手动实现对数据库中【单行】数据的查询操作(以Customers表为例)
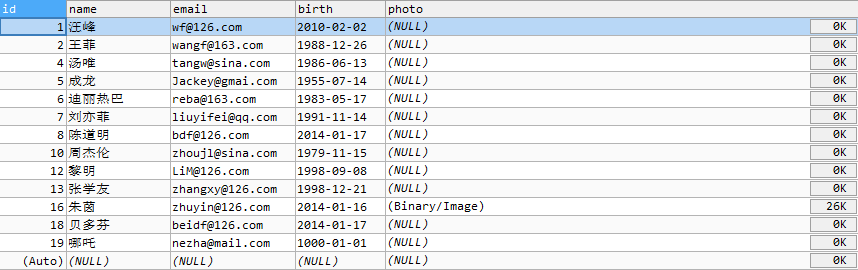
Customers表
仅仅针对于Customers表的已知列的查询操作:
1 /*** 2 * 3 * @Description 针对于Customer表的查询操作 4 * @author XiaoFeng 5 * @throws Exception 6 * @date 2020年8月21日下午2:14:45 7 */ 8 @Test 9 public void CustomerForQuery() { 10 Connection conn = null; 11 PreparedStatement ps = null; 12 ResultSet rs = null; 13 try { 14 // 建立与数据库的连接 15 // 加载资源 16 InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); 17 Properties pros = new Properties(); 18 pros.load(is); 19 // 获取资源 20 String user = pros.getProperty("user"); 21 String password = pros.getProperty("password"); 22 String url = pros.getProperty("url"); 23 String driver = pros.getProperty("driverClass"); 24 // 加载数据库驱动 25 Class.forName(driver); 26 // 获取数据库连接 27 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); 28 // 操作数据库 29 // 预编译SQL语句,返回PreparedStatement实例对象 30 String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?"; 31 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 32 // 填充占位符 33 ps.setObject(1, 5); 34 // 执行ps中传入的SQL语句并返回结果集 35 rs = ps.executeQuery(); 36 // 获取结果集中每列的值并封装到数据表对应类的实例化对象中 37 // next():判断结果集的下一行是否有数据。如果有数据,返回true并且指针下移;如果返回false,指针不下移。 38 if (rs.next()) { 39 // 获取当前行中各个字段的值 40 int id = rs.getInt(1); 41 String name = rs.getString(2); 42 String email = rs.getString(3); 43 java.sql.Date birth = rs.getDate(4); 44 // 将获取的字段值封装到数据表对应类的实例化对象中 45 Customer customer = new Customer(id, name, email, birth); 46 System.out.println(customer); 47 } 48 System.out.println("查询完成"); 49 } catch (Exception e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } finally { 52 // 关闭资源 53 if (rs != null) { 54 try { 55 rs.close(); 56 } catch (SQLException e) { 57 e.printStackTrace(); 58 } 59 } 60 if (ps != null) { 61 try { 62 ps.close(); 63 } catch (SQLException e) { 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 } 67 if (conn != null) { 68 try { 69 conn.close(); 70 } catch (SQLException e) { 71 e.printStackTrace(); 72 } 73 } 74 75 } 76 77 }
Customers表的通用查询操作:
1 /*** 2 * 3 * @Description 针对于customers表的通用的查询操作 4 * @author XiaoFeng 5 * @date 2020年8月21日下午2:52:27 6 * @return 7 * @throws Exception 8 */ 9 public Customer queryForCustomer(String sql, Object... args) { 10 Connection conn = null; 11 PreparedStatement ps = null; 12 ResultSet rs = null; 13 try { 14 // 建立与数据库的连接 15 // 加载资源 16 InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); 17 Properties pros = new Properties(); 18 pros.load(is); 19 // 读取资源 20 String user = pros.getProperty("user"); 21 String password = pros.getProperty("password"); 22 String url = pros.getProperty("url"); 23 String driver = pros.getProperty("driverClass"); 24 // 加载数据库驱动 25 Class.forName(driver); 26 // 获取数据库连接 27 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); 28 // 操作数据库 29 // 预编译SQL语句,返回PreparedStatement实例对象 30 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 31 // 填充占位符 32 for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { 33 ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); 34 } 35 // 执行ps中的SQL语句并返回结果集 36 rs = ps.executeQuery(); 37 // 获取结果集的元数据 38 ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); 39 // 通过元数据获取结果集的列数,从而确定在获取值时循环的次数 40 int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); 41 // 获取结果集中每一行的每个列值并将值封装到对应的类对象中 42 if (rs.next()) { 43 Customer customer = new Customer(); 44 // 循环获取每一行的所有列值 45 for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { 46 Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i + 1); 47 48 // 将获取到的列值对应的封装到对象的属性中 49 50 // 通过结果集元数据获取每一列的列名 51 String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1); 52 53 // 通过属性名获取属性类型,考虑利用反射中 getDeclaredField() 54 Field field = Customer.class.getDeclaredField(columnLabel); 55 // 确保当前的属性是可访问的 56 field.setAccessible(true); 57 field.set(customer, columnValue); 58 } 59 System.out.println("查询完成"); 60 return customer; 61 } 62 } catch (Exception e) { 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 } finally { 65 // 关闭资源 66 if (rs != null) { 67 try { 68 rs.close(); 69 } catch (SQLException e) { 70 e.printStackTrace(); 71 } 72 } 73 if (ps != null) { 74 try { 75 ps.close(); 76 } catch (SQLException e) { 77 e.printStackTrace(); 78 } 79 } 80 if (conn != null) { 81 try { 82 conn.close(); 83 } catch (SQLException e) { 84 e.printStackTrace(); 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 return null; 89 }
测试代码:
1 @Test 2 public void testQueryForCustomer() { 3 String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?"; 4 Customer customer = queryForCustomer(sql, 16); 5 System.out.println(customer); 6 }