Java 流程控制
Scanner



public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个扫描器对象,用于接收键盘数据
//new Scanner(System.in); //alt+enter
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用next方式接收:");
//判断用户有没有输入字符串
if(scanner.hasNext()){
//使用next方式接收
String str = scanner.next();
System.out.println("输出内容为:"+str);
}
//!!!凡是属于IO流的类如果不关闭会一直占用资源,要养成好习惯用完就关掉!!!
scanner.close();
}
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);的快捷键输入方式:
- 键盘输入new Scanner(System.in);
- alt+enter--->选择Introduce local variable--->Replcae this occurrence only
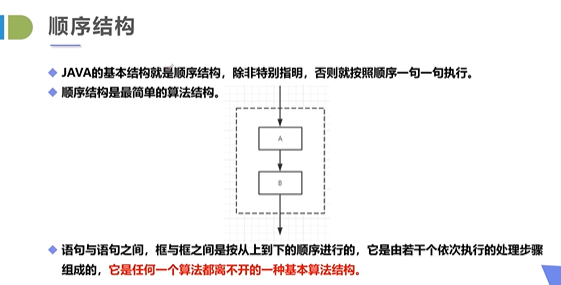
顺序结构
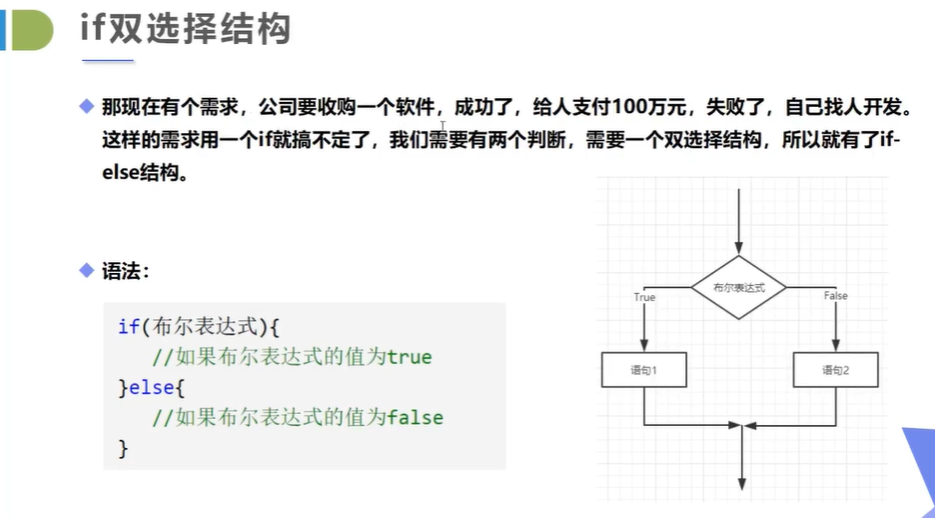
选择结构


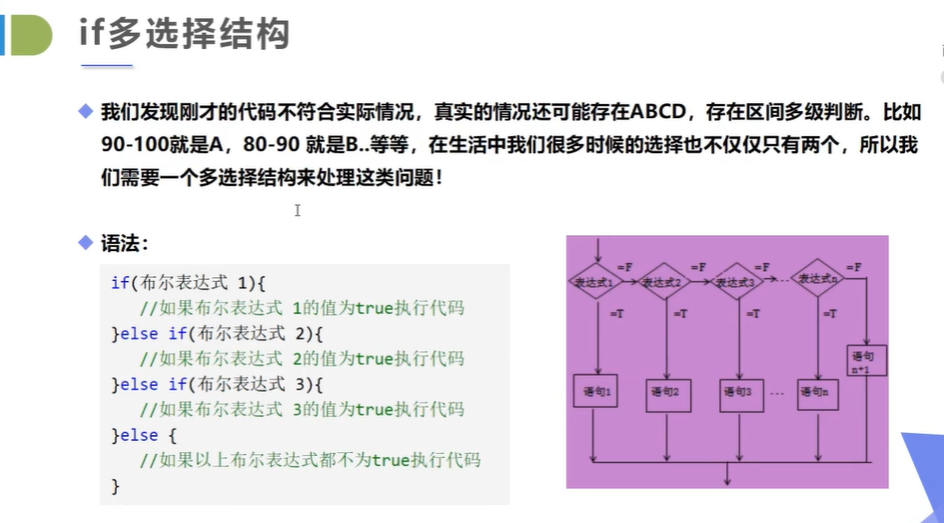
一旦其中一个else if语句检测为true,其他的else if以及else语句都将跳过执行。


