1. systemctl 管理指令
- 基本语法:
systemctl [start | stop | restart | status] 服务名 systemctl指令管理的服务在 /usr/lib/systemd/system查看

2. systemctl 设置服务的自启动状态
systemctl list-unit-files [ | grep 服务名](查看服务开机启动状态,grep可以进行过滤)

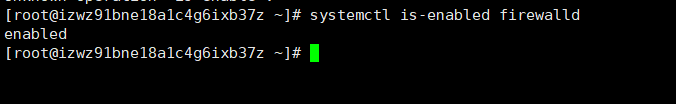
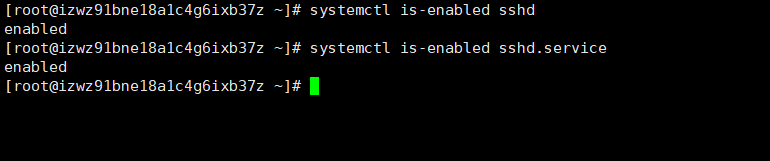
systemctl enable 服务名(设置服务开机启动),对3(无界面)和5(GUI)运行级别都生效systemctl disable 服务名(关闭服务开机启动),对3(无界面)和5(GUI)运行级别都生效systemctl is-enabled 服务名(查询某个服务是否是自启动的)
3. 应用案例:
- 查看当前防火墙的状况,关闭防火墙和重启防火墙。=>
firewalld.service(服务名)
可以写一半再查看完整的服务名,一般也可以简写:firewalld.service = firewall
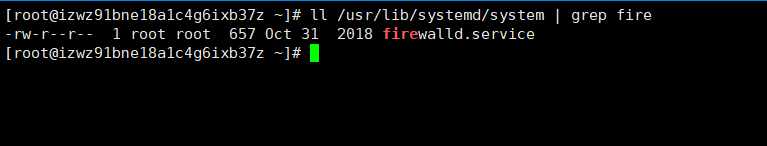
- 说明防火墙是一个自启的状态,Linux系统启动的时候防火墙也会自启。

- 查看防火墙的状态,现在是运行中:
systemctl status firewalld

- 关闭防火墙:
systemctl stop firewalld

- 开启防火墙:
systemctl start firewalld

4. 细节讨论:
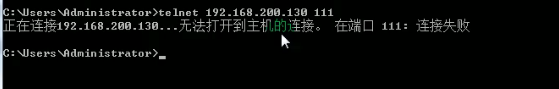
- 关闭或者启用防火墙后,立即生效。[telnet 测试 某个端口即可]

- 案例演示:查看 111 端口的状态


- 访问不到,说明防火墙没放行这个端口
- 当把防火墙关闭的时,就能连接上111端口了,其他端口都是开启的状态

- 这种方式(
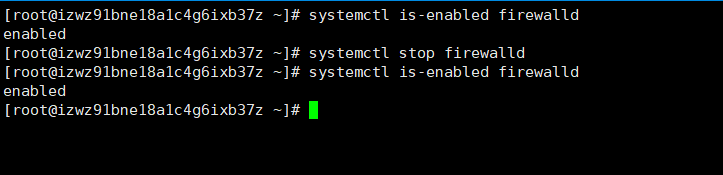
systemctl start/stop firewalld)开启或关闭某个服务只是临时生效,当重启系统后,还是回归以前对服务的设置。 - 如果希望设置某个服务自启动或关闭永久生效,要使用
systemctl [enable|disable] 服务名
- 先用
systemctl is-enabled 服务名(查询某个服务是否是自启动的) 命令查看这个服务是不是自启动的状态
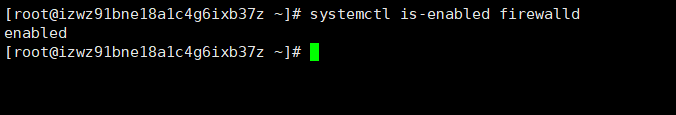
- 使用
systemctl stop firewalld关闭防火墙,发现还是处于自启动状态。
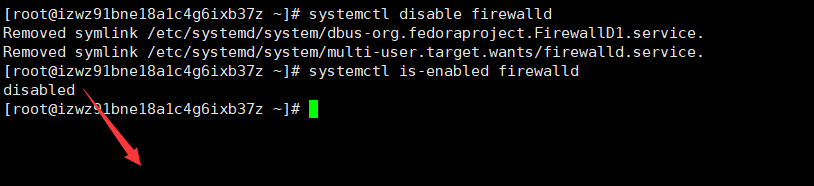
- 使用
systemctl disable firewalld时,下次重启系统时防火墙还是处于关闭的状态
- 重新打开自启动防火墙:
