数据协商:客户端给服务端发送一个请求的时候,客户端会声明我希望这个请求我想要拿到的数据格式以及数据相关的一些限制,服务端会根据请求里面表示的想要拿到什么样的数据之后,然后做出一个判断,服务端可能会有很多不同类型的数据返回,服务端可以根据头信息进行区分
请求声明Accept:
Accept: 声明我想要怎么样的数据,声明数据类型 Accept-Encoding: 代表数据是怎么样的编码方式 Accept-Language: 判断返回的信息是什么语言 User-Agent: 表示浏览器的一些相关的信息
与之对应的就是服务端Content:
Content-Type: 对应Accept,Accept可以接收很多种数据格式,Content-Type会在里面选择一种数据格式返回,在返回的时候声明返回的数据格式 Content-Encoding: 对应Accept-Encoding,告诉客户端,我究竟用了什么样的压缩数据的方式 Content-Language: 是否根据请求返回对应的语言
//server.js const http = require('http'); const fs = require('fs'); http.createServer(function(req,res){ console.log('req come', req.url); const html = fs.readFileSync('test.html', 'utf8'); res.writeHead(200,{ 'Content-Type': 'text/html', 'X-Content-Type-Options': 'nosniff' // 当没有content-type的时候,会去预测是什么类型,导致运行失败,这个是为了告诉,不要随意预测 }) res.end(html); }).listen(8888); console.log('server listening on 8888'); console.log('http://localhost:8888/');
