Linux运维第一天:
配置云主机、安装使用Xmanager Enterprise 4工具
Linux运维第二天:
安装虚拟机(vmware+Linux6.5/7.2)
虚拟机三种方式实现上网功能(host-only、Bridge、Nat)
host-only需要设置一下主机和两块网卡(上网网卡和vmnet1 ),然后配置虚拟机网卡
上网网卡共享给vmnet1,vmnet1设置dns:上网网卡使用的dns或8.8.8.8
vmnet1与虚拟机网卡要在一个网段上,dns:上网网卡使用的实际dns或8.8.8.8
bridege、nat很简单
1-1-UnixLinux系统介绍、可用试验环境和创建快照
Linux的优点及vmware使用技巧
优点:1、模块化程度高;2、源码公开;3、广泛的硬件支持;4、安全性及可靠性;5、具有优秀的开发工具;6、很好的网络支持文件系统;7、与UNIX完全兼容
vmware使用技巧:
1、增加虚拟机可用物理内存(最好关机状态调整)
2、硬件设备添加(可以开机状态添加)
3、控制权切换快捷方式:ctrl+alt;alt+G
安装配置虚拟机(RHEL7.2)
第一步:联网(最好使用固定IP)
第二步:关闭防火墙(systemctl disable firewalld)
第三步:关闭selinux(/etc/selinux/config)
第四步:开机挂载光驱(echo “/dev/cdrom /mnt iso9660 defaults 0 0” >> /etc/fstab)
第五步:配置YUM源(/etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo)
配置文件如下:注意[]中不要出现空格什么的
[RHEL7_SERVER]
name = rhel server
baseurl = file:///mnt
enable = 1
gpgcheck = 0
1-2 Linux基本命令
Linux系统中两种终端(控制台终端、pts虚拟终端)
ctrl+alt+F2~F6 切换控制台终端(tty1~tty6) alt + F1 (返回tty1)
pts虚拟终端(远程连接等pseudo-tty)
shell提示符
[root@xiaogan ~]#简介 root当前用户、@xiaogan主机名 ~ 当前目录 #/$权限描述符
Linux命令
ls 查看目录
pwd查看路径
cd切换目录
hwclock查看硬件时间
date查看系统时间
获取帮助的方式三种(1、date --help;2、fdisk -h;3、man find)
关机、重启等操作(shutdown -h关机和 –r 重启、reboot重启、init 0关机、init 6重启、定时关机)
rhel7中也可以使用 systemctl reboot 或 systemctl poweroff
Linux7个启动级别
init命令切换、systemd中的systemctl isolate切换
0 poweroff
0 系统停机模式,系统默认运行级别不能设置为0,否则不能正常启动,机器关闭。
1 单用户模式,root权限,用于系统维护,禁止远程登陆,就像Windows下的安全模式登录。
2 多用户模式,没有NFS网络支持。
3 完整的多用户文本模式,有NFS,登陆后进入控制台命令行模式。
4 系统未使用,保留一般不用,在一些特殊情况下可以用它来做一些事情。例如在笔记本电脑的电池用尽时,可以切换到这个模式来做一些设置。
5 图形化模式,登陆后进入图形GUI模式,X Window系统。
6 重启模式,默认运行级别不能设为6,否则不能正常启动。运行init 6机器就会重启。
RHEL7中不再使用/etc/inittab进行默认启动级别配置,systemd使用target替代
第三运行级别(命令行界面)multi-user.target
第五运行级别(图形界面)graphical.target
切换运行级别:init 0~6 或 systemctl isolate …target
设置默认运行级别:systemctl set-default …target
查看当当前默认运行级别:systemctl get-default
1-3 文件的基本管理和xfs文件系统备份恢复
Linux系统目录结构--->一切都是文件
/目录下文件详解
/dev设备文件
/etc配置文件
/proc、/sys运行时系统信息
/boot启动目录(Grub引导)
/bin、/sbin命令
/lib、/lib64库文件
/usr 源码目录
/share 帮助信息等
/var、/tmp临时文件目录
/root、/home用户默认登录目录
相对路径、绝对路径
相对路径相对而言,一般以. 或.. 开头
绝对目录绝对而言,一般以 / 开头
文件的创建、复制、删除
touch 创建文件
cp 复制
mv 移动或重命名
