公有与私有
Private Sub test() 'privete私有的,这有在这个模块下可以被调用,相反为 public公有的 MsgBox "aaa" End Sub --------------------- Sub test1() Call test End Sub
还有一个小知识点
Dim i As Integer ‘将i 定义在外面,那么所有的过程及sub都能对i进行调用 ---------------- '在这种情况下,只能在同一个模块下可以任意调用 Sub test() i = 1 End Sub ---------------- Sub test1() ‘跨过程调用 MsgBox i End Sub
在这种情况下可以跨模块进行调用,这个谨慎使用,占用内存,且容易出现错误
模块1 Public i As Integer -------------------- Sub test() i = 1 End Sub ------------------- Sub test1() MsgBox i End Sub ------------------- 模块2 Sub test1() MsgBox i End Sub
如果非要跨模块取值的话,可以使用这种方法
模块1 Dim i As Integer ----------------- Sub test() i = 1 End Sub ----------------- Sub test1() MsgBox i End Sub ----------------- Function qbl() '定义一个函数来取值,具有通用性 qbl = i End Function ------------------ 模块2 Sub test2() MsgBox i End Sub
可以作为小的存储空间
Dim str As String '定义在外面那么可以作为一个小存储空间 --------------------- Sub test() str = InputBox("请输入考生名") End Sub --------------------- Sub test1() '在执行完test后,数据存储在str,在最后考生结束考试,可以 MsgBox str ‘点击test1输出考生名 End Sub
类模块
这里主要是讲理论,去理解什么是类模块,它的作用是自己可以创建个对象,以及它的属性等
例如之前我们学习过的,创建表
Sub test() Dim sht, sht1 As Worksheet For Each sht In Sheets If sht.Name = "一月" Then k = k + 1 End If Next If k = 0 Then Set sht1 = Sheets.Add sht1.Name = "一月" End If End Sub
优化成带参数的过程:减少代码
Sub test1() Call test("二月") End Sub ------------------------------- Sub test(str As String) Dim sht, sht1 As Worksheet For Each sht In Sheets If sht.Name = str Then k = k + 1 End If Next If k = 0 Then Set sht1 = Sheets.Add sht1.Name = str End If End Sub
另再增加删除表
Sub test1() 'Call Sadd("二月") Call Sdelete("二月") End Sub ------------------------------ Sub Sadd(str As String) Dim sht, sht1 As Worksheet For Each sht In Sheets If sht.Name = str Then k = k + 1 End If Next If k = 0 Then Set sht1 = Sheets.Add sht1.Name = str End If End Sub ------------------------------ Sub Sdelete(str As String) Dim sht As Worksheet For Each sht In Sheets If sht.Name = str Then Application.DisplayAlerts = False sht.Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True End If Next End Sub
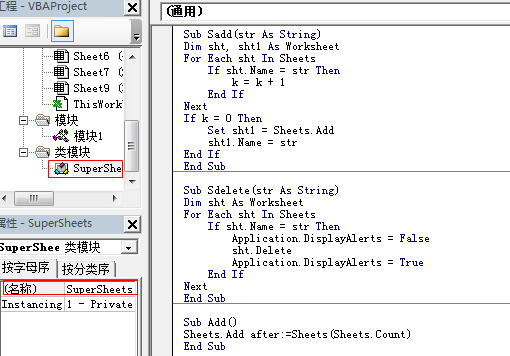
以此为切入点讲解什么是类模块:在这里面定义的都是方法
类模块
Sub Sadd(str As String) Dim sht, sht1 As Worksheet For Each sht In Sheets If sht.Name = str Then k = k + 1 End If Next If k = 0 Then Set sht1 = Sheets.Add sht1.Name = str End If End Sub ------------------------------------ Sub Sdelete(str As String) Dim sht As Worksheet For Each sht In Sheets If sht.Name = str Then Application.DisplayAlerts = False sht.Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True End If Next End Sub ------------------------------------- Sub Add() Sheets.Add after:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) End Sub
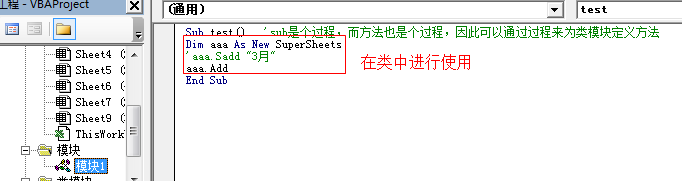
在模块中再使用 :
Sub test() 'sub是个过程,而方法也是个过程,因此可以通过过程来为类模块定义方法 Dim aaa As New SuperSheets 'aaa.Sadd "3月" aaa.Add End Sub
属性:分为两种只读属性,写入属性
Sub test() Range("a1") = Sheets.Count '只读属性,只能读取 Sheet1.Name = 999 '可以进行赋值的属性,写入属性 End Sub
在模块里有sub过程和function函数计算过程,对应的在类模块,sub对应方法,function对应属性
Sub test() Range("a1") = Scount() End Sub ------------------------- Function Scount() ;不用参数,直接计算出结果 Scount = Sheets.Count End Function
但是在类模块中声明一个属性用的是Property 声明它有三个值 get:只读的;let:写属性入的属性,set:子对象,它就相当于模块中的function函数
Do While循环