以一个连接一个线程为例,也就是thread_handling为one-thread-per-connection模式,这也是社区版本的唯一模式。
[dba_yix@127.0.0.1][(none)]> show variables like '%thread_hand%';
+-----------------+---------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+---------------------------+
| thread_handling | one-thread-per-connection |
+-----------------+---------------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
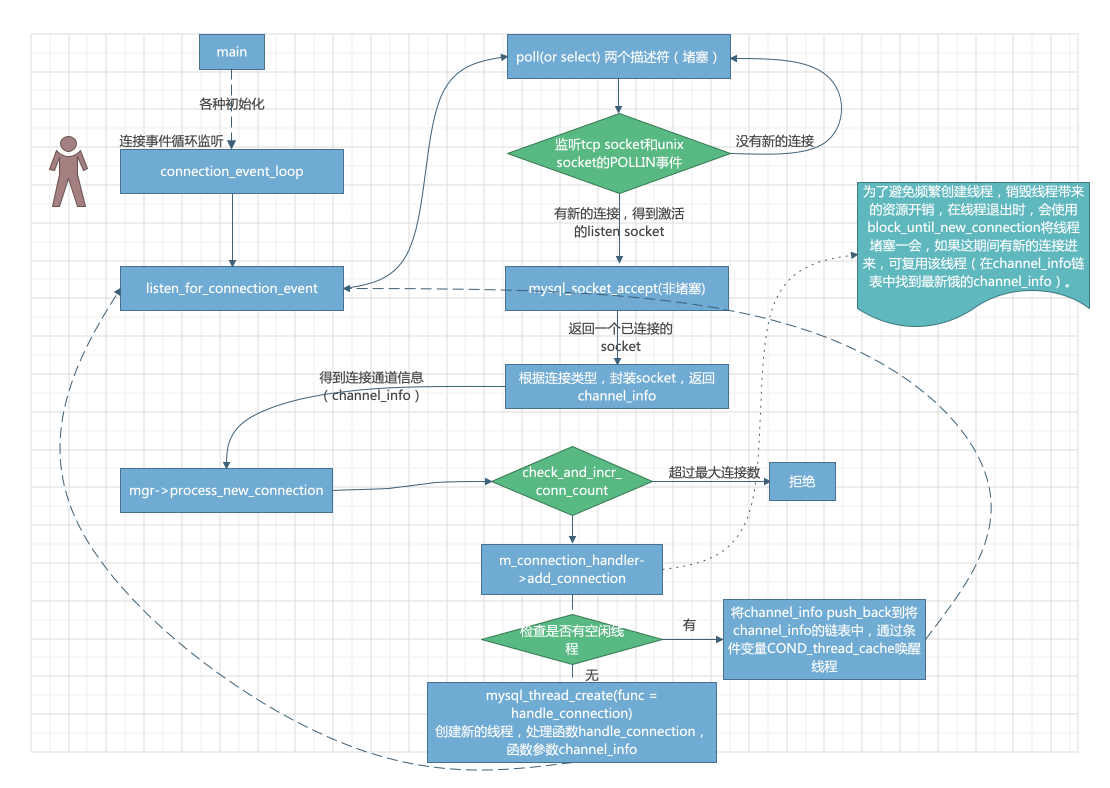
- 监听连接
关键字: listen_for_connection_event, process_new_connection,poll
/**
连接接受器循环以接受来自客户端的连接。
*/
void connection_event_loop()
{
Connection_handler_manager *mgr= Connection_handler_manager::get_instance();
while (!abort_loop)
{
Channel_info *channel_info= m_listener->listen_for_connection_event();
/* 重点在这个listen_for_connection_event方法里面,调用了poll处理这个监听描述符,poll传递的参数timeout传递的是-1,也就是堵塞等待 */
if (channel_info != NULL)
/* 处理一个新的连接,channel_info里面包含了连接信息。
不出错的情况下,会使用mysql_thread_create创建一个线程,线程的入口函数是handle_connection。见3
如果有空闲的线程会复用。 */
mgr->process_new_connection(channel_info);
}
}
- 处理监听
Channel_info* Mysqld_socket_listener::listen_for_connection_event()
{
int retval= poll(&m_poll_info.m_fds[0], m_socket_map.size(), -1);
/* setup_listener 中设置了和tcp socket监听和unix socket监听,存在map类型m_socket_map中。
所以m_socket_map.size()为2,监听两个描述符的POLLIN事件。*/
for (uint i= 0; i < m_socket_map.size(); ++i)
{
if (m_poll_info.m_fds[i].revents & POLLIN)
{
listen_sock= m_poll_info.m_pfs_fds[i];
is_unix_socket= m_socket_map[listen_sock];
/* 遍历监听描述符,判断是否是unix套接字。*/
break;
}
}
for (uint retry= 0; retry < MAX_ACCEPT_RETRY; retry++)
{
socket_len_t length= sizeof(struct sockaddr_storage);
/* 由于触发了POLLIN事件,所以这里accept不会被堵塞。 */
connect_sock= mysql_socket_accept(key_socket_client_connection, listen_sock,
(struct sockaddr *)(&cAddr), &length);
}
Channel_info* channel_info= NULL;
/* 封装连接通道,隐藏UNIX socket和tcp socket的差异。 */
if (is_unix_socket)
channel_info= new (std::nothrow) Channel_info_local_socket(connect_sock);
else
channel_info= new (std::nothrow) Channel_info_tcpip_socket(connect_sock);