rm 、rmdir删除
cat、more、less、head、tail查看文件内容
实战:xfs文件系统的备份和恢复
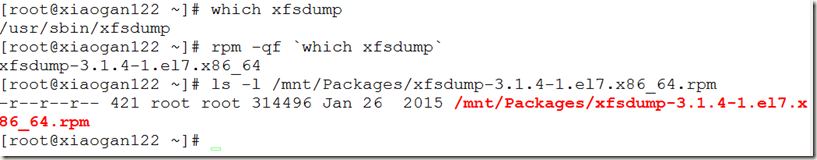
使用工具xfsdump、xfsrestore
[root@xiaogan122 ~]# xfsdump –help #查看帮助信息
xfsdump: version 3.1.4 (dump format 3.0) #版本信息
xfsdump: usage: xfsdump [ -a (dump DMF dualstate files as offline) ]
[ -b <blocksize> ] #设置块大小
[ -c <media change alert program> ]
[ -d <dump media file size> ]
[ -e (allow files to be excluded) ]
[ -f <destination> ... ] #指定目标目录
[ -h (help) ] #帮助信息
[ -l <level> ] #设置备份级别
[ -m (force usage of minimal rmt) ]
[ -o (overwrite tape) ]
[ -p <seconds between progress reports> ]
[ -q <use QIC tape settings> ]
[ -s <subtree> ... ]
[ -t <file> (use file mtime for dump time ]
[ -v <verbosity {silent, verbose, trace}> ]
[ -z <maximum file size> ]
[ -A (don't dump extended file attributes) ]
[ -B <base dump session id> ]
[ -D (skip unchanged directories) ]
[ -E (pre-erase media) ]
[ -F (don't prompt) ]
[ -I (display dump inventory) ]
[ -J (inhibit inventory update) ]
[ -K (generate format 2 dump) ]
[ -L <session label> ] #指定session标签
[ -M <media label> ... ] #指定media标签
[ -O <options file> ] #指定options file (选项文件列表),一条命令-o只能使用一次
[ -R (resume) ]
[ -T (don't timeout dialogs) ]
[ -Y <I/O buffer ring length> ]
[ - (stdout) ]
[ <source (mntpnt|device)> ]
备份系统:
备份整个文件系统
xfsdump -f /opt/dump_sdb1 /dev/sdb1 -L dump_sdb1_01 –M media0
将/dev/sdb1设备中的文件备份到/opt/dump_sdb1中,session标签为dump_sdb1_01,media标签为media0
-f 指定生成备份文件路径
-L指定session标签
-M指定media标签
添加-L、-M选项,可实现无交互备份
备份单个文件
xfsdump -f /opt/dump_passwd -s /sdb1/passwd /sdb1 -L dump_passwd -M passwd
-s指定备份文件
恢复文件或文件系统:xfsrestore -f /opt/dump_sdb1 /sdb1
第一步:首先关闭系统,添加一个硬盘
第二步:查看新添加硬盘的文件名为sdb,对sdb进行分区
第三步:对新建立的分区格式化,使用mkfs.xfs
第四步:挂载/dev/sdb1分区
第五步:复制一个文件到/sdb1目录下,新建一个目录到/sdb1目录下,留作测试用
第六步:备份文件系统
第七步:文件恢复,删除文件制造误删假象,然后使用xfsrestore命令恢复文件
1-5-vim编辑的使用和Xmanager远程工具的使用
vim编辑器的使用
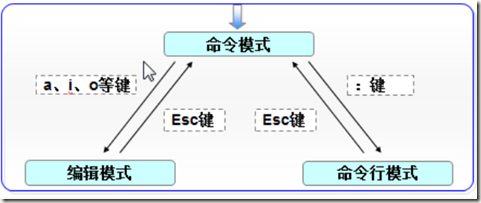
vim有三种模式
命令行模式、编辑模式、命令模式
三种通过命令模式互相切换,如图:
主要操作方式:
i 当前光标后插入
a 当前光标前插入
A当前光标行末插入
o 当前光标行下插入
O当前光标行上插入
dd删除当前前光标所在行
ndd / dnd 删除当前光标在内的N行
yy复制当前光标所在行
nyy / yny复制当前光标在内的n行
dw删除当前光标及后的一个单词
ndw / dnw删除当前光标及后的n个单词
