老规矩,先上原题
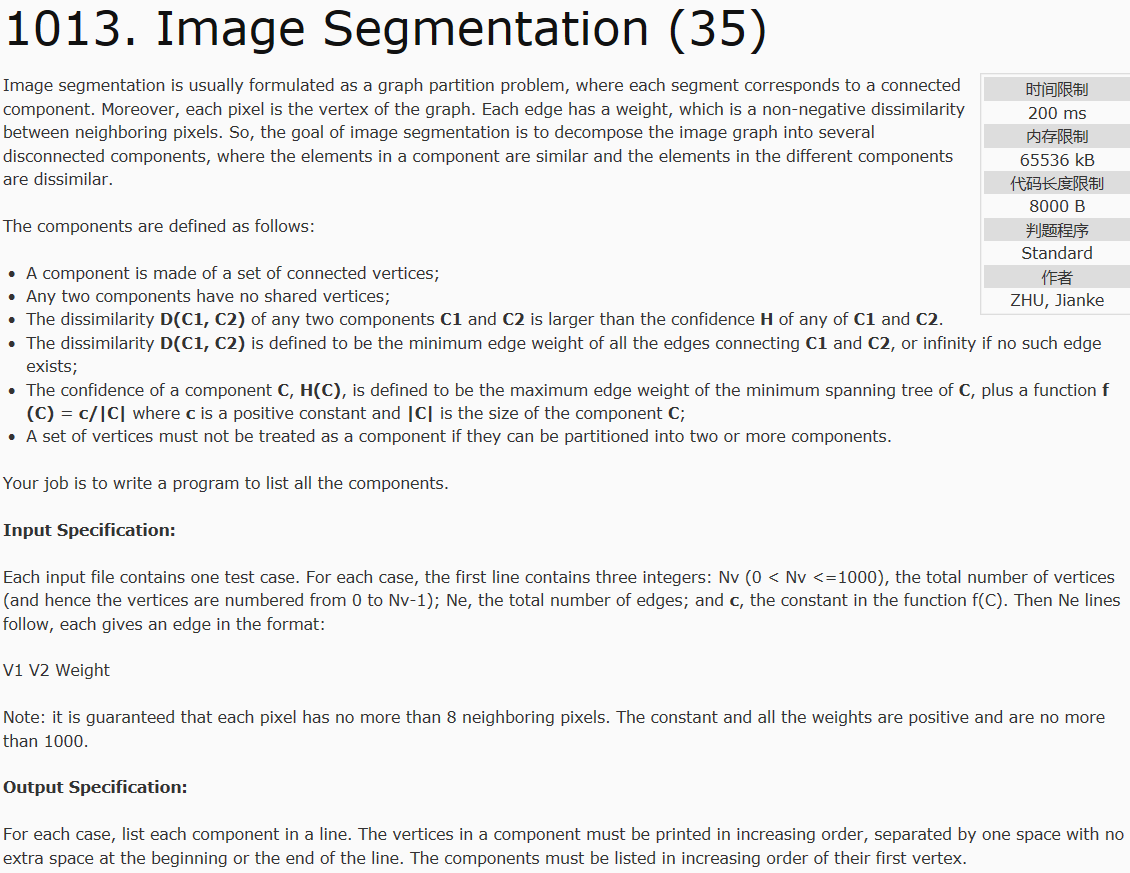
题目大意就是将一个图的节点拆分成尽可能多的若干块连通分量,并且任意两块分量间要满足以下性质:
D(C1,C2)>H(C1) or D(C1,C2)>H(C2)
其中:D=连接C1,C2的所有边中权值最小的边的权值 H=最小生成树的权值最大边的权值+常数c/块内的点数
这里要注意是大于其中一个任意一个就行了,文中用词是any而不是both
这题乍一看毫无思路,借鉴了http://blog.csdn.net/jtjy568805874/article/details/53435235的逆向思维做法后豁然开朗!
不过这哥们居然证明都略了,我还是费了点脑子的:
一开始每个节点都独立成块。
把所有边按权值从小到大排序(可以看出就是kruskal的变型)。
按权值从小到大依次取出一条边e:
如果边的两端分别属于不同的块C1,C2,则判断如果不连上这条边,C1,C2是否会不满足支持他们相互独立的条件e.weight>=D(C1,C2)>H(C1) or D(C1,C2)>H(C2),用如果不满足就合并这两个块。
所有边取完了,结果也就出来了。
这个算法之所以正确,精妙之处在于由于是从小到大取,当前这条边(e)权值必然比以后所有边都小的,所有用于连接(合并本来的不合并的块)的边的必然恰好构成最小生成树,且任意两块之间最多只有一条边相连,因此只要当前的C1,C2由于这条边e的存在无法满足独立性,假设后续某一时刻t由于某种方式C1,C2两块东西重新分离开了,分离的可能性:
1.新出现块C3,C2与C3合并为C23。C1与C23这两块竟然可以相互独立,须满足e>c/(C(C2)+C(C3))+最大边(C23);
2.新出现块C3,C1与C3合并为C13。C1与C13这两块竟然可以相互独立,须满足e>c/(C(C1)+C(C3))+最大边(C13);
3.新出现块C3,C4,C23与C14相互独立,且C23合并发生在C14之前,且C14连接出现之前C23和C1不能相互独立
4.新出现块C3,C4,C23与C14相互独立,且C14合并发生在C23之前,且C23连接出现之前C14和C2不能相互独立
由于1,2对称我们先证明情况1
设C23发生合并的边为e2,则e2>=C23中所有的边,更大于等于e(因为e2最后加入),则e2>=e>c/(C(C2)+C(C3))+最大边(C23);而此时最大边(C23)==e2,推出了e2>c/(C(C2)+C(C3))+e2,又c为正数,产生矛盾,故情况1,2不成立。
由于3,4对称我们来证明3,设连接C23的边为e2,连接C14的边为e3,则满足e>c/(C(1)+C(4))+最大边(C14),根据题设顺序可得e<=e2<=e3,即e3>c/(C(1)+C(4))+最大边(C14),而此时最大边(C14)==e3,又c为正数,同样产生矛盾,故情况3,4不成立。
综上,只要两块东西由于边e发生相连无法维持其相互独立性,不管是最终两块东西都与其他块发生合并,还是只有其中一块与其他块发生合并,都不会影响e相连导致的这次失去独立性的正确性,
#include "stdafx.h"//提交时去掉此行 #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <queue> #define rep(i,j,k) for(int i=j;i<=k;i++) #define range(i,j,k) for(int i=j;i<k;i++) #define println3(a,b,c) cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<" " using namespace std; const int oo = 999999999; class Edge { public: int v1 = 0, v2 = 0; float weight = 0; void my_read() { cin >> v1 >> v2 >> weight; } void my_write() { println3(v1,v2,weight); } }; class Component { public: void init(int node_index) { bcj_root = node_index; members.resize(1); members[0] = node_index; } vector<int> members;//包含根节点在内 int bcj_root=0;//根节点//排序前自己的下标不等于这个说明自己被并到别人那里了 void write_me() { range(i, 0, members.size()) { if (i==members.size()-1) { cout << members[i]; } else cout << members[i] << " "; } cout << " "; } void sort_members() { sort(members.begin(),members.end()); } }; class Graph { public: vector<Edge> edges; vector<int> bcj_root;// vector<Component> components;//连通分量 int bcj_getroot(int i) { if (bcj_root[i]==i) { } else { bcj_root[i] = bcj_getroot(bcj_root[i]); } return bcj_root[i]; } vector<int> mst_edge_weight_max;//下标为连通分量的root的节点序号 void init(int Nv,int Ne) { this->Nv = Nv; this->Ne = Ne; edges.resize(Ne); bcj_root.resize(Nv); components.resize(Nv); mst_edge_weight_max.resize(Nv);//不是根的连通分量可能始终是0 range(i, 0, Nv) { bcj_root[i] = i; components[i].init(i); mst_edge_weight_max[i] = 0; } } int Nv=0; int Ne = 0; void read_edges() { range(i,0,Ne) { edges[i].my_read(); } } void sort_edges() { auto cmp = [](Edge& e1, Edge& e2) { if (e1.weight<e2.weight) { return true; } return false; }; sort(edges.begin(),edges.end(),cmp); } void write_edges() { range(i, 0, Ne) { edges[i].my_write(); } } }; string my_itoa(int x) { char ans_[30]; sprintf(ans_, "%d", x); return string(ans_); } void myoutput(Graph& graph) { vector<Component> components_new; components_new.reserve(graph.Nv); range(i,0,graph.Nv) { if (graph.components[i].bcj_root == i) { graph.components[i].sort_members(); components_new.push_back(graph.components[i]); } } auto cmp = [](Component& c1,Component& c2) {//size至少为1不用担心0没有 if (c1.members[0]<c2.members[0]) { return true; } return false; }; sort(components_new.begin(),components_new.end(),cmp); range(i, 0, components_new.size()) { components_new[i].write_me(); } } void myinput(Graph& graph,float& c) { int Nv = 0, Ne = 0; cin >> Nv >> Ne >> c; graph.init(Nv,Ne); graph.read_edges(); } float func_H(float mew,float c,int C) { return mew + c / ((float)C); } int main() { Graph graph; float c = 0; myinput(graph,c); graph.sort_edges(); //graph.write_edges(); range(i, 0, graph.Ne) { Edge& edge_now = graph.edges[i]; int root1 = graph.bcj_getroot(edge_now.v1); int root2 = graph.bcj_getroot(edge_now.v2); if (root1==root2) { continue;//已经是一伙的了 } float weightnow = edge_now.weight; float func_H_now1 = func_H(graph.mst_edge_weight_max[root1],c,graph.components[root1].members.size()); if (weightnow>func_H_now1) { continue;//说明目前还可以维持分开 } float func_H_now2 = func_H(graph.mst_edge_weight_max[root2], c, graph.components[root2].members.size()); if (weightnow>func_H_now2) { continue; } //说明这条边的加入迫使这两个合并了 graph.bcj_root[root1] = root2; graph.mst_edge_weight_max[root2] = weightnow;//新加的必然最大,其实就是kruskal graph.components[root1].bcj_root = root2; range(j,0, graph.components[root1].members.size()) graph.components[root2].members.push_back(graph.components[root1].members[j]);//nv复杂度?这句话应该不会tle吧 } myoutput(graph); system("pause");//提交时去掉此行 return 0; }
Sample Input 1:
10 21 100
0 1 10
0 3 60
0 4 90
1 2 90
1 3 50
1 4 200
1 5 86
2 4 95
2 5 5
3 4 95
3 6 15
3 7 101
4 5 500
4 6 100
4 7 101
4 8 101
5 7 300
5 8 50
6 7 90
7 8 84
7 9 34
Sample Output 1:
0 1 3 6
2 5 8
4
7 9
Sample Input 2:
7 7 100
0 1 10
1 2 61
2 3 50
3 4 200
4 5 82
5 0 200
3 6 90
Sample Output 2:
0 1
2 3 6
4 5