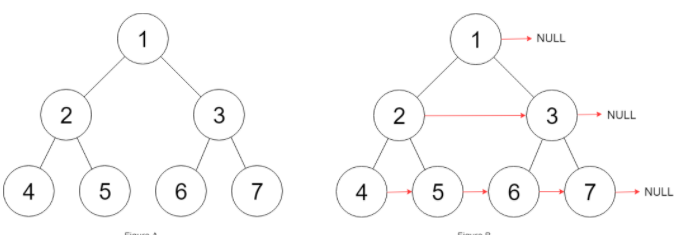
给定一个完美二叉树,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
使用层次遍历
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) {
return nullptr;
}
//层次遍历
queue <Node*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
//记录当前层的节点数
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
//取出最左节点
auto now = que.front();
que.pop();
//除了最右边的节点,其他节点都能连到他右边的节点
if (i < size - 1) {
now->next = que.front();
}
if (now->left) {
que.push(now->left);
}
if (now->right) {
que.push(now->right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
};
递归版
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
help(root);
return root;
}
void help(Node* root) {
if (!root || !root->left) {
return;
}
root->left->next = root->right;
if (root->next) {
root->right->next = root->next->left;
}
help(root->left);
help(root->right);
}
};