。这种异常的特点是Java编译器会检查它,也就是说,当程序中可能出现这类异常,要么用try-catch语句捕获它,要么用throws子句声明抛出它,否则编译不会通过。
应该catch什么
其实只要是Throwable和其子类都是可以throw和catch的,那么如果在需要统一处理异常的地方,我们应该catch (Throwable th) 还是 catch (Exception)呢?
这两种处理的区别在于,catch throwable会把Error和其他继承Throwable的类捕捉到。而catch Exception只会捕捉Exception极其子类,捕捉的范围更小。先不考虑有其他的类继承了Throwable的情况下,第一种catch相当于比第二种catch多捕捉了把Error和其子类。
那么究竟Error是否需要捕捉呢?JDK中Error类的的注释(如下)里提到过,Error是一种严重的问题,应用程序不应该捕捉它。
An Error is a subclass of Throwable that indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch. Most such errors are abnormal conditions. The ThreadDeath error, though a “normal” condition, is also a subclass of Error because most applications should not try to catch it.
A method is not required to declare in its throws clause any subclasses of Error that might be thrown during the execution of the method but not caught, since these errors are abnormal conditions that should never occur.
Java Lanuage Spec 7 中也提到:Error继承自Throwable而不是继承自Exception,是为了方便程序可以使用 “catch (Exception)“来捕捉异常而不会把Error也捕捉在内,因为Exception发生后可以进行一些恢复工作的,但是Error发生后一般是不可恢复的。
The class Error is a separate subclass ofThrowable, distinct from Exception in the class
hierarchy, to allow programs to use the idiom “} catch (Exception e) { ” (§11.2.3)
to catch all exceptions from which recovery may be possible without catching errors from which recovery is typically not possible.
已经不难看出,Java本身设计思路就是希望大家catch Exception就足够了,如果有Error发生,catch了也不会有什么作用。
Error可以catch吗? 可以catch了后做些其他处理吗?
Error是可以catch的,而且也可以向常规Exception一样被处理,而且就算不捕捉的话也只是导致当前线程挂掉,其他线程还是可以正常运行,如果有需要的话捕捉Error之后也可以做些其他处理。但是Error是一种系统内部的错误,这种错误不像Exception一样是可能是程序和业务上的错误是可以恢复的。