- fopen fclose
- fread fwrite
- fflush-
- fseek-
- fgetc getc getchar
- fputc putc putchar
- fgets gets
- printf fprintf sprintf
- scanf fscanf sscanf

2. fwrite fread
标准I/O库 常用函数使用
1.fopen函数 :用于文件和终端的输入和输出。
#include <stdio.h>
FILE * fopen(const char* filename, const char *mod);
2.fclose函数:关闭指定的文件流stream。
#include <stdio.h>
int fclose(FILE *stream);
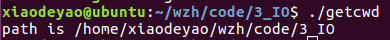
3.getcwd函数:把当前目录的名字写入buf中。
#include<unistd.h>
char* getcwd(char* buf ,size_t size);
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> int main() { char acFilePath [50] = {0}; getcwd(acFilePath, sizeof(acFilePath)); printf("path is %s ", acFilePath); return 0; }
ex:
4.fgets函数:从输入文件流stream中读取一个字符串。
#include <stdio.h>
char *fgets(char *s, int n ,FILE *stream);
fgets把一个字符串写到s指向的的字符串里,直到出现以下某种情况:
- 遇到换行符
- 已经传输了n-1个字符
- 到达文件尾。
它会把遇到的换行符号也传递到接收字符串里,再加上一个表示结尾的空字节�。一次最多只能传输n-1个字符。
5格式化输入输出
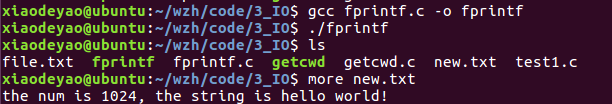
#include <stdio.h>
int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...)
把自己的输出送到一个指定的文件流中。
#include<stdio.h> int main() { FILE *pfile = fopen("/home/xiaodeyao/wzh/code/3_IO/new.txt","wb+"); fprintf(pfile, "the num is %d, the string is %s", 1024, "hello world!"); return 0; }
ex:
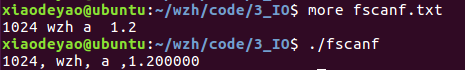
#include <stdio.h>
int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...)
从流 stream 读取格式化输入。
#include<stdio.h> int main() { FILE *pfile = fopen("/home/xiaodeyao/wzh/code/3_IO/fscanf.txt", "r"); int a = 0; char acDate[20] = {0}; float dou = 0; char c = 0; fscanf(pfile, "%d %s %c %f", &a, acDate, &c, &dou); printf("%d, %s, %c ,%f ", a, acDate, c, dou); return 0; }
ex:
ps:这里文件mod如果是“w‘”,会有问题。但是某些情况下是可以用“w"的。例如:http://www.runoob.com/cprogramming/c-function-fscanf.html
这里待深究一下。
6.fseek()
为下一次文件读写操作指定位置。
int fseek(FILE *stream, long int offset, int whence)
stream -- 这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象标识了流。
offset -- 这是相对 whence 的偏移量,以字节为单位。
whence -- 这是表示开始添加偏移 offset 的位置。它一般指定为下列常量之一:
常量 描述
SEEK_SET 文件的开头
SEEK_CUR 文件指针的当前位置
SEEK_END 文件的末尾
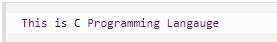
#include <stdio.h> int main () { FILE *fp; fp = fopen("file.txt","w+"); fputs("This is w3cschool.cc", fp); fseek( fp, 7, SEEK_SET ); fputs(" C Programming Langauge", fp); fclose(fp); return(0); }
ex:
7.ftell()
long int ftell(FILE *stream)
参数
stream -- 这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象标识了流。
返回值
该函数返回位置标识符的当前值。如果发生错误,则返回 -1L,全局变量 errno 被设置为一个正值。
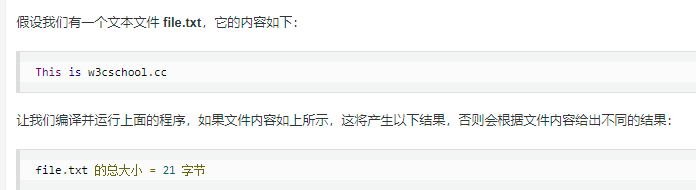
#include <stdio.h> int main () { FILE *fp; int len; fp = fopen("file.txt", "r"); if( fp == NULL ) { perror ("打开文件错误"); return(-1); } fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END); len = ftell(fp); fclose(fp); printf("file.txt 的总大小 = %d 字节 ", len); return(0); }
ex:
参考:
http://www.runoob.com/cprogramming/c-function-ftell.html
ps:C语言文本方式和二进制方式读写操作的区别 http://blog.csdn.net/junbopengpeng/article/details/13091045