Lombok的简介
Lombok是一款Java开发插件,公司项目到处使用,整体效果很棒,代码更干净。Java开发人员可以节省出重复构建,诸如hashCode和equals这样的方法以及各种业务对象模型的accessor和ToString等方法的大量时间。对于这些方法,它能够在编译源代码期间自动帮我们生成这些方法,并没有如反射那样降低程序的性能。
Lombok的基本使用示例
1.Val可以将变量申明是final类型。
public static void main (String[] args){
val setVar = new HashSet<String>();
val listsVar = new ArrayList<String>();
val mapVar = new HashMap<String, String>();
//=>上面代码相当于如下:
final Set<String> setVar2 = new HashSet<>();
final List<String> listsVar2 = new ArrayList<>();
final Map<String, String> maps2 = new HashMap<>();
}
2.@NonNull注解能够为方法或构造函数的参数提供非空检查。
public void notNullExample(@NonNull String string) {
//方法内的代码
}
//=>上面代码相当于如下:
public void notNullExample(String string) {
if (string != null) {
//方法内的代码相当于如下:
} else {
throw new NullPointerException("null");
}
}
3.@Cleanup注解能够自动释放资源。
public void jedisExample(String[] args) {
try {
@Cleanup Jedis jedis = redisService.getJedis();
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.error(“Jedis异常:”,ex)
}
//=>上面代码相当于如下:
Jedis jedis= null;
try {
jedis = redisService.getJedis();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(“Jedis异常:”,ex)
} finally {
if (jedis != null) {
try {
jedis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4.@Getter/@Setter注解可以针对类的属性字段自动生成Get/Set方法。
public class OrderCreateDemoReq{
@Getter
@Setter
private String customerId;
@Setter
@Getter
private String poolId;
}
//上面请求Req类的代码相当于如下:
public class OrderCreateDemoReq{
private String customerId;
private String poolId;
public String getCustomerId(){
return customerId;
}
public String getPoolId(){
return poolId;
}
public void setCustomerId(String customerId){
this.customerId = customerId;
}
public void setPoolId(String poolId){
this.pool = pool;
}
}
5.@ToString注解,为使用该注解的类生成一个toString方法,默认的toString格式为:ClassName(fieldName= fieleValue ,fieldName1=fieleValue)。
@ToString(callSuper=true,exclude="someExcludedField")
public class Demo extends Bar {
private boolean someBoolean = true;
private String someStringField;
private float someExcludedField;
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class Demo extends Bar {
private boolean someBoolean = true;
private String someStringField;
private float someExcludedField;
@ Override
public String toString() {
return "Foo(super=" + super.toString() +
", someBoolean=" + someBoolean +
", someStringField=" + someStringField + ")";
}
}
6.@EqualsAndHashCode注解,为使用该注解的类自动生成equals和hashCode方法。
@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude = {"id"}, callSuper =true)
public class LombokDemo extends Demo{
private int id;
private String name;
private String gender;
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class LombokDemo extends Demo{
private int id;
private String name;
private String gender;
@Override
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o == null)
return false;
if (o.getClass() != this.getClass())
return false;
if (!super.equals(o))
return false;
final LombokDemo other = (LombokDemo)o;
if (this.name == null ? other.name != null : !this.name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (this.gender == null ? other.gender != null : !this.gender.equals(other.gender)) return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 31;
int result = 1;
result = result * PRIME + super.hashCode();
result = result * PRIME + (this.name == null ? 0 : this.name.hashCode());
result = result * PRIME + (this.gender == null ? 0 : this.gender.hashCode());
return result;
}
}
7.@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor,这几个注解分别为类自动生成了无参构造器、指定参数的构造器和包含所有参数的构造器。
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public class ConstructorExample<T> {
private int x, y;
@NonNull private T description;
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class NoArgsExample {
@NonNull private String field;
}
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class ConstructorExample<T> {
