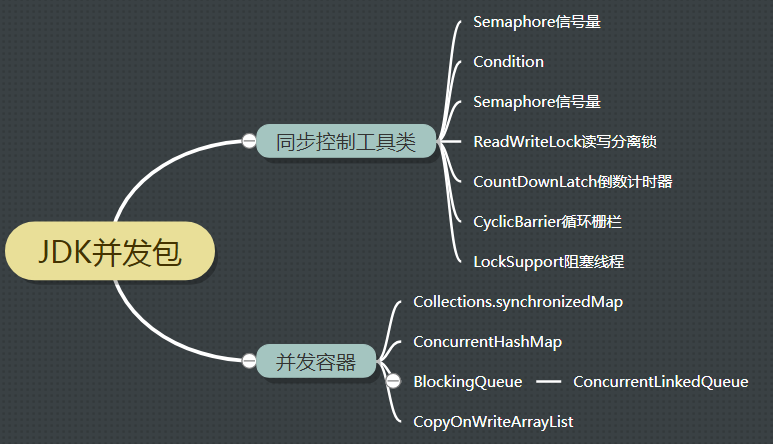
本文主要介绍jdk中常用的同步控制工具以及并发容器, 其结构如下:
同步控制工具类
ReentrantLock
简而言之, 就是自由度更高的synchronized, 主要具备以下优点.
- 可重入: 单线程可以重复进入,但要重复退出
- 可中断: lock.lockInterruptibly()
- 可限时: 超时不能获得锁,就返回false,不会永久等待构成死锁
- 公平锁: 先来先得, public ReentrantLock(boolean fair), 默认锁不公平的, 根据线程优先级竞争.
示例
1 public class ReenterLock implements Runnable { 2 public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 3 public static int i = 0; 4 5 @Override 6 public void run() { 7 for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) { 8 lock.lock(); 9 // 超时设置 10 // lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 11 try { 12 i++; 13 } finally { 14 // 需要放在finally里释放, 如果上面lock了两次, 这边也要unlock两次 15 lock.unlock(); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 21 ReenterLock tl = new ReenterLock(); 22 Thread t1 = new Thread(tl); 23 Thread t2 = new Thread(tl); 24 t1.start(); 25 t2.start(); 26 t1.join(); 27 t2.join(); 28 System.out.println(i); 29 } 30 }
中断死锁
线程1, 线程2分别去获取lock1, lock2, 触发死锁. 最终通过DeadlockChecker来触发线程中断.
1 public class DeadLock implements Runnable{ 2 3 public static ReentrantLock lock1 = new ReentrantLock(); 4 public static ReentrantLock lock2 = new ReentrantLock(); 5 int lock; 6 7 public DeadLock(int lock) { 8 this.lock = lock; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void run() { 13 try { 14 if (lock == 1){ 15 lock1.lockInterruptibly(); 16 try { 17 Thread.sleep(500); 18 }catch (InterruptedException e){} 19 lock2.lockInterruptibly(); 20 21 }else { 22 lock2.lockInterruptibly(); 23 try { 24 Thread.sleep(500); 25 }catch (InterruptedException e){} 26 lock1.lockInterruptibly(); 27 28 } 29 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 }finally { 32 if (lock1.isHeldByCurrentThread()) 33 lock1.unlock(); 34 if (lock2.isHeldByCurrentThread()) 35 lock2.unlock(); 36 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + "线程中断"); 37 } 38 } 39 40 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 41 DeadLock deadLock1 = new DeadLock(1); 42 DeadLock deadLock2 = new DeadLock(2); 43 // 线程1, 线程2分别去获取lock1, lock2. 导致死锁 44 Thread t1 = new Thread(deadLock1); 45 Thread t2 = new Thread(deadLock2); 46 t1.start(); 47 t2.start(); 48 Thread.sleep(1000); 49 // 死锁检查, 触发中断 50 DeadlockChecker.check(); 51 52 } 53 }

1 public class DeadlockChecker { 2 private final static ThreadMXBean mbean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean(); 3 final static Runnable deadLockCheck = new Runnable() { 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 while (true) { 7 long[] deadlockedThreadlds = mbean.findDeadlockedThreads(); 8 9 if (deadlockedThreadlds != null) { 10 ThreadInfo[] threadInfos = mbean.getThreadInfo(deadlockedThreadlds); 11 for (Thread t : Thread.getAllStackTraces().keySet()) { 12 for (int i = 0; i < threadInfos.length; i++) { 13 if (t.getId() == threadInfos[i].getThreadId()) { 14 t.interrupt(); 15 try { 16 Thread.sleep(5000); 17 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 }; 26 27 public static void check() { 28 Thread t = new Thread(deadLockCheck); 29 t.setDaemon(true); 30 t.start(); 31 } 32 }
Condition
类似于 Object.wait()和Object.notify(), 需要与ReentrantLock结合使用.