d$删除当前光标及后到行尾的内容
shift ^ 定位到行首
shift $ 定位到行末
gg定位到文件开始文职
shift + g 定位到文件末尾
ctrl + g 显示当前光标位置及文件信息
% 移动到配对的()[]{}位置去
:s/old/new 一行内替换第一个出现的old为new
:s/old/new/g 一行内替换所有old为new
:m,ns/old/new/g 在m-n行之间替换所有old为new
:%s/old/new/g 全文替换所有old为new
:%s/old/new/gc 全文替换,每次替换前询问
视图模式:一次在多行前添加内容
第一步:ctrl + v 进入视图模式
第二步:移动光标,选中需要添加或删除内容的行
第三步:输入大写的I或小写的x编辑内容
第四步:ESC键退出即可
实战:转码工具的使用iconv
windows中的文本导入到linux系统中,会出现乱码问题解决方法:
[root@xiaogan122 ~]# iconv --help
Usage: iconv [OPTION...] [FILE...]#格式
Convert encoding of given files from one encoding to another.
Input/Output format specification:
-f, --from-code=NAME encoding of original text #指定源文件编码
-t, --to-code=NAME encoding for output #指定目标文件编码
Information:
-l, --list list all known coded character sets #列出已知编码
Output control:
-c omit invalid characters from output #忽略无效的字符输出
-o, --output=FILE output file #指定输出文件名称
-s, --silent suppress warnings #保持沉默,即抑制警告
--verbose print progress information
-?, --help Give this help list
--usage Give a short usage message #给出使用格式
-V, --version Print program version
Mandatory or optional arguments to long options are also mandatory or optional
for any corresponding short options.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/libc/bugs.html>.
实战:在RHEL6.5中恢复误删除的文件
extundelete命令的使用
背景:ext文件系统存储原理
每个文件名对应一个inode结点,每个inode结点对应一个实际物理存储位置。
在我们创建文件时,会指定文件的文件名,然后,系统会给文件名分配一个inode结点,和对应的物理存储位置。
在我们删除文件时,linux系统直接删除的是文件名,只是我们看不到的inode结点号和实际物理存储位置中的信息并没有擦出。
但是,当我们再次创建文件时,可能linux系统会使用掉这个inode节点号,并将对应的物理存储位置中的数据覆盖。
操作流程:误删除文件后立刻卸载文件系统,并以只读方式挂载,防止文件被覆盖。使用extundelete命令扫描该文件系统节点号,查找已删除的文件节点号,并通过节点号、文件名等方式恢复文件
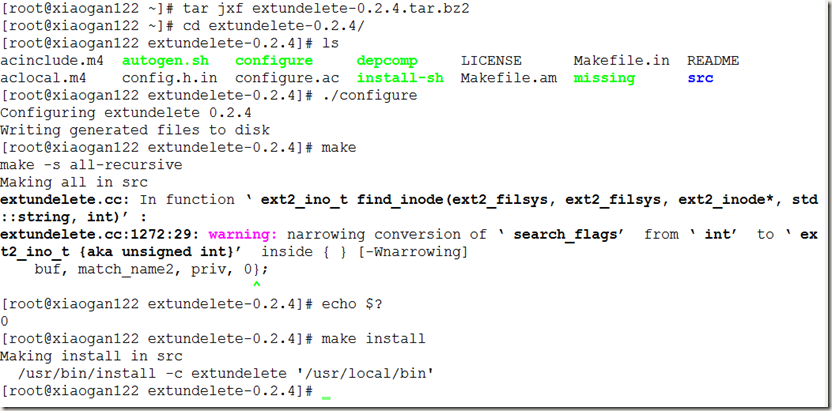
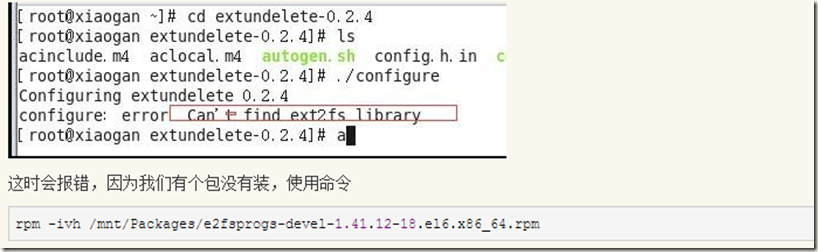
使用extendelete命令需要安装对应的软件包:extundelete-0.2.4.tar.bz2
http://sourceforge.net 开源软件发布中心
tar jxf extundelete*.tar.bz2
./configure
make
make install (源码包安装通用三部曲)
extundelete命令:
[root@xiaogan122 ~]# extundelete --help
Usage: extundelete [options] [--] device-file #格式
Options:
--version, -[vV] Print version and exit successfully.
--help, Print this help and exit successfully.
--superblock Print contents of superblock in addition to the rest.
