在tensorboard上显示运行图:
import tensorflow as tf a = tf.constant(10,name="a") b = tf.constant(90,name="b") y = tf.Variable(a+b*2,name='y') init=tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: merged = tf.summary.merge_all() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('C:/Users/1/Desktop/1',sess.graph) #自定义tensor到给定路径中,奇葩的tensorboard路径只能设置在文件夹下,不能直接设置在桌面,否则报错 sess.run(init) print(sess.run(y))
通过在终端输入如下:
cd 路径
tensorboard --logdir=路径
浏览器输入:http://localhost:6006/ 得到tensorboard展示
另一个例子:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #python的结果可视化模块 def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, n_layer, activation_function=None): layer_name = 'layer%s' % n_layer with tf.name_scope(layer_name): with tf.name_scope("wights"): Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]), name='W') #定义权重矩阵 #tf.summary.histogram用于保存变量的变化 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name+'/weights', Weights) with tf.name_scope("biases"): biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1, name='b')#定义偏置 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases) with tf.name_scope("Wx_plus_b"): Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases #预测出的值 if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b #线性激活 else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) #非线性激活 tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/outputs', outputs) return outputs #定义输入,linspace产生等差数列,加上数据的维度,定义输入数据为300个例子 x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis] # print(x_data.shape) noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) #定义噪声点 y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise # y=x_data*x_data - 0.5 #定义命名空间,使用tensorboard进行可视化 with tf.name_scope("inputs"): xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name="x_input") #模型的输入x值 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], name="y_input") #模型的输入y值 #隐藏层 l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, n_layer=1, activation_function=tf.nn.relu) #输出层 prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, n_layer=2, activation_function=None) #损失函数 with tf.name_scope("loss"): loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) #用于观察常量的变化 #模型训练 with tf.name_scope("train"): train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() #初始化所有变量 with tf.Session() as sess: merged = tf.summary.merge_all() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("C:/Users/1/Desktop/1", sess.graph) #保存神经网络的所有的信息,方便浏览器访问 sess.run(init) for i in range(1001): sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) if i % 50 == 0:#每训练50次,合并一下结果 result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) writer.add_summary(result, i)
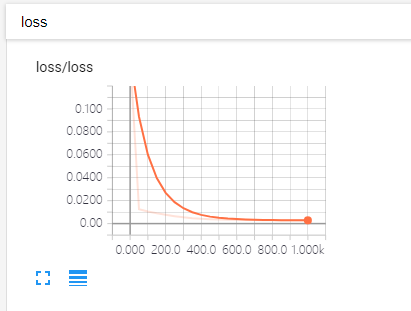
展示tensorboard(损失函数随epoch增加的变化情况):