一、定义
给定一个语言,定义它的文法表示,并定义一个解释器,这个解释器使用该标识来解释语言中的句子。
主要解决:对于一些固定文法构建一个解释句子的解释器。
何时使用:如果一种特定类型的问题发生的频率足够高,那么可能就值得将该问题的各个实例表述为一个简单语言中的句子。这样就可以构建一个解释器,该解释器通过解释这些句子来解决该问题。
如何解决:构件语法树,定义终结符与非终结符。
二、结构
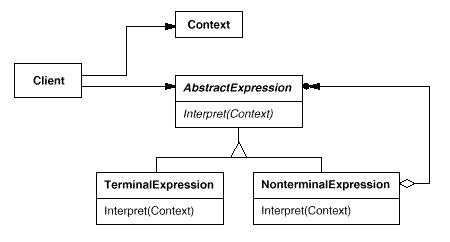
组成:
AbstractExpression(抽象表达式):定义解释器的接口,约定解释器的解释操作。
TerminalExpression(终结符表达式):用来实现语法规则中和终结符相关的操作,不再包含其它的解释器,如果用组合模式来构建抽象语法树的话,就相当于组合模式中的叶子对象,可以有多种终结符解释器。
NonterminalExpression(非终结符表达式):用来实现语法规则中非终结符相关的操作,通常一个解释器对应一个语法规则,可以包含其它的解释器,如果用组合模式来构建抽象语法树的话,就相当于组合模式中的组合对象,可以有多种非终结符解释器。
Context(上下文):它包含了解释器之外一些其他的全局信息;通常包含各个解释器需要的数据,或是公共的功能。
Client(客户端):指的是使用解释器的客户端,通常在这里去把按照语言的语法做的表达式,转换成为使用解释器对象描述的抽象语法树,然后调用解释操作。
三、适用场景
1、可以将一个需要解释执行的语言中的句子表示为一个抽象语法树。
2、一些重复出现的问题可以用一种简单的语言来进行表达。
3、一个简单语法需要解释的场景。
四、优缺点
优点: 1、可扩展性比较好,灵活。 2、增加了新的解释表达式的方式。 3、易于实现简单文法。
缺点: 1、可利用场景比较少。 2、对于复杂的文法比较难维护。 3、解释器模式会引起类膨胀。 4、解释器模式采用递归调用方法。
五、实现
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace DesignPatterns.Interpreter { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine(ReplyClient.ApplyContent("Y0001")); Console.WriteLine(ReplyClient.ApplyContent("y0002")); Console.WriteLine(ReplyClient.ApplyContent("N0003")); Console.WriteLine(ReplyClient.ApplyContent("n0004")); } } /// <summary> /// 回复内容 /// </summary> public class ReplyContent { private string _ReplyText; public string ReplyText { get { return _ReplyText; } set { _ReplyText = value; } } } public abstract class InterPreter { public string ConvertContent(ReplyContent content) { if (content.ReplyText.Length == 0) return "请按规则回复审批短信."; return Excute(content.ReplyText); } public abstract string Excute(string key); } public class Approve : InterPreter { public override string Excute(string key) { if (key == "Y" || key == "y") { return "同意"; } else if (key == "N" || key == "n") { return "拒绝"; } else { return "回复内容有误,请重新回复."; } } } public class DocumentNum : InterPreter { public Dictionary<string, string> OddNum { get { Dictionary<string, string> OddID = new Dictionary<string, string>(); OddID.Add("0001", "123890890892345"); OddID.Add("0002", "123456717012345"); OddID.Add("0003", "123456669012345"); OddID.Add("0004", "123423444012345"); OddID.Add("0005", "123467845345345"); OddID.Add("0006", "123231234564345"); OddID.Add("0007", "128797897867745"); return OddID; } } public override string Excute(string key) { string value = null; if (OddNum.TryGetValue(key, out value)) { return value; } else { return "没找到对应的单号."; } } } public class ReplyClient { public static string ApplyContent(string replayValue) { string result = string.Empty; string approvevalue = replayValue.Substring(0, 1); string oddIDvalue = replayValue.Substring(1, 4); ReplyContent content = new ReplyContent(); content.ReplyText = approvevalue; InterPreter expression = new Approve(); result = string.Format("你{0}", expression.ConvertContent(content)); expression = new DocumentNum(); content.ReplyText = oddIDvalue; result += string.Format("单号是{0}的申请. ", expression.ConvertContent(content)); return result; } } }
参考
http://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/interpreter-pattern.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/JsonShare/p/7367535.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/springyangwc/archive/2011/05/05/2037146.html