If no action is specified then this option is implied.
--journal Show content of journal. #显示过程信息?!
--after dtime Only process entries deleted on or after 'dtime'. #只针对在删除时间在dtime之后的文件
--before dtime Only process entries deleted before 'dtime'. #只针对删除时间在dtime之前的文件
Actions:
--inode ino Show info on inode 'ino'. #列出节点号为ino上的信息
--block blk Show info on block 'blk'. #列出块号为blk上的信息
--restore-inode ino[,ino,...] #还原节点号为ino的文件
Restore the file(s) with known inode number 'ino'.
The restored files are created in ./RECOVERED_FILES
with their inode number as extension (ie, file.12345).
--restore-file 'path' Will restore file 'path'. 'path' is relative to root #还原path文件
of the partition and does not start with a '/'
The restored file is created in the current
directory as 'RECOVERED_FILES/path'.
--restore-files 'path' Will restore files which are listed in the file 'path'.#还原path文件中列出的文件
Each filename should be in the same format as an option
to --restore-file, and there should be one per line.
--restore-directory 'path' #还原path目录
Will restore directory 'path'. 'path' is relative to the
root directory of the file system. The restored
directory is created in the output directory as 'path'.
--restore-all Attempts to restore everything. #还原所有
-j journal Reads an external journal from the named file.
-b blocknumber Uses the backup superblock at blocknumber when opening
the file system.
-B blocksize Uses blocksize as the block size when opening the file
system. The number should be the number of bytes.
--log 0 Make the program silent. #保持沉默
--log filename Logs all messages to filename.#将日志保存到filename中
--log D1=0,D2=filename Custom control of log messages with comma-separated
Examples below: list of options. Dn must be one of info, warn, or
--log info,error error. Omission of the '=name' results in messages
--log warn=0 with the specified level to be logged to the console.
--log error=filename If the parameter is '=0', logging for the specified
level will be turned off. If the parameter is
'=filename', messages with that level will be written
to filename.