<!--test.html--> <body> </body>
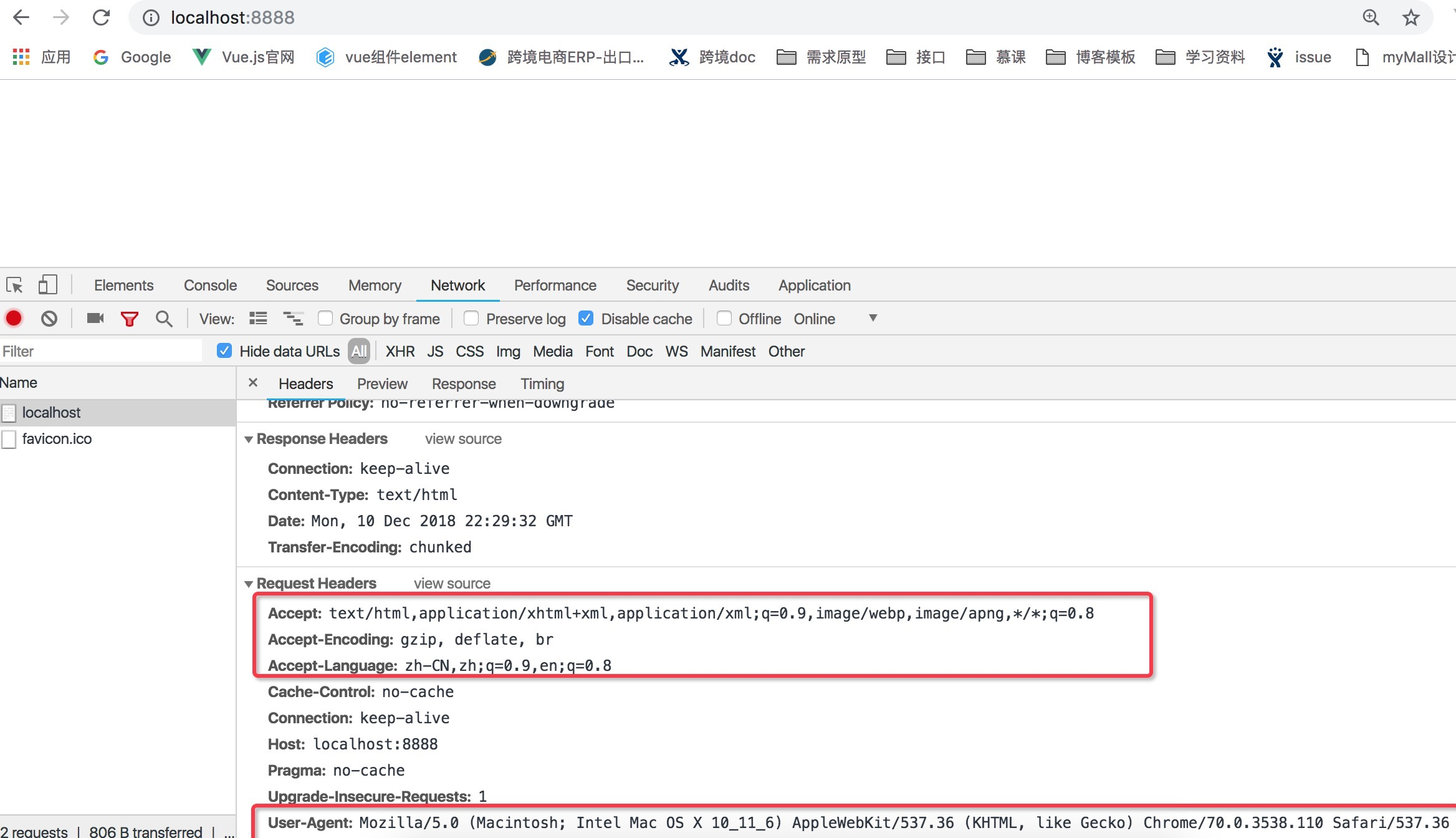
启动服务,返回html,里面的Accpet表示这些格式都可以接收,甚至一张图片,虽然客户端声明了这些格式,服务端不一定强制返回你想要的,Accept-Encoding压缩方式,Accept-Language默认是中文,因为中国发的,q表示权重,权重越多,越希望返回什么,User-Agent浏览器信息,Mozilla/5.0因为最开始是网景公司,AppleWebKit浏览器内核,服务端看到要不要适应这个浏览器

压缩格式演示,一开始是403b,压缩后的返回
//server.js const http = require('http'); const fs = require('fs'); const zlib = require('zlib') http.createServer(function(req,res){ console.log('req come', req.url); const html = fs.readFileSync('test.html'); res.writeHead(200,{ 'Content-Type': 'text/html', 'Content-Encoding': 'gzip' }) res.end(zlib.gzipSync(html)); }).listen(8888);

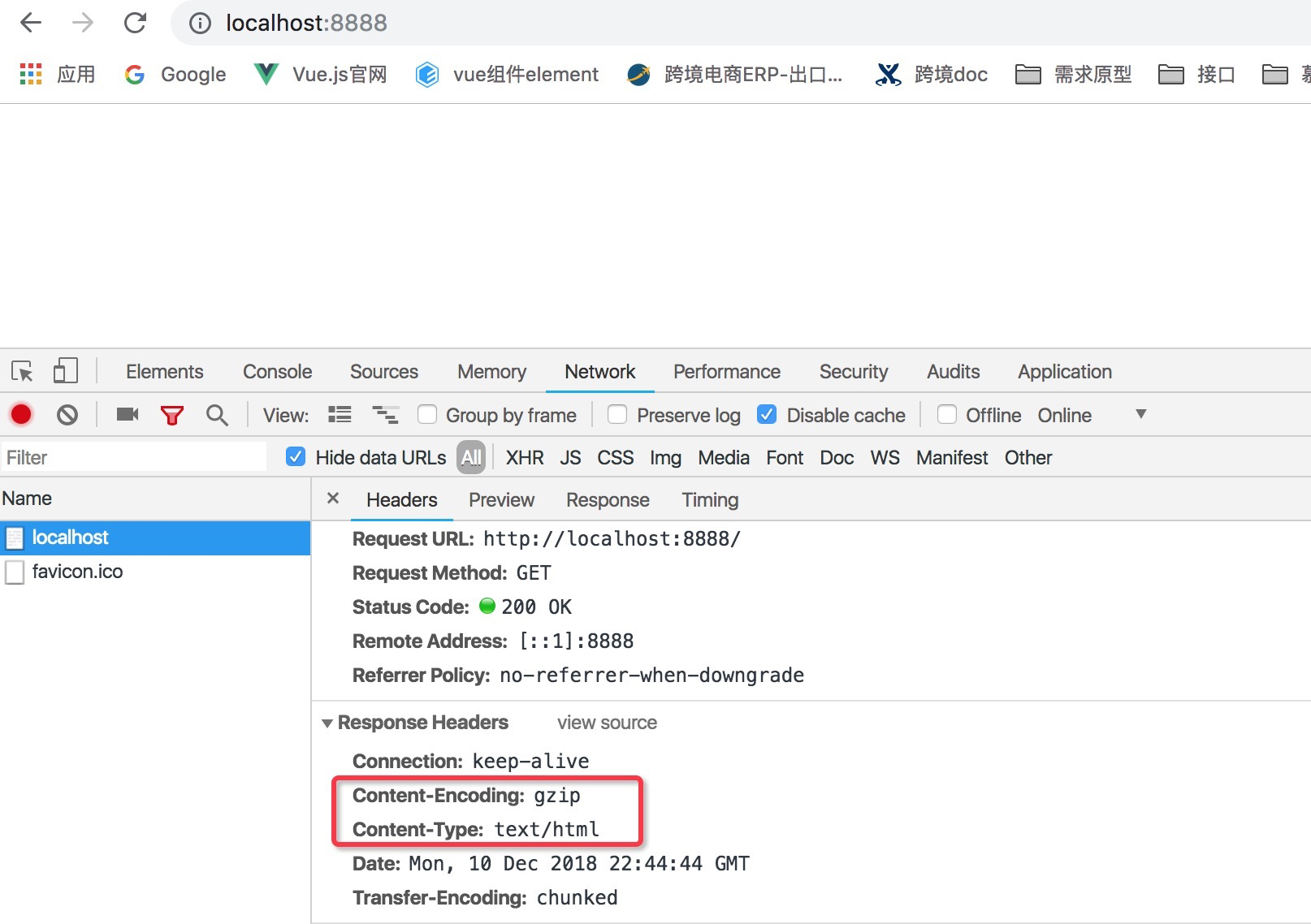
如图,编程了362b,同样的内容,传输大小是有变化的,因为传输过程中,gzip进行压缩了