具体API如下:
1 // await()方法会使当前线程等待,同时释放当前锁,当其他线程中使用signal()时或者signalAll()方法时, 2 // 线程会重新获得锁并继续执行。或者当线程被中断时,也能跳出等待。这和Object.wait()方法很相似。 3 void await() throws InterruptedException; 4 // awaitUninterruptibly()方法与await()方法基本相同,但是它并不会再等待过程中响应中断。 5 void awaitUninterruptibly(); 6 long awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException; 7 boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; 8 boolean awaitUntil(Date deadline) throws InterruptedException; 9 // singal()方法用于唤醒一个在等待中的线程。相对的singalAll()方法会唤醒所有在等待中的线程。 10 // 这和Obejct.notify()方法很类似。 11 void signal(); 12 void signalAll();
示例
1 public class ReenterLockCondition implements Runnable{ 2 3 public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 4 public static Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 5 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 try { 9 lock.lock(); 10 condition.await(); 11 System.out.println("Thread is going on"); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } finally { 15 // 注意放到finally中释放 16 lock.unlock(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 21 ReenterLockCondition t1 = new ReenterLockCondition(); 22 Thread tt = new Thread(t1); 23 tt.start(); 24 Thread.sleep(2000); 25 System.out.println("after sleep, signal!"); 26 // 通知线程tt继续执行. 唤醒同样需要重新获得锁 27 lock.lock(); 28 condition.signal(); 29 lock.unlock(); 30 } 31 }
Semaphore信号量
锁一般都是互斥排他的, 而信号量可以认为是一个共享锁,
允许N个线程同时进入临界区, 但是超出许可范围的只能等待.
如果N = 1, 则类似于lock.
具体API如下, 通过acquire获取信号量, 通过release释放
1 public void acquire() 2 public void acquireUninterruptibly() 3 public boolean tryAcquire() 4 public boolean tryAcquire(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 5 public void release()
示例
模拟20个线程, 但是信号量只设置了5个许可.
因此线程是按序每2秒5个的打印job done.
1 public class SemapDemo implements Runnable{ 2 3 // 设置5个许可 4 final Semaphore semp = new Semaphore(5); 5 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 try { 9 semp.acquire(); 10 // 模拟线程耗时操作 11 Thread.sleep(2000L); 12 System.out.println("Job done! " + Thread.currentThread().getId()); 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } finally { 16 semp.release(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args){ 21 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20); 22 final SemapDemo demo = new SemapDemo(); 23 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 24 service.submit(demo); 25 } 26 } 27 }
ReadWriteLock
读写分离锁, 可以大幅提升系统并行度.
- 读-读不互斥:读读之间不阻塞。
- 读-写互斥:读阻塞写,写也会阻塞读。
- 写-写互斥:写写阻塞。
示例
使用方法与ReentrantLock类似, 只是读写锁分离.
1 private static ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock=new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); 2 private static Lock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); 3 private static Lock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock();
CountDownLatch倒数计时器
一种典型的场景就是火箭发射。在火箭发射前,为了保证万无一失,往往还要进行各项设备、仪器的检查。
只有等所有检查完毕后,引擎才能点火。这种场景就非常适合使用CountDownLatch。它可以使得点火线程,
等待所有检查线程全部完工后,再执行.