-o directory Save the recovered files to the named directory. #将恢复的文件保存到指定目录
The restored files are created in a directory
named 'RECOVERED_FILES/' by default.
tree命令,用来查看目录树形结构
rpm -ivh /mnt/Packages/tree-1.5.3-2.el6.x86_64
查看设备inode结点信息(若不指定-o选项,这恢复到当前目录下)
extundelete /dev/sdb1 –-inode 2 #依次查看,知道出现结点信息为止
五种方式恢复文件:
第一种:通过节点号恢复(通过查询inode结点信息获得节点号)
extundelete /dev/sdb1 --restore-inode 12
第二种:通过文件名恢复(通过查询inode结点信息获得文件名)
extundelete /dev/sdb1 --restore-file passwd
第三种:通过读取文件,恢复文件列出的文件
extundelete /dev/sdb1 –-restore-files file #file中存储的是要恢复的文件列表
第四种:恢复目录
extundelete /dev/sdb1 --restore-directory dir #恢复目录dir
第五种:恢复所有文件
extundelete /dev/sdb1 --restore-all
可使用tree命令查看目录结构,看看是不是所有的文件都恢复了,这是我们会发现,extundelete不能恢复空文件或空目录!!!
1-6-RHEL7用户管理、RHEL6及RHEL7root密码破解、RHEL6安装vmware tools
用户管理
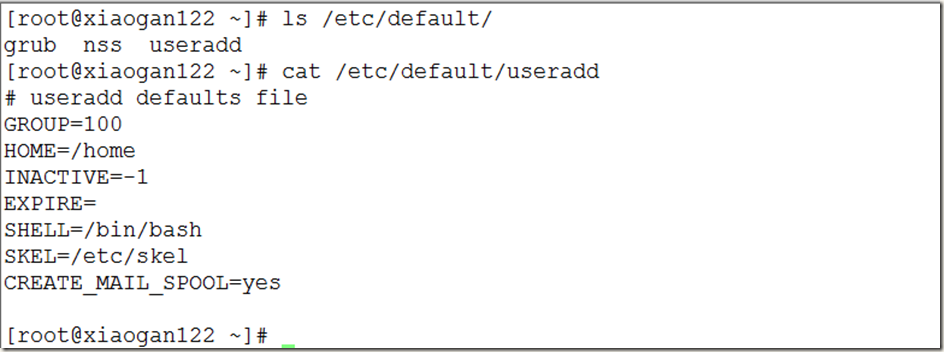
三种用户:超级用户(root)、本地用户、系统用户[一般根据id可判断其类型]
用户配置文件/etc/passwd;密码/etc/shadow
用户组配置文件/etc/group;密码/etc/gshadow
/etc/passwd信息格式:
用户名:密码占位符:UID:GID:用户组:默认目录:登录shell
/etc/shadow信息格式:
用户名:加密密码:最近改密时间:连续改密时间间隔:密码过期时间:改密提醒:过期期限:过期时间:保留
命令管理:
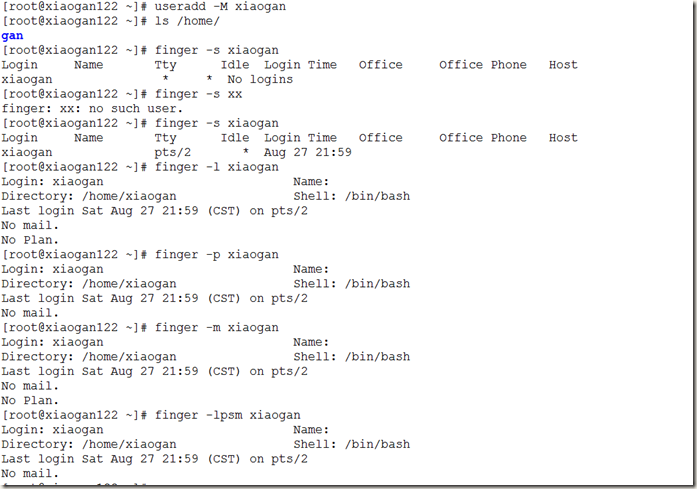
useradd [用户名] #添加用户
[root@xiaogan122 ~]# useradd --help
Usage: useradd [options] LOGIN #3种格式
useradd -D
useradd -D [options]
Options:
-b, --base-dir BASE_DIR base directory for the home directory of the new account
-c, --comment COMMENT GECOS field of the new account
-d, --home-dir HOME_DIR home directory of the new account #指定新账户的主目录
-D, --defaults print or change default useradd configuration #查看或修改useradd默认设置 或使用默认设置创建用户
-e, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE expiration date of the new account
-f, --inactive INACTIVE password inactivity period of the new account
-g, --gid GROUP name or ID of the primary group of the new #指定新账户的起始组ID
account
-G, --groups GROUPS list of supplementary groups of the new
account#指定用户附加组ID
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-k, --skel SKEL_DIR use this alternative skeleton directory
-K, --key KEY=VALUE override /etc/login.defs defaults
-l, --no-log-init do not add the user to the lastlog and
faillog databases
-m, --create-home create the user's home directory#为用户创建默认登录目录
-M, --no-create-home do not create the user's home directory #不创建用户目录
-N, --no-user-group do not create a group with the same name as
the user
-o, --non-unique allow to create users with duplicate
(non-unique) UID
-p, --password PASSWORD encrypted password of the new account