如果不写break,会存在case穿透现象
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "xg";
//!!!JDK7的新特性,表达式结果可以是字符串!!!
//字符的本质还是数字
switch(str){
case "XG":
System.out.println("XG");
case "xg":
System.out.println("xg");
}
}
}
反编译:java文件编译之后变成class文件(字节码文件) 字节码文件是人看不懂的,要能看懂需要进行反编译。
反编译的工具很多,这里用IDEA实现反编译
程序能够执行,一定是生成了class文件
IDEA反编译
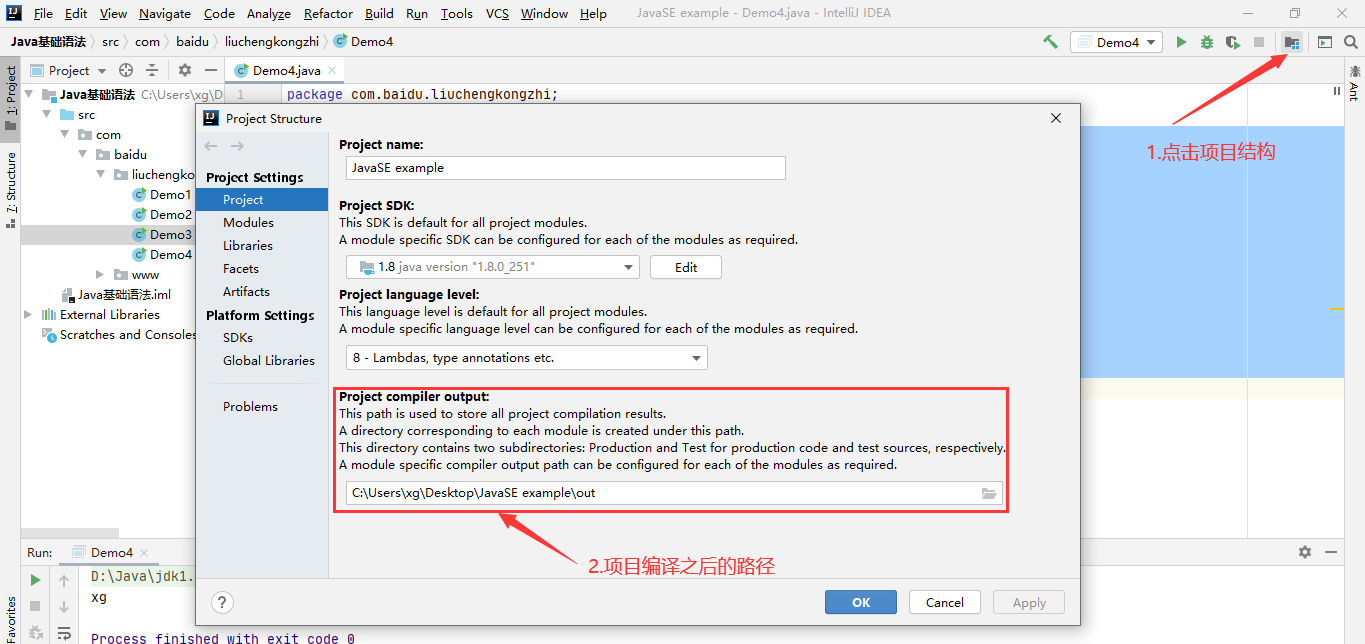
-
将路径打开
-
里面有执行的class文件,打开class文件,里面是一堆乱码,需要进行反编译