示例
1 public class CountDownLatchDemo implements Runnable{ 2 static final CountDownLatch end = new CountDownLatch(10); 3 static final CountDownLatchDemo demo = new CountDownLatchDemo(); 4 5 @Override 6 public void run() { 7 try { 8 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10) * 1000); 9 System.out.println("check complete!"); 10 end.countDown(); 11 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 } 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 17 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); 18 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 19 service.submit(demo); 20 } 21 // 等待检查 22 end.await(); 23 // 所有线程检查完毕, 发射火箭. 24 System.out.println("fire"); 25 service.shutdown(); 26 } 27 }
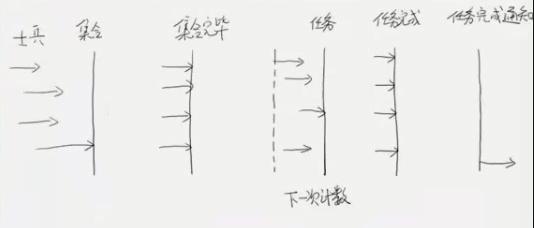
CyclicBarrier循环栅栏
Cyclic意为循环,也就是说这个计数器可以反复使用。比如,假设我们将计数器设置为10。那么凑齐
第一批10个线程后,计数器就会归零,然后接着凑齐下一批10个线程.
示例
1 public class CyclicBarrierDemo { 2 3 public static class Soldier implements Runnable { 4 5 private String soldier; 6 private final CyclicBarrier cyclic; 7 8 Soldier(CyclicBarrier cyclic, String soldier) { 9 this.cyclic = cyclic; 10 this.soldier = soldier; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void run() { 15 try { 16 // 等待所有士兵到期 17 cyclic.await(); 18 doWork(); 19 // 等待所有士兵完成工作 20 cyclic.await(); 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 28 void doWork() { 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(Math.abs(new Random().nextInt() % 10000)); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 System.out.println(soldier + " 任务完成!"); 35 } 36 } 37 38 public static class BarrierRun implements Runnable { 39 boolean flag; 40 int N; 41 42 public BarrierRun(boolean flag, int n) { 43 this.flag = flag; 44 N = n; 45 } 46 47 @Override 48 public void run() { 49 if (flag) { 50 System.out.println("士兵:" + N + "个, 任务完成!"); 51 } else { 52 System.out.println("士兵:" + N + "个, 集合完毕!"); 53 flag = true; 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 58 public static void main(String[] args){ 59 final int N = 5; 60 Thread[] allSoldier = new Thread[N]; 61 boolean flag = false; 62 CyclicBarrier cyclic = new CyclicBarrier(N, new BarrierRun(flag, N)); 63 // 设置屏障点, 主要为了执行这个方法. 64 System.out.println("集合任务!"); 65 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 66 System.out.println("士兵" + i + " 报到!"); 67 allSoldier[i] = new Thread(new Soldier(cyclic, "士兵" + i)); 68 allSoldier[i].start(); 69 } 70 71 } 72 }
结果
集合任务!
士兵0 报到!
士兵1 报到!
士兵2 报到!
士兵3 报到!
士兵4 报到!
士兵:5个, 集合完毕!
士兵3 任务完成!
士兵1 任务完成!
士兵0 任务完成!
士兵4 任务完成!
士兵2 任务完成!
士兵:5个, 任务完成!
LockSupport
一个线程阻塞工具, 可以在任意位置让线程阻塞.
与suspend()比较, 如果unpark发生在park之前, 并不会导致线程冻结, 也不需要获取锁.
API
1 LockSupport.park(); 2 LockSupport.unpark(t1);
中断响应
能够响应中断,但不抛出异常。
中断响应的结果是,park()函数的返回,可以从Thread.interrupted()得到中断标志
1 public class LockSupportDemo { 2 public static Object u = new Object(); 3 static ChangeObjectThread t1 = new ChangeObjectThread("t1"); 4 static ChangeObjectThread t2 = new ChangeObjectThread("t2"); 5 public static class ChangeObjectThread extends Thread { 6 7 public ChangeObjectThread(String name) { 8 super(name); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void run() { 13 synchronized (u) { 14 System.out.println("in " + getName()); 15 LockSupport.park(); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 21 t1.start(); 22 Thread.sleep(100); 23 t2.start(); 24 LockSupport.unpark(t1); 25 LockSupport.unpark(t2); 26 t1.join(); 27 t2.join(); 28 } 29 }
并发容器
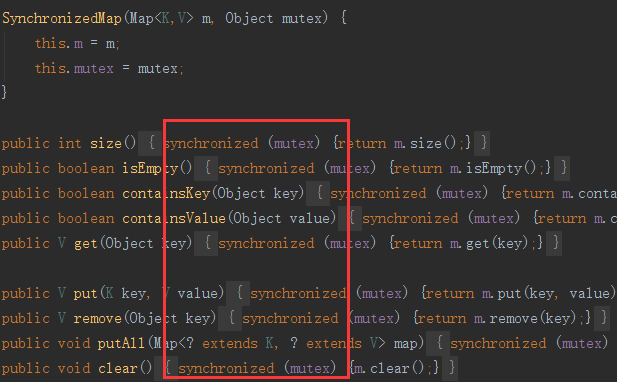
Collections.synchronizedMap
其本质是在读写map操作上都加了锁, 因此不推荐在高并发场景使用.
ConcurrentHashMap
内部使用分区Segment来表示不同的部分, 每个分区其实就是一个小的hashtable. 各自有自己的锁.
只要多个修改发生在不同的分区, 他们就可以并发的进行. 把一个整体分成了16个Segment, 最高支持16个线程并发修改.
代码中运用了很多volatile声明共享变量, 第一时间获取修改的内容, 性能较好.
1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 ConcurrentHashMap.Segment<K,V> s; 3 if (value == null) 4 throw new NullPointerException(); 5 int hash = hash(key); 6 int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; 7 // 通过unsafe对j进行偏移来寻找key所对应的分区 8 if ((s = (ConcurrentHashMap.Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck 9 (segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment 10 // 如果分区不存在, 则创建新的分区 11 s = ensureSegment(j); 12 // kv放到分区中 13 return s.put(key, hash, value, false); 14 }
Segment.put源码
1 Segment(float lf, int threshold, ConcurrentHashMap.HashEntry<K,V>[] tab) { 2 this.loadFactor = lf; 3 this.threshold = threshold; 4 this.table = tab; 5 } 6 7 final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { 8 // tryLock通过无锁cas操作尝试获取锁(无等待), 继承自ReentrantLock. 9 // 如果成功则, node = null 10 // 如果不成功, 则可能其他线程已经在插入数据了, 11 // 此时会尝试继续获取锁tryLock, 自旋MAX_SCAN_RETRIES次, 若还是拿不到锁才开始lock 12 ConcurrentHashMap.HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : 13 scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); 14 V oldValue; 15 try { 16 ConcurrentHashMap.HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; 17 // 获取分区中哪一个entry链的index 18 int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash; 19 // 获取第一个entry 20 ConcurrentHashMap.HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index); 21 for (ConcurrentHashMap.HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { 22 // e != null , 存在hash冲突, 把他加到当前链表中 23 if (e != null) { 24 K k; 25 if ((k = e.key) == key || 26 (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { 27 oldValue = e.value; 28 if (!onlyIfAbsent) { 29 e.value = value; 30 ++modCount; 31 } 32 break; 33 } 34 e = e.next; 35 } 36 else { 37 // 无hash冲突, new entry 38 if (node != null) 39 node.setNext(first); 40 else 41 node = new ConcurrentHashMap.HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first); 42 int c = count + 1; 43 // 空间大小超出阈值, 需要rehash, 翻倍空间. 44 if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) 45 rehash(node); 46 else 47 //放到分区中 48 setEntryAt(tab, index, node); 49 ++modCount; 50 count = c; 51 oldValue = null; 52 break; 53 } 54 } 55 } finally { 56 unlock(); 57 } 58 return oldValue; 59 }
如果想要对ConcurrentHashMap排序, 则可以使用ConcurrentSkipListMap,
他支持并发排序, 是一个线程安全的类似TreeMap的实现.
BlockingQueue
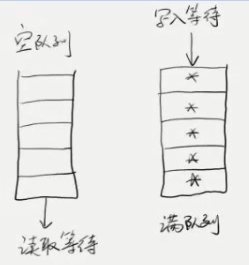
阻塞队列, 主要用于多线程之间共享数据.
当一个线程读取数据时, 如果队列是空的, 则当前线程会进入等待状态.
如果队列满了, 当一个线程尝试写入数据时, 同样会进入等待状态.
适用于生产消费者模型.
其源码实现也相对简单.
1 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { 2 checkNotNull(e); 3 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 4 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 5 try { 6 // 队列满了, 写进入等待 7 while (count == items.length) 8 notFull.await(); 9 insert(e); 10 } finally { 11 lock.unlock(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 16 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 17 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 18 try { 19 // 队列空的, 读进入等待 20 while (count == 0) 21 notEmpty.await(); 22 return extract(); 23 } finally { 24 lock.unlock(); 25 } 26 }
因为BlockingQueue在put take等操作有锁, 因此非高性能容器,
如果需要高并发支持的队列, 则可以使用ConcurrentLinkedQueue. 他内部也是运用了大量无锁操作.
