附William Pugh的论文 Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees
写在前面
以下内容针对的是Skip List的插入和删除,建议你先到其他地方大概了解一下Skip List长什么样子的,然后再过来看看这篇,最好还是看一眼论文先,部分挺容易看懂的。Redis中的Sorted Set基本就是使用Skip List,只是稍作修改。
初识 Skip List
Skip List 是一种数据结构,实质上为一个链表,专门用于存储有序元素,提供的查找速度可与平衡二叉树媲美,优点是实现简单。
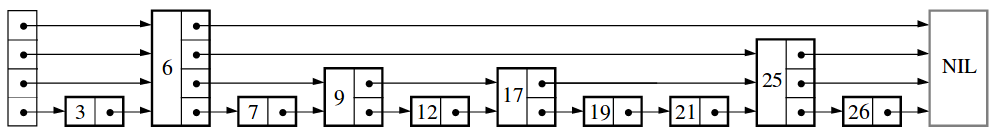
论文中Skip List就是长上面这样的,每个节点有多个forward指针,指向在其后面的元素。将forward指针分层,称为level,level为1的那层就是单纯的有序单链表,随着层次递增,元素会越来越少。比如level的取值范围可以是[1, 32]。
Skip List 的插入
先快速看一眼下面翻译过来的伪码实现。
void Insert(list, searchKey, newValue)
{
local update[1..MaxLevel];
x = list->header;
// 查找searchKey应存放的位置
for(i = list->level to 1)
{
while(x->forward[i]->key < searchKey)
x = x->forward[i];
// 位置关系: x->key < searchKey <= x->forward[i]->key
update[i] = x; // 看上行注释便知update保存的是什么
}
x = x->forward[1]; // 这在最低层
if(x->key == searchKey)
{
// 已有相同的key,替换即可
x->value = newValue;
}
else
{
lv = randomLevel(); // 为新节点随机取个level
if(lv > list->level) // 特殊处理:新节点level比当前最大level高
{
for(i = list->level+1 to lv)
update[i] = list->header;
list->level = lv;
}
x = createNode(v, searchKey, newValue);
for(i = 1 to lv) // 调整相关指针
{
x->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = x;
}
}
}
实现原理是,用一个update数组保存"最大且小于searchKey的元素",用它来调整涉及到的指针指向。搜索时从高层往低层搜索,顺便记录update数组,调整指针时从低层往高层调整。可能出现的情况是,新节点的level大于原来list的最大level,此时需要更新一下list的最大level。
randomLevel()比较容易实现,就是抛硬币法,有概率性,越高的level出现频率越低,因为不能直接一下子就返回过大的数字。返回一个数字n表示抛了n+1次才出现反面,但要求n<=MaxLevel。这种取level的方式很巧妙。
Skip List 的删除
void Delete(list, searchKey)
{
int update[1..MaxLevel];
x = list->header;
// 查找searchKey的存放位置
for(i = list->level to 1)
{
while(x->forward[i]->key < searchKey)
x = x->forward[i];
update[i] = x;
}
x = x->forward[i];
if(x->key == searchKey) // 若命中,则删
{
// 调整指向x的指针
for(i = 1 to list->level)
{
if(update[i]->forward[i] != x) break;
update[i]->forward[i] = x->forward[i]
}
free(x);
// 可能需要更新list的max level
while(list->level > 1 && !list->header->forward[list->level])
list->level = list->level - 1;
}
}
看过Insert之后,这个不用解释也能看懂了。