-
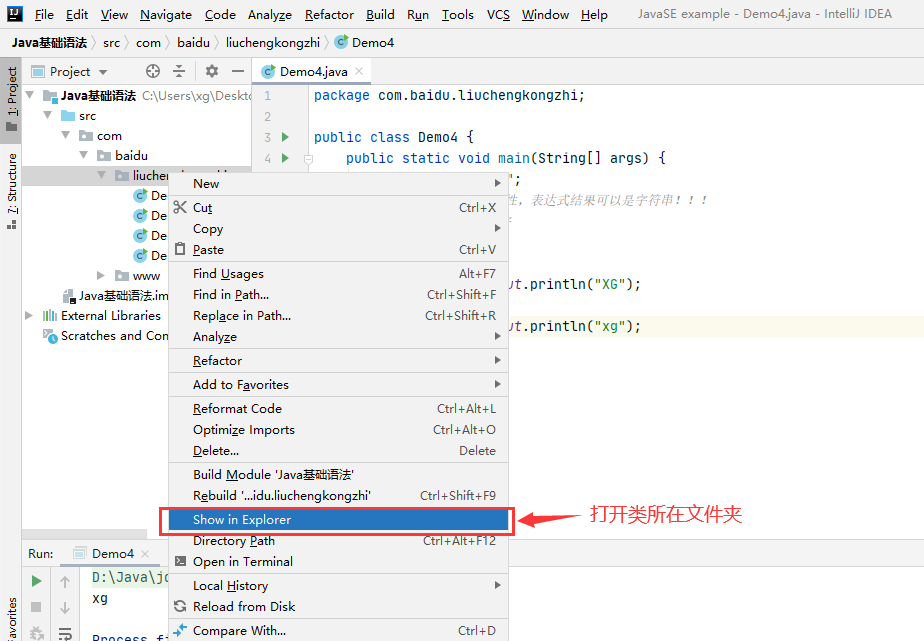
-

-
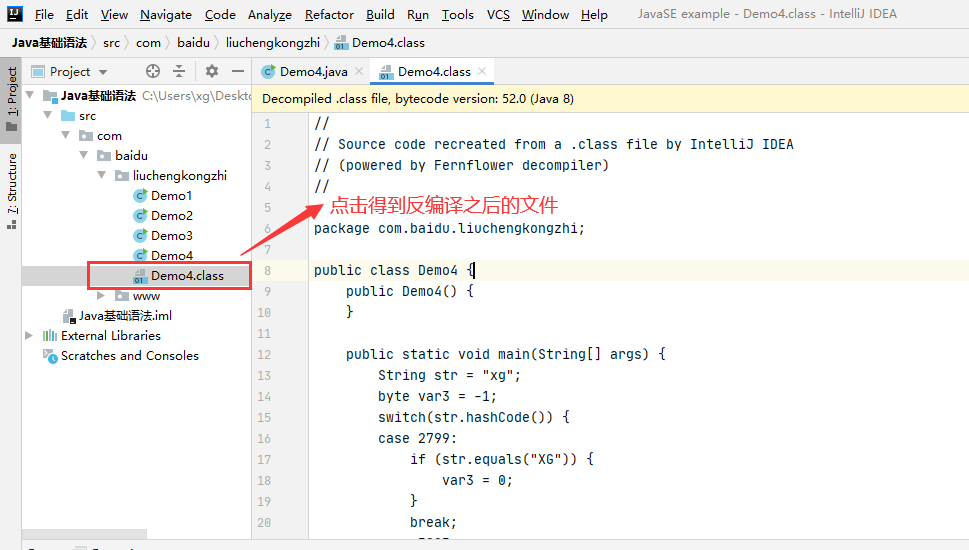
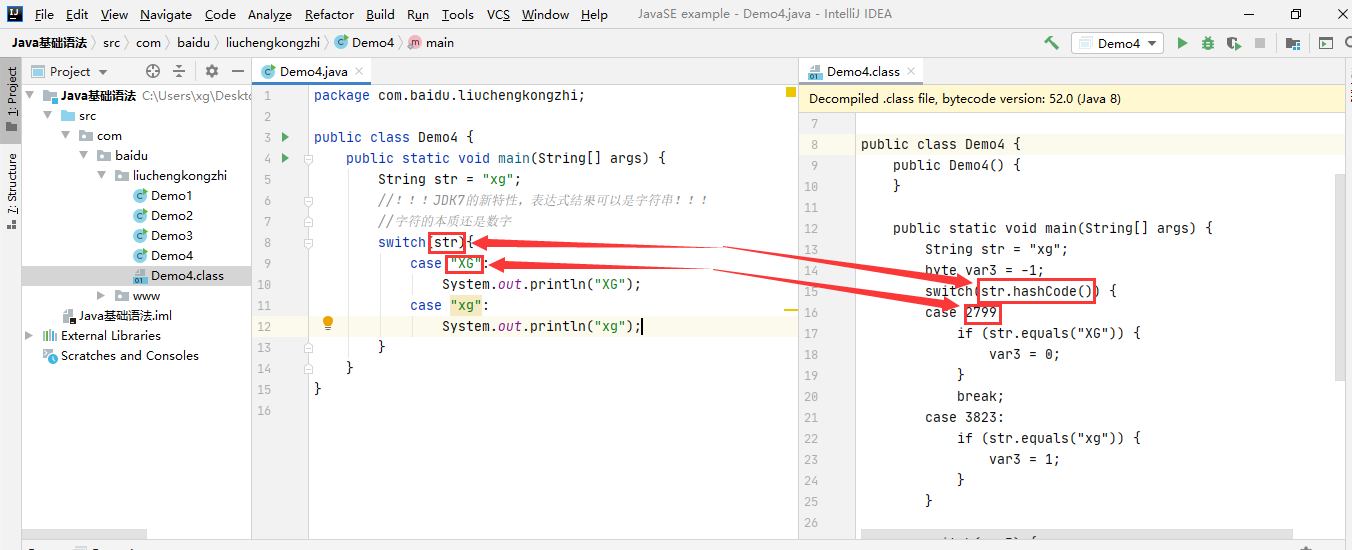
反编译之后的文件为什么switch能支持?
最后编译完还是去找的一个具体的数字
每一个对象都有自己的hashCode,它是通过一些特定算法生成的
要学会看源码
循环结构

