一、RBAC介绍
在Kubernetes中,授权有ABAC(基于属性的访问控制)、RBAC(基于角色的访问控制)、Webhook、Node、AlwaysDeny(一直拒绝)和AlwaysAllow(一直允许)这6种模式。
从1.6版本起,Kubernetes 默认启用RBAC访问控制策略。从1.8开始,RBAC已作为稳定的功能。通过设置--authorization-mode=RBAC,启用RABC。在RABC API中,通过如下的步骤进行授权:
定义角色:在定义角色时会指定此角色对于资源的访问控制的规则;
绑定角色:将主体与角色进行绑定,对用户进行访问授权。
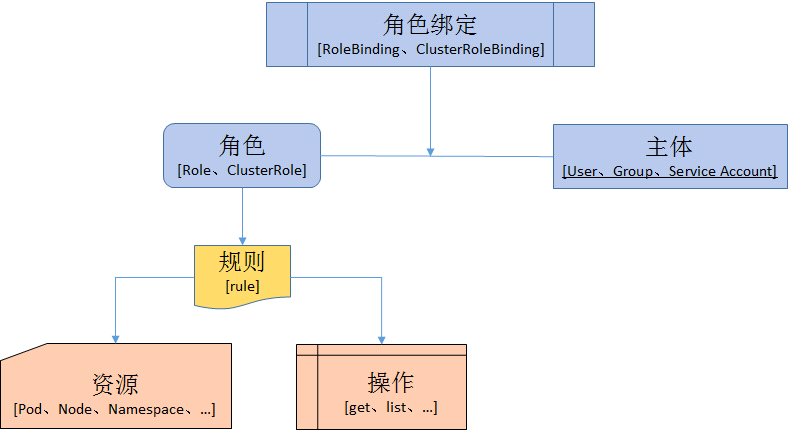
1.1、角色和集群角色
在 RBAC API 中,角色包含代表权限集合的规则。在这里,权限只有被授予,而没有被拒绝的设置。在 Kubernetes 中有两类角色,即普通角色(Role)和集群角色(ClusterRole)。可以通过Role定义在一个命名空间中的角色,或者可以使用ClusterRole定义集群范围的角色。一个Role只能被用来授予访问单一命令空间中的资源。下面是在 default 命令空间中定义了一个名为 pod-reader 的角色,此角色能够对在 default 命名空间中访问 Pod:
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
ClusterRole可用于授予与Role相同的权限。他们能够被授予如下资源的权限:
- 集群范围的资源(类似于Node)
- 非资源端点(类似于”/healthz”)
- 集群中所有命名空间的资源(类似Pod)
下面的ClusterRole可用于授予对任何特定namespaces中的秘密的读取访问权限,或跨所有命名空间的访问权限。
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
# "namespace" omitted since ClusterRoles are not namespaced
name: secret-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
1.2、RoleBinding 和 ClusterRoleBinding
角色绑定用于将角色与一个或一组用户进行绑定,从而实现将对用户进行授权的目的。主体分为用户、组和服务帐户。角色绑定也分为角色普通角色绑定和集群角色绑定。角色绑定只能引用同一个命名空间下的角色。
在下面的例子中,在 default 命名空间中角色绑定将 jane 用户和 pod-reader 角色进行了绑定,这就授予了 jane 能够访问 default 命名空间下的 Pod。
# This role binding allows "jane" to read pods in the "default" namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: User
name: jane # Name is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role #this must be Role or ClusterRole
name: pod-reader # this must match the name of the Role or ClusterRole you wish to bind to
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
角色绑定也可以通过引用集群角色授予访问权限,当主体对资源的访问仅限与本命名空间,这就允许管理员定义整个集群的公共角色集合,然后在多个命名空间中进行复用。
例如,下面的角色绑定引用了集群角色,但是 dave 用户也仅仅只能读取 development 命名空间中的 secret s资源:
# This role binding allows "dave" to read secrets in the "development" namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-secrets
namespace: development # This only grants permissions within the "development" namespace.
subjects:
- kind: User
name: dave # Name is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
集群角色可以被用来在集群层面和整个命名空间进行授权。下面的示例允许在 manager 组的用户能够访问所有命名空间中的保密字典资源。
# This cluster role binding allows anyone in the "manager" group to read secrets in any namespace.
kind:ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion:rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name:read-secrets-global
subjects:
- kind:Group
name:manager
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind:ClusterRole
name:secret-reader
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
1.3、资源
在Kubernets中,主要的资源包括:Pods、Nodes、Services、Deployment、Replicasets、Statefulsets、Namespace、Persistents、Secrets和ConfigMaps等。另外,有些资源下面存在子资源,例如:Pod下就存在log子资源:
GET /api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name}/log
下面的例子显示, pod-and-pod-logs-reader 角色能够对 pods 和 pods/log 进行访问:
kind:Role
apiVersion:rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace:default
name:pod-and-pod-logs-reader
rules:
- apiGroups:[""]
resources:["pods","pods/log"]
verbs:["get","list"]
也可以通过 resourceNamess 指定特定的资源实例,以限制角色只能够对实例进行访问控制:
kind:Role
apiVersion:rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace:default
name:configmap-updater
rules:
- apiGroups:[""]
resources:["configmaps"]
resourceNames:["my-configmap"]
verbs:["update","get"]
1.4、主体
RBAC授权中的主体可以是组,用户或者服务帐户。用户通过字符串表示,比如“alice”、 “bob@example.com”等,具体的形式取决于管理员在认证模块中所配置的用户名。system: 被保留作为用来 Kubernetes 系统使用,因此不能作为用户的前缀。组也有认证模块提供,格式与用户类似。
在角色绑定主体的例子:
名称为 “alice@example.com”用户:
subjects:
- kind:User
name:"alice@example.com"
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
名称为“frontend-admins”的组:
subjects:
- kind:Group
name:"frontend-admins"
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
在 kube-system 命名空间中,名称为“default”的服务帐户:
subjects:
- kind:ServiceAccount
name:default
namespace:kube-system
在“qa”命名空间中,所有的服务帐户:
subjects:
- kind:Group
name:system:serviceaccounts:qa
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有的服务帐户:
subjects:
- kind:Group
name:system:serviceaccounts
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有被认证的用户 (version 1.5+):
subjects:
- kind:Group
name:system:authenticated
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有未被认证的用户 (version 1.5+):
subjects:
- kind:Group
name:system:unauthenticated
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有用户(version 1.5+):
subjects:
- kind:Group
name:system:authenticated
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- kind:Group
name:system:unauthenticated
apiGroup:rbac.authorization.k8s.io
二、命令行工具
Kubernetes可以通过命令工具进行角色绑定。
2.1、kubectl create rolebinding
在指定的命名空间中进行角色绑定:
1)在acme命名空间中,将admin集群角色授予bob用户:
$ kubectl create rolebinding bob-admin-binding --clusterrole=admin --user=bob --namespace=acme
2)在acme命名空间中,将admin集群角色授予acme:myapp服务帐户:
$ kubectl create rolebinding myapp-view-binding --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=acme:myapp --namespace=acme
2.2、kubectl create clusterrolebinding
在整个集群中进行角色绑定:
1)在整个集群中,授予cluster-admin集群角色给root用户:
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding root-cluster-admin-binding --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=root
2)在整个集群中,授予system:node集群角色给kubelet用户:
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding kubelet-node-binding --clusterrole=system:node --user=kubelet
3)在整个集群中,授予view集群角色给acme:myapp服务帐户:
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding myapp-view-binding --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=acme:myapp
三、服务帐户权限
默认情况下,RBAC策略授予控制板组件、Node和控制器作用域的权限,但是未授予kube-system命名空间外服务帐户的访问权限。这就允许管理员按照需要将特定角色授予服务帐户。
从最安全到最不安全的顺序,方法如下:
- 1)授予角色给一个指定应用的服务帐户(最佳实践)
这要求在Pod规格中指定ServiveAccountName,同时此服务帐户已被创建(通过API、kubectl create serviceaccount等)。例如,在my-namespace命名空间内,授予my-sa服务帐户view集群角色:
kubectl create rolebinding my-sa-view
--clusterrole=view
--serviceaccount=my-namespace:my-sa
--namespace=my-namespace
- 2)在一个命名空间授予
view集群角色给default服务帐户
如果应用没有指定serviceAccountName,它将使用default服务帐户。例如,例如,在my-namespace命名空间内,授予default服务帐户view集群角色:
kubectl create rolebinding default-view
--clusterrole=view
--serviceaccount=my-namespace:default
--namespace=my-namespace
当前,在 kube-system 命名空间中,很多插件作为 default 服务帐户进行运行。为了允许超级用户访问这些插件,在 kube-system 命名空间中授予 cluster-admin 角色给 default 帐户。
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding add-on-cluster-admin
--clusterrole=cluster-admin
--serviceaccount=kube-system:default
- 3)在一个命名空间中,授予角色给所有的服务帐户:
如果希望在一个命名空间中的所有应用都拥有一个角色,而不管它们所使用的服务帐户,可以授予角色给服务帐户组。例如,在 my-namespace 命名空间中,将 view 集群角色授予 system:serviceaccounts:my-namespace 组:
$ kubectl create rolebinding serviceaccounts-view
--clusterrole=view
--group=system:serviceaccounts:my-namespace
--namespace=my-namespace
- 4)在整个集群中授予一个角色给所有的服务帐户 (不推荐)
如果不想按照每个命名空间管理权限,可以在整个集群的访问进行授权。例如,在整个集群层面,将 view 集群角色授予 sytem:serviceaccounts :
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding serviceaccounts-view
--clusterrole=view
--group=system:serviceaccounts
- 5)在整个集群中授予超级用户访问所有的服务帐户 (强烈不推荐)
如果对访问权限不太重视,可以授予超级用户访问所有的服务帐户。
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding serviceaccounts-cluster-admin
--clusterrole=cluster-admin
--group=system:serviceaccounts
- 6)宽松的RBAC权限
下面的策略允许所有的服务帐户作为集群管理员。在容器中运行的应用将自动的收取到服务帐户证书,并执行所有的API行为。包括查看保密字典恩将和修改权限,这是不被推荐的访问策略。
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding permissive-binding
--clusterrole=cluster-admin
--user=admin
--user=kubelet
--group=system:serviceaccounts
官方文档:https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/