private int x, y;
@NonNull private T description;
private ConstructorExample(T description) {
if (description == null) throw new NullPointerException("description");
this.description = description;
}
public static <T> ConstructorExample<T> of(T description) {
return new ConstructorExample<T>(description);
}
@java.beans.ConstructorProperties({"x", "y", "description"})
protected ConstructorExample(int x, int y, T description) {
if (description == null) throw new NullPointerException("description");
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.description = description;
}
public static class NoArgsExample {
@NonNull private String field;
public NoArgsExample() {
}
}
}
8.@Data注解作用比较全,其包含注解的集合 @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode,所有字段的 @Getter和所有非final字段的 @Setter, @RequiredArgsConstructor。相当于以上几个注解的集合体。
9.@Builder注解提供了一种比较推崇的构建值对象的方式。
@Builder
public class BuilderExample {
private String name;
private int age;
@Singular private Set<String> occupations;
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class BuilderExample {
private String name;
private int age;
private Set<String> occupations;
BuilderExample(String name, int age, Set<String> occupations) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.occupations = occupations;
}
public static BuilderExampleBuilder builder() {
return new BuilderExampleBuilder();
}
public static class BuilderExampleBuilder {
private String name;
private int age;
private java.util.ArrayList<String> occupations;
BuilderExampleBuilder() {
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder name(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder age(int age) {
this.age = age;
return this;
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder occupation(String occupation) {
if (this.occupations == null) {
this.occupations = new java.util.ArrayList<String>();
}
this.occupations.add(occupation);
return this;
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder occupations(Collection<? extends String> occupations) {
if (this.occupations == null) {
this.occupations = new java.util.ArrayList<String>();
}
this.occupations.addAll(occupations);
return this;
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder clearOccupations() {
if (this.occupations != null) {
this.occupations.clear();
}
return this;
}
public BuilderExample build() {
Set<String> occupations = new HashSet<>();
return new BuilderExample(name, age, occupations);
}
@verride
public String toString() {
return "BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder(name = " + this.name + ", age = " + this.age + ", occupations = " + this.occupations + ")";
}
}
}
10.@Synchronized注解类似Java中的Synchronized 关键字,但是可以隐藏同步锁。
public class SynchronizedExample {
private final Object readLock = new Object();
@Synchronized
public static void hello() {
System.out.println("world");
}
@Synchronized("readLock")
public void foo() {
System.out.println("bar");
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class SynchronizedExample {
private static final Object $LOCK = new Object[0];
private final Object readLock = new Object();
public static void hello() {
synchronized($LOCK) {
System.out.println("world");
}
}
public void foo() {
synchronized(readLock) {
System.out.println("bar");
}
}
}
Lombok背后的自定义注解原理
Lombok这款插件正是依靠可插件化的Java自定义注解处理API(JSR 269: Pluggable Annotation Processing API)来实现在Javac编译阶段利用“Annotation Processor”对自定义的注解进行预处理后生成真正在JVM上面执行的“Class文件”.其大致执行原理图如下:
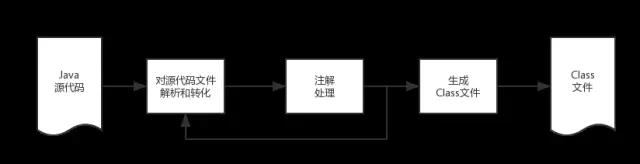
从上面的这个原理图上可以看出Annotation Processing是编译器在解析Java源代码和生成Class文件之间的一个步骤。其中Lombok插件具体的执行流程如下:

从上面的Lombok执行的流程图中可以看出,在Javac 解析成AST抽象语法树之后, Lombok 根据自己编写的注解处理器,动态地修改 AST,增加新的节点(即Lombok自定义注解所需要生成的代码),最终通过分析生成JVM可执行的字节码Class文件。使用Annotation Processing自定义注解是在编译阶段进行修改,而JDK的反射技术是在运行时动态修改,两者相比,反射虽然更加灵活一些但是带来的性能损耗更加大。