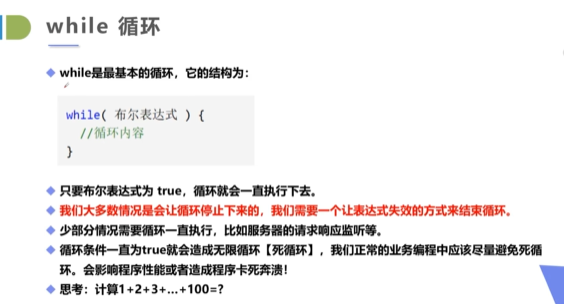



for循环的快捷键:
输入100.for回车会自动生成
for(i = 0;i<= 100;i++){
}


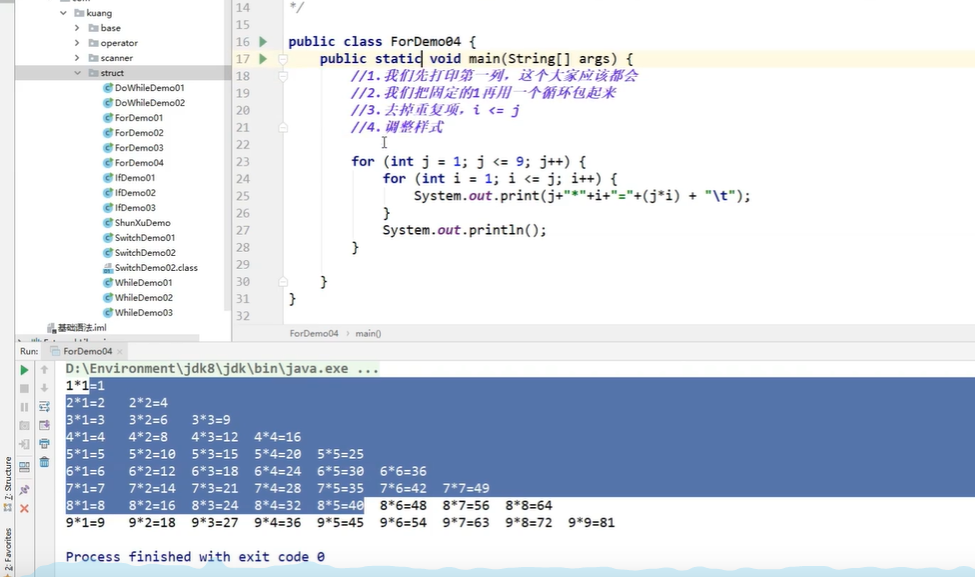
- 打印出第一列,此时1为常量
- 横看1为变量,在外套一层循环
- 去掉重复项
- 调整样式

int []number = {10,20,30,40,50};
for(int x:numbers){
System.out.println(x); //将numbers每一项的值赋值给x
}
break、continue、goto

break:辞职 continue:请假