一.Mybatis连接池技术
我们经过了解接触过数据库连接池技术,在Mybatis中也有自己的连接池技术,我们可以在Mybatis的SqlMapConfig.xml配置文件中,通过过<dataSource type=”pooled”>来实现 Mybatis 中连接池的配置。
1.Mybaits连接池分类
POOLED:实现dataSource接口,并且使用了池的思想。
UNPOOLED:同样也是实现了dataSource接口,但是该类型并没有使用池的思想。
JDNI:采用服务器提供的JDNI技术实现的,并且在不同服务器之间获取的连接池是不一样的。
其具体结构如下:
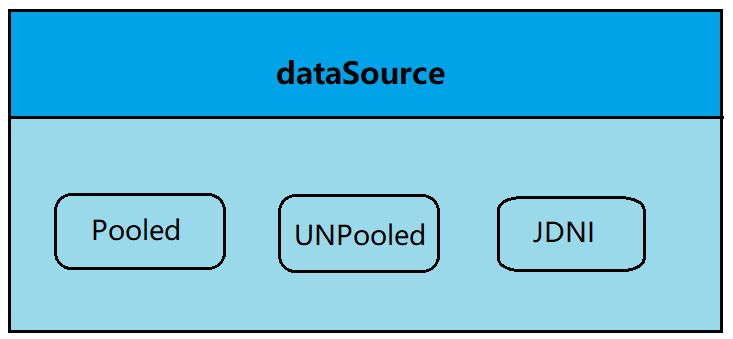
相应的MyBatis 内部分别定义了实现了 java.sql.DataSource 接口的 UnpooledDataSource,PooledDataSource 类来表示 UNPOOLED、POOLED 类型的数据源。
2.Mybaits连接池原理
在这三种数据源中,我们一般采用的是 POOLED 数据源,这里我们详细介绍下POOLED和UNPOOLED数据源代码原理。
(1)POOLED
使用连接池实现数据源。
连接池:其实就是用于存储连接对象的一个容器。该容器是一个集合,而且必须是线程安全的,即两个线程不能拿到同一个连接对象。同时还要具备队列的特性:先进先出原则。
连接池的好处:可以避免频繁创建和关闭数据库连接造成系统资源开销,节省系统资源。
程序运行实例分析:
第一步:将SqlMapConfig.xml数据库连接池改成“POOLED”
<!-- 配置数据源 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource>
当我们MyBatis初始化时,根据我们配饰的数据库连接类型<dataSource>的type属性来创建相应类型的的数据源DataSource即UnpooledDataSource,PooledDataSource,JNDI的话会从JNDI服务上查找DataSource实例,然后返回使用。
第二步,启动测试程序
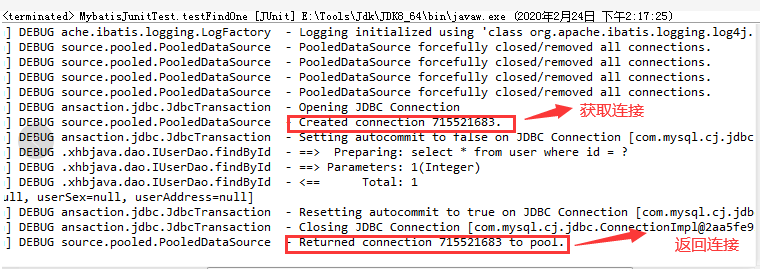
第三步,源码分析
MyBatis是通过工厂模式来创建数据源DataSource对象的,MyBatis定义了抽象的工厂接口:org.apache.ibatis.datasource.DataSourceFactory,通过其getDataSource()方法返回数据源DataSource:
package org.apache.ibatis.datasource; import java.util.Properties; import javax.sql.DataSource; /** * @author Clinton Begin */ public interface DataSourceFactory { void setProperties(Properties props); DataSource getDataSource(); }
MyBatis创建了DataSource实例后,会将其放到Configuration对象内的Environment对象中, 供以后使用,当我们需要创建SqlSession对象并需要执行SQL语句时,这时候MyBatis才会去调用dataSource对象来创建java.sql.Connection对象。
打开XMLConfigBuilder类源码,我找到
public Configuration parse() { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }
第四步,连接获取
@Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection(); } @Override public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { return popConnection(username, password).getProxyConnection(); }
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { boolean countedWait = false; PooledConnection conn = null; long t = System.currentTimeMillis(); int localBadConnectionCount = 0; while (conn == null) { synchronized (state) { if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) { // Pool has available connection conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool."); } } else { // Pool does not have available connection if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) { // Can create new connection conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + "."); } } else { // Cannot create new connection PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0); long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime(); if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) { // Can claim overdue connection state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++; state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime; state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime; state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection); if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) { try { oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback(); } catch (SQLException e) { /* Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following statement like nothing happend. Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help to not intterupt current executing thread and give current thread a chance to join the next competion for another valid/good database connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null. */ log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back"); } } conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this); conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp()); conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp()); oldestActiveConnection.invalidate(); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + "."); } } else { // Must wait try { if (!countedWait) { state.hadToWaitCount++; countedWait = true; } if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection."); } long wt = System.currentTimeMillis(); state.wait(poolTimeToWait); state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt; } catch (InterruptedException e) { break; } } } } if (conn != null) { // ping to server and check the connection is valid or not if (conn.isValid()) { if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) { conn.getRealConnection().rollback(); } conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password)); conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()); conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()); state.activeConnections.add(conn); state.requestCount++; state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t; } else { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection."); } state.badConnectionCount++; localBadConnectionCount++; conn = null; if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database."); } throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database."); } } } } } if (conn == null) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection."); } throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection."); } return conn; }
从上面popConnection方法分析如下:
1>看是否有空闲(idle)状态下的PooledConnection对象,如果有,就直接返回一个可用的PooledConnection对象;否则进行第2步。
2>查看活动状态的PooledConnection池activeConnections是否已满;如果没有满,则创建一个新的PooledConnection对象,然后放到activeConnections池中,然后返回此PooledConnection对象;否则进行第三步;
3>看最先进入activeConnections池中的PooledConnection对象是否已经过期:如果已经过期,从activeConnections池中移除此对象,然后创建一个新的PooledConnection对象,添加到activeConnections中,然后将此对象返回;否则进行第4步。
4>线程等待,循环2步
处理流程提如下:

(2)UPOOLED
上面我们已经知道MyBatis 内部分别定义了实现了 java.sql.DataSource 接口的 UnpooledDataSource,我们通过程序运行分析其原理。
第一步:将SqlMapConfig.xml数据库连接池改成“UNPOOLED”
<environments default="mysql"> <!-- 配置mysql环境 --> <environment id="mysql"> <!-- 配置事务类型 --> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <dataSource type="UNPOOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
第二步:运行测试类
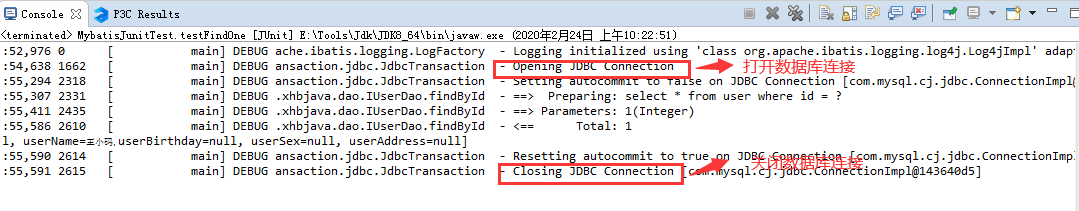
不难发现,UPOOLED没吃都创建一个新的的数据库连接。
第三步:源码剖析
我们找到UnpooledDataSource类,发现有连接数据的信息
private String driver; private String url; private String username; private String password;
接着我们找到了getConnection()方法
@Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return doGetConnection(username, password); }
接着继续跟踪doGetConnection()方法,看到将数据库用名密码封装到Properties中去了,然后调用 doGetConnection
private Connection doGetConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { Properties props = new Properties(); if (driverProperties != null) { props.putAll(driverProperties); } if (username != null) { props.setProperty("user", username); } if (password != null) { props.setProperty("password", password); } return doGetConnection(props); }
接着跟踪doGetConnection(props);
private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException { initializeDriver(); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties); configureConnection(connection); return connection; }