-r, --system create a system account
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-s, --shell SHELL login shell of the new account #指定默认登录shell
-u, --uid UID user ID of the new account #指定用户ID
-U, --user-group create a group with the same name as the user #组名和用户名相同
-Z, --selinux-user SEUSER use a specific SEUSER for the SELinux user mapping
userdel [用户名] #删除用户
[root@xiaogan122 ~]# userdel --help > userdel.help
[root@xiaogan122 ~]# cat userdel.help
Usage: userdel [options] LOGIN
Options:
-f, --force force some actions that would fail otherwise
#强制删除 e.g. removal of user still logged in
or files, even if not owned by the user
-h, --help #帮助信息 display this help message and exit
-r, --remove#删除用户目录 remove home directory and mail spool
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
#应用的变化从CHROOT_DIR读取,CHROOT_DIR目录和使用配置文件目录。
-Z, --selinux-user remove any SELinux user mapping for the user
passwd [用户名] #修改用户密码
[root@xiaogan122 ~]# passwd --help
Usage: passwd [OPTION...] <accountName> #格式
-k, --keep-tokens keep non-expired authentication tokens #密码永不过期
-d, --delete delete the password for the named account (root only) #删除用户密码
-l, --lock lock the password for the named account (root only) #禁止修改密码
-u, --unlock unlock the password for the named account (root only) #解除限制
-e, --expire expire the password for the named account (root only) #终止用户密码
-f, --force force operation #强制执行
-x, --maximum=DAYS maximum password lifetime (root only) #密码最长有效时间
-n, --minimum=DAYS minimum password lifetime (root only) #密码最短有效时间
-w, --warning=DAYS number of days warning users receives before password expiration
(root only) #提前多少天提醒用户修改密码
-i, --inactive=DAYS number of days after password expiration when an account becomes
disabled (root only)
-S, --status report password status on the named account (root only) #查询用户密码状态
--stdin read new tokens from stdin (root only) #从标准输入读取数据
Help options:
-?, --help Show this help message
--usage Display brief usage message #用法格式
usermod [用户名] #modify a user account修改用户账户设置
Usage: usermod [options] LOGIN
Options:
-c, --comment COMMENT new value of the GECOS field
-d, --home HOME_DIR new home directory for the user account #修改用户默认目录
-e, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE set account expiration date to EXPIRE_DATE #设置账户有效期
-f, --inactive INACTIVE set password inactive after expiration
to INACTIVE #设置密码过期后活跃天数