CopyOnWriteArrayList
CopyOnWriteArrayList通过在新增元素时, 复制一份新的数组出来, 并在其中写入数据, 之后将原数组引用指向到新数组.
其Add操作是在内部通过ReentrantLock进行锁保护, 防止多线程场景复制多份数组.
而Read操作内部无锁, 直接返回数组引用, 并发下效率高, 因此适用于读多写少的场景.
源码
1 public boolean add(E e) { 2 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 3 // 写数据的锁 4 lock.lock(); 5 try { 6 Object[] elements = getArray(); 7 int len = elements.length; 8 // 复制到新的数组 9 Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); 10 // 加入新元素 11 newElements[len] = e; 12 // 修改引用 13 setArray(newElements); 14 return true; 15 } finally { 16 lock.unlock(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 final void setArray(Object[] a) { 21 array = a; 22 } 23 24 // 读的时候无锁 25 public E get(int index) { 26 return get(getArray(), index); 27 }
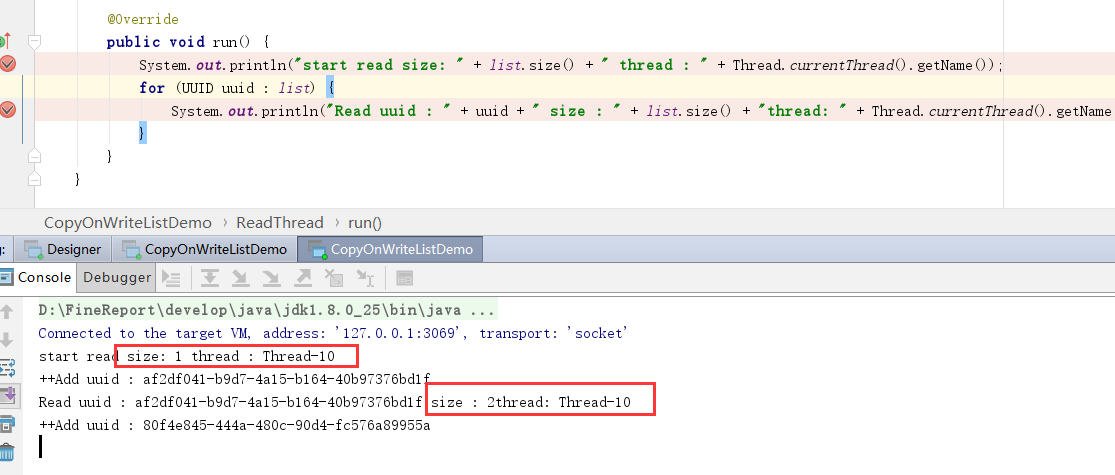
示例
使用10个读线程, 100个写线程. 如果使用ArrayList实现, 那么有可能是在运行过程中抛出ConcurrentModificationException.
原因很简单, ArrayList在遍历的时候会check modCount是否发生变化, 如果一边读一边写就会抛异常.
1 public class CopyOnWriteListDemo { 2 3 static List<UUID> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<UUID>(); 4 // static List<UUID> list = new ArrayList<UUID>(); 5 6 // 往list中写数据 7 public static class AddThread implements Runnable { 8 9 @Override 10 public void run() { 11 UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID(); 12 list.add(uuid); 13 System.out.println("++Add uuid : " + uuid); 14 15 } 16 } 17 18 // 从list中读数据 19 public static class ReadThread implements Runnable { 20 21 @Override 22 public void run() { 23 System.out.println("start read size: " + list.size() + " thread : " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 24 for (UUID uuid : list) { 25 System.out.println("Read uuid : " + uuid + " size : " + list.size() + "thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 30 31 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 32 initThread(new AddThread(), 10); 33 initThread(new ReadThread(), 100); 34 } 35 36 private static void initThread(Runnable runnable, int maxNum) throws InterruptedException { 37 Thread[] ts = new Thread[maxNum]; 38 for (int k = 0; k < maxNum; k++) { 39 ts[k] = new Thread(runnable); 40 } 41 for (int k = 0; k < maxNum; k++) { 42 ts[k].start(); 43 } 44 } 45 }
下图运行结果中可以看出来, 同一个线程, 即使在读的过程中发生了size变化, 也不会抛出ConcurrentModificationException