我们分析initializeDriver()方法,是之前jdbc注册驱动方法
private synchronized void initializeDriver() throws SQLException { if (!registeredDrivers.containsKey(driver)) { Class<?> driverType; try { if (driverClassLoader != null) { driverType = Class.forName(driver, true, driverClassLoader); } else { driverType = Resources.classForName(driver); } // DriverManager requires the driver to be loaded via the system ClassLoader. // http://www.kfu.com/~nsayer/Java/dyn-jdbc.html Driver driverInstance = (Driver)driverType.newInstance(); DriverManager.registerDriver(new DriverProxy(driverInstance)); registeredDrivers.put(driver, driverInstance); } catch (Exception e) { throw new SQLException("Error setting driver on UnpooledDataSource. Cause: " + e); } }
此时会发现就是一个注册驱动,生成连接返回连接的过程。所以每次调用就会产生一个新的connection对象。
(3)JNDI
JNDI:Java Naming and Directory Interface。是SUN公司推出的一套规范,属于JavaEE技术之一。目的是模仿windows系统中的注册表
分析JndiDataSourceFactory类关键代码
private static Properties getEnvProperties(Properties allProps) { final String PREFIX = ENV_PREFIX; Properties contextProperties = null; for (Entry<Object, Object> entry : allProps.entrySet()) { String key = (String) entry.getKey(); String value = (String) entry.getValue(); if (key.startsWith(PREFIX)) { if (contextProperties == null) { contextProperties = new Properties(); } contextProperties.put(key.substring(PREFIX.length()), value); } } return contextProperties; }
我们通过JNDI的上下文中找到datasource并返回。
二、Mybatis事务
通过sqlsession对象的commit方法和rollback方法实现事务的提交和回滚。
这里我们简单的了解下,关于复杂的事务控制在Sping的学习中在深入了解。
(1)Mybatis中事务的提交方式
@Test public void testSave() { User user = new User(); user.setUserName("王小李"); user.setUserAddress("北京"); user.setUserSex("男"); user.setUserBirthday(new Date()); userDao.saveUser(user); System.out.println("保存:" + user); }
@Before public void init() { // 1.读取配置文件 try { in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml"); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // 2.创建构建者 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); // 3.创建session工厂 factory = builder.build(in); // 4.创建session对象 session = factory.openSession(); // 5.创建Dao的代理对象 userDao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class); }
@After // 在测试方法执行完成之后执行 public void destroy() throws Exception { // 提交事务 session.commit(); // 7.释放资源 session.close(); in.close(); }
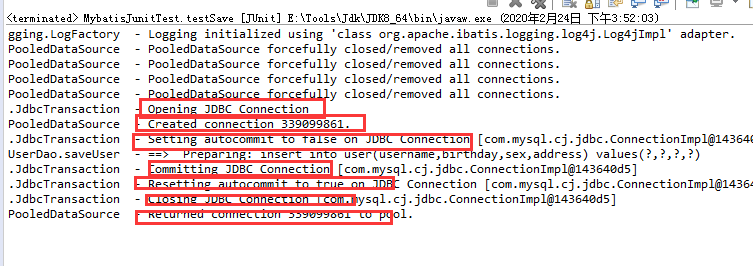
我们观察测试执行过程发现的Connection 的整个变化过程,通过分析我们能够发现之前的 CUD 操作过程中,我们都要手动进行事务的提交,原因是 setAutoCommit()方法,在执行时它的值被设置为 false 了,所以我们在 CUD 操作中,必须通过 sqlSession.commit()方法来执行提交操作。
@Test public void testSave() { User user = new User(); user.setUserName("王小二"); user.setUserAddress("北京"); user.setUserSex("男"); user.setUserBirthday(new Date()); userDao.saveUser(user); System.out.println("保存:" + user); }
@Before public void init() { // 1.读取配置文件 try { in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml"); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // 2.创建构建者 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); // 3.创建session工厂 factory = builder.build(in); // 4.创建session对象 session = factory.openSession(true); // 5.创建Dao的代理对象 userDao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class); }
@After // 在测试方法执行完成之后执行 public void destroy() throws Exception { // 7.释放资源 session.close(); in.close(); }
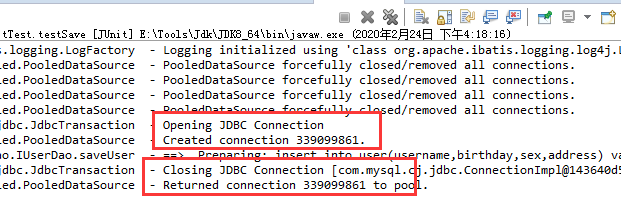
我们发现此时我们的事务自动提交了,在我们实际工作中我们会根据业务实际情况控制事务的提交,因此我们设置事务自动提交方式为false方式更常用。