-g, --gid GROUP force use GROUP as new primary group#使用Group为新的主组
-G, --groups GROUPS new list of supplementary GROUPS #附加组
-a, --append append the user to the supplemental GROUPS #添加用户到组
mentioned by the -G option without removing
him/her from other groups
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-l, --login NEW_LOGIN new value of the login name #改名
-L, --lock lock the user account #锁定账户
-m, --move-home move contents of the home directory to the #移动用户主目录
new location (use only with -d)
-o, --non-unique allow using duplicate (non-unique) UID#允许使用重复的UID
-p, --password PASSWORD use encrypted password for the new password 使用加密的密码
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-s, --shell SHELL new login shell for the user account #指定登录shell
-u, --uid UID new UID for the user account #指定UID
-U, --unlock unlock the user account #解锁
-Z, --selinux-user SEUSER new SELinux user mapping for the user account
groupadd [组名] #添加组
groupdel [组名] #删除组
su [用户名] #切换用户
su – [用户名] #切换用户和环境变量
id [用户名] #查看年用户ID信息
w #查看登录信息
who #查看登录信息
whoami #查看当前使用用户
who am i #查看当前登录用户
finger #user information lookup program查询用户信息
usage: finger [-lmps] [login ...] #格式
实战:RHEL6、RHEL7系统root密码破解
RHEL6系统root密码破解:开机,进入选择操作系统界面,e编辑启动项,再次输入e编辑第二行命令,在代码最后输入空格和1,(即输入" 1"),回车确认,然后按b键,启动进入单用户模式。ok,passwd改密码吧!!!
RHEL7系统root密码破解:
(背景,系统selinux需要处于开机自动关闭状态,即/etc/selinux/config中selinux=disabled)。
开机,进入选择系统界面,按e键,进入编辑,找到加载内核的那一行,如下图:
将ro删除,输入如下:
rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh
意思是ro是只读,改成rw读写模式,初始化进入救援模式
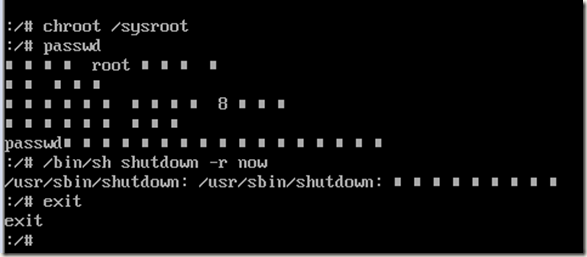
进入后,输入换根命令:
chroot /sysroot
然后就可以改密码了!!!输入passwd改密码吧!!!
在急救模式中重启命令如下:
两次退出后,输入/bin/sh/ shutdown –r now
实战:RHEL6安装vmware工具
其实很简单!我都不想写…
打开虚拟机,开机状态,在虚拟机的菜单栏,选择虚拟机--->安装vmware-tools
然后,系统就会自动挂载vmware-tools的linux.iso镜像
在终端输入df查看镜像挂载位置,并将其重新挂载到/mnt #其实这个没必要,只是我有强迫症
然后,拷贝压缩包到当前目录下,解压,运行立面的vmware-install.pl安装即可!!!
命令如下:
umount /dev/cdrom #卸载光驱
umount /dev/mnt #卸载/mnt
mount /dev/cdrom /mnt #挂载光驱到/mnt
cp /mnt/VMwareTools-*.tar.gz . #复制源码到当前目录
tar zxf VMwareTools-*.tar.gz #解压到当前目录
./vmware*/vmware-install.pl #运行,开始安装,我试过了,这么做是可以的!!!使用*匹配
#剩下的就是一路回车!!!不需要修改什么设置
#你也可以将上面的写成脚本,一键搞定!!!
#!/bin/bash
umount /dev/cdrom #卸载光驱
umount /dev/mnt #卸载/mnt
mount /dev/cdrom /mnt #挂载光驱到/mnt
cp /mnt/VMwareTools-*.tar.gz . #复制源码到当前目录
tar zxf VMwareTools-*.tar.gz #解压到当前目录
./vmware-tools-distrib/vmware-install.pl #运行,开始安装
#输入回车这个没研究
先到这里吧!!!其他的等有时间了把,明天出去玩啊,早睡早起!!!