return channel_info;
}
- 处理连接
代码路径conn_handler/connection_handler_per_thread.cc:249
关键字:channel_info, thd_manager, handler_manager, init_new_thd,do_command,thd
代码概要:
void *handle_connection(void *arg)
{
Global_THD_manager *thd_manager= Global_THD_manager::get_instance();
// 获取一个全局的线程管理器(单例模式)
// thd_manager类似一个门卫,对每个来访的客人(连接)进行登记,注册, 销毁等操作。
// 此外还包括其他后台线程
Connection_handler_manager *handler_manager= Connection_handler_manager::get_instance();
// 获取一个连接处理器(单例模式)。与上面不同的是,这个只处理连接线程。
// 例如增加全局的connection记数,通过reset_max_used_connections响应set max_collections = 2000这样的请求等。
Channel_info* channel_info= static_cast<Channel_info*>(arg);
// Channel_info抽象基类表示有关新连接的连接通道信息。子类封装了不同连接通道类型之间的差异。
// 所谓的不同连接类型比如,本地套接字,tcp/ip链接、命名管道,共享内存等。(后两者只存在windows平台)
for (;;){
THD *thd= init_new_thd(channel_info); /* 使用连接通道初始化一个新的线程,
这个线程里面携带了连接信息,以后每次处理query的时候,
实际上就是这个thd里面携带了客户端以及客户端请求的各种信息。
如果这里出错了,会增加Aborted_connects的状态值。同时减少全局的连接计数。
*/
PSI_thread *psi= PSI_THREAD_CALL(get_thread)();/* 。psi用于performance监控。(PSI_THREAD_CALL为ps惯用宏,pfs_get_thread_v1)
这个函数最终调用了pthread库的pthread_getspecific,用于操作线程中的全局变量。
*/
thd->set_psi(psi); // 挂到线程中,以便后续用这个psi进行性能监控。
thd_manager->add_thd(thd);// 通过线程管理器将这个线程对象加到线程链表中。
if (thd_prepare_connection(thd)) // 连接前检查,包括握手、授权客户端和更新线程ACL,
// 判断是tcpip还是本地套接字链接。设置长链接等。来访者ip是否允许访问等等。
handler_manager->inc_aborted_connects(); // 如果检查失败需要中断链接
else
{
while (thd_connection_alive(thd))
{
if (do_command(thd)) // ✨✨连*状态是ok的话,会一直执行线程的命令请求。这里就是我们函数的交互入口了。
break;
}
end_connection(thd); // 连接结束处理。
}
close_connection(thd, 0, false, false); // 关闭连接
thd->get_stmt_da()->reset_diagnostics_area(); // 释放资源
thd->release_resources(); 。
thd_manager->remove_thd(thd); // 线程管理器移除这个连接线程
Connection_handler_manager::dec_connection_count(); // 减少全局connection计数。
delete thd; // 释放内存。
if (abort_loop) // 服务器关闭中需要结束pthread。正常来说,不会走这个路线。
break; // abort_loop 是一个全局变量,当数据库关闭时,会设置为true。
channel_info= Per_thread_connection_handler::block_until_new_connection();
// 连接重用。
}
}
综上画了一个图: