ChannelFuture
吧自定义的处理器修改下。
class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { System.out.println("Receive client : [" + ((ByteBuf) msg).toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8) + "]"); ChannelFuture channelFuture = ctx.write(msg); channelFuture.addListener(future -> { if (future.isSuccess()) { System.out.println(future); } }); ctx.flush(); } }
如果希望发送一个消息出去,等发完了告诉我,需要这么写,为什么把write和flush分开呢,因为连在一起可能会直接发出去,这个时候连事件还没监听就有了结果了,再监听就直接返回结果了,就是同步了。
调用写的时候他会创建一个可写的异步回调。
AbstractChannelHandlerContext#write
public ChannelFuture write(Object msg) { return write(msg, newPromise()); }
创建异步回调newPromise
会将当前的通道和事件循环执行器传进去,这样就能保证回调的时候我们就能拿到通道实例。
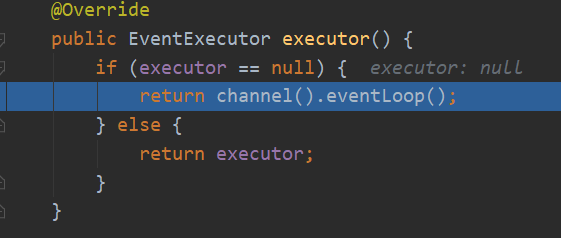
这里还要有个执行器,因为这里的执行器是处理器上下文的执行器,可能和通道的不一样,看创建的时候有没传了。
public ChannelPromise newPromise() { return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel(), executor()); }
执行器不一定是通道的,如果创建的时候没传,那就用通道的,否则可能是其他通道的执行器哦。
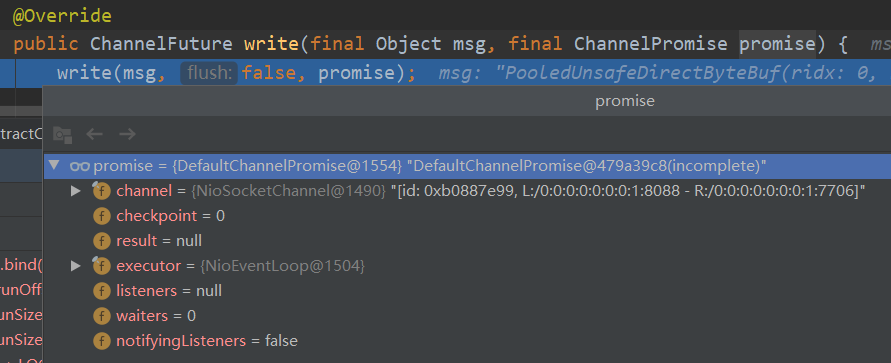
创建异步回调promise
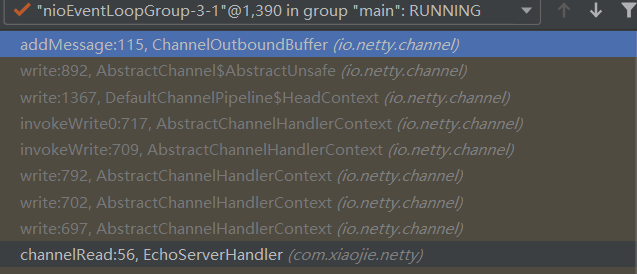
直接跳到ChannelOutboundBuffer的addMessage
调用链路:
public void addMessage(Object msg, int size, ChannelPromise promise) { Entry entry = Entry.newInstance(msg, size, total(msg), promise); if (tailEntry == null) { flushedEntry = null; } else { Entry tail = tailEntry; tail.next = entry; } tailEntry = entry; if (unflushedEntry == null) { unflushedEntry = entry; } // increment pending bytes after adding message to the unflushed arrays. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1619 incrementPendingOutboundBytes(entry.pendingSize, false); }
Entry的newInstance
最后被封装到Entry中,也就是出站缓冲区里,没有写什么结果,write是没回调的,只有flush了才有。
static Entry newInstance(Object msg, int size, long total, ChannelPromise promise) { Entry entry = RECYCLER.get(); entry.msg = msg; entry.pendingSize = size + CHANNEL_OUTBOUND_BUFFER_ENTRY_OVERHEAD; entry.total = total; entry.promise = promise; return entry; }
监听写回调结果
这个时候还没任何结果,添加监听器:
DefaultChannelPromise的addListener
public ChannelPromise addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super Void>> listener) { super.addListener(listener); return this; }
DefaultPromise#addListener
public Promise<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener) { checkNotNull(listener, "listener"); //同步添加 synchronized (this) { addListener0(listener); } if (isDone()) {//如果完成了,就直接通知 notifyListeners(); } return this; }
DefaultPromise#addListener0
这个方法在外面添加了同步操作,避免多线同时添加的安全问题,然后把监听器添加进去,如果监听器是DefaultFutureListeners类型就直接添加,否则就把监听器封装成DefaultFutureListeners类型。
private void addListener0(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener) { if (listeners == null) {//没有监听器 listeners = listener; } else if (listeners instanceof DefaultFutureListeners) {//是DefaultFutureListeners就添加 ((DefaultFutureListeners) listeners).add(listener); } else {//创建一个,放进去 listeners = new DefaultFutureListeners((GenericFutureListener<?>) listeners, listener); } }
DefaultFutureListeners
这个是个单独的类型,是个容器,主要是用来放监听器的,我们可以看到,初始某人有个监听器数组,长度是2,如果超出了就会扩容2倍。而且他还能统计有多少个是GenericProgressiveFutureListener类型的。
final class DefaultFutureListeners { private GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<?>>[] listeners;//监听器数组 private int size;//监听器个数,也是添加的索引 private int progressiveSize; // the number of progressive listeners 进度监听器数 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") DefaultFutureListeners( GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<?>> first, GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<?>> second) { listeners = new GenericFutureListener[2]; listeners[0] = first; listeners[1] = second; size = 2; if (first instanceof GenericProgressiveFutureListener) { progressiveSize ++; } if (second instanceof GenericProgressiveFutureListener) { progressiveSize ++; } } //添加监听回调器,满了就扩容,每次2倍 public void add(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<?>> l) { GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<?>>[] listeners = this.listeners; final int size = this.size; if (size == listeners.length) { this.listeners = listeners = Arrays.copyOf(listeners, size << 1); } listeners[size] = l; this.size = size + 1; if (l instanceof GenericProgressiveFutureListener) { progressiveSize ++;//进度监听器数+1 } } //移除回调监听器 public void remove(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<?>> l) { final GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<?>>[] listeners = this.listeners; int size = this.size; for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) { if (listeners[i] == l) { int listenersToMove = size - i - 1; if (listenersToMove > 0) {//向前移动数组元素 System.arraycopy(listeners, i + 1, listeners, i, listenersToMove); } listeners[-- size] = null; this.size = size; if (l instanceof GenericProgressiveFutureListener) { progressiveSize --; } return; } } } //所有监听器 public GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<?>>[] listeners() { return listeners; } public int size() { return size; } public int progressiveSize() { return progressiveSize; } }
DefaultChannelPromise的isDone
这个时候还没结果:
public boolean isDone() { return isDone0(result); }
继续flush
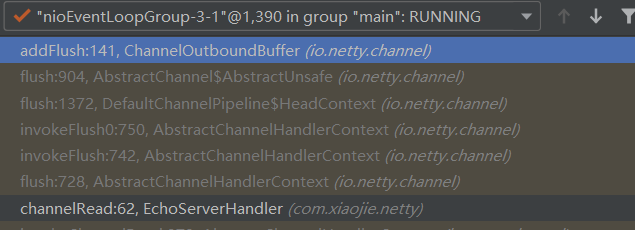
ChannelOutboundBuffer的addFlush
这里就是快要发送了,要把消息设置成不可取消状态:
调用链路:
public void addFlush() { // There is no need to process all entries if there was already a flush before and no new messages // where added in the meantime. // // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2577 Entry entry = unflushedEntry; if (entry != null) { if (flushedEntry == null) { // there is no flushedEntry yet, so start with the entry flushedEntry = entry; } do { flushed ++;//冲刷数+1 if (!entry.promise.setUncancellable()) { // Was cancelled so make sure we free up memory and notify about the freed bytes int pending = entry.cancel(); decrementPendingOutboundBytes(pending, false, true); } entry = entry.next; } while (entry != null); // All flushed so reset unflushedEntry unflushedEntry = null; } }
DefaultPromise的setUncancellable
如果设置成功,就说明已经不可取消了,如果没有什么设置过就能设置成功,result变为UNCANCELLABLE对象:
public boolean setUncancellable() { if (RESULT_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, null, UNCANCELLABLE)) { return true; } Object result = this.result; return !isDone0(result) || !isCancelled0(result); }
NioSocketChannel的doWrite
发送完成之后要进行删除操作:
调用链路:

protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception { SocketChannel ch = javaChannel(); int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount(); do { if (in.isEmpty()) { // All written so clear OP_WRITE clearOpWrite(); // Directly return here so incompleteWrite(...) is not called. return; } // Ensure the pending writes are made of ByteBufs only. int maxBytesPerGatheringWrite = ((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).getMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(); ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = in.nioBuffers(1024, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); int nioBufferCnt = in.nioBufferCount(); // Always use nioBuffers() to workaround data-corruption. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2761 switch (nioBufferCnt) { case 0: // We have something else beside ByteBuffers to write so fallback to normal writes. writeSpinCount -= doWrite0(in); break; case 1: { // Only one ByteBuf so use non-gathering write // Zero length buffers are not added to nioBuffers by ChannelOutboundBuffer, so there is no need // to check if the total size of all the buffers is non-zero. ByteBuffer buffer = nioBuffers[0]; int attemptedBytes = buffer.remaining(); final int localWrittenBytes = ch.write(buffer); if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) { incompleteWrite(true); return; } adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attemptedBytes, localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes); --writeSpinCount; break; } default: { // Zero length buffers are not added to nioBuffers by ChannelOutboundBuffer, so there is no need // to check if the total size of all the buffers is non-zero. // We limit the max amount to int above so cast is safe long attemptedBytes = in.nioBufferSize(); final long localWrittenBytes = ch.write(nioBuffers, 0, nioBufferCnt); if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) { incompleteWrite(true); return; } // Casting to int is safe because we limit the total amount of data in the nioBuffers to int above. adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite((int) attemptedBytes, (int) localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes); --writeSpinCount; break; } } } while (writeSpinCount > 0); incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0); }
ChannelOutboundBuffer的remove
调用链路:
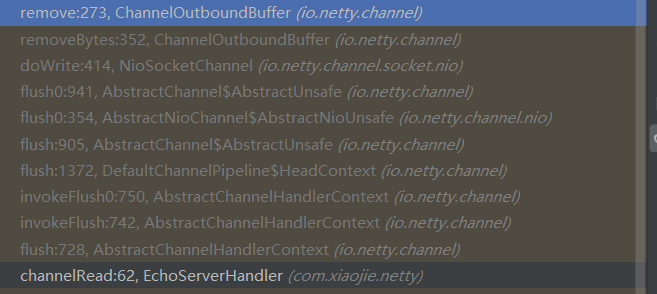
public boolean remove() { Entry e = flushedEntry; if (e == null) { clearNioBuffers(); return false; } Object msg = e.msg; ChannelPromise promise = e.promise; int size = e.pendingSize; removeEntry(e); if (!e.cancelled) { // only release message, notify and decrement if it was not canceled before. ReferenceCountUtil.safeRelease(msg);//释放资源 safeSuccess(promise);//写成功结果 decrementPendingOutboundBytes(size, false, true); } // recycle the entry e.recycle(); return true; }
safeSuccess(promise);
result是null
private static void safeSuccess(ChannelPromise promise) { // Only log if the given promise is not of type VoidChannelPromise as trySuccess(...) is expected to return // false. PromiseNotificationUtil.trySuccess(promise, null, promise instanceof VoidChannelPromise ? null : logger); }
ChannelOutboundBuffer的trySuccess
调用了Promise的trySuccess:
public static <V> void trySuccess(Promise<? super V> p, V result, InternalLogger logger) { if (!p.trySuccess(result) && logger != null) { Throwable err = p.cause(); if (err == null) { logger.warn("Failed to mark a promise as success because it has succeeded already: {}", p); } else { logger.warn( "Failed to mark a promise as success because it has failed already: {}, unnotified cause:", p, err); } } }
DefaultPromise的setSuccess0
设置SUCCESS对象。
public boolean trySuccess(V result) { return setSuccess0(result); }
这个时候result其实有值了,就是前面设置的UNCANCELLABLE对象。所以第一个判断为false,第二个是true。
private boolean setValue0(Object objResult) { if (RESULT_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, null, objResult) || RESULT_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, UNCANCELLABLE, objResult)) { if (checkNotifyWaiters()) { notifyListeners(); } return true; } return false; }
DefaultPromise的checkNotifyWaiters
通知之前,得检查下是否有监听器,没有就不通知了,而且还要看是否有人因为等通知而wait阻塞在,也需要唤醒。
private synchronized boolean checkNotifyWaiters() { if (waiters > 0) { notifyAll(); } return listeners != null; }
DefaultPromise的notifyListeners
private void notifyListeners() { EventExecutor executor = executor(); if (executor.inEventLoop()) {//IO线程 final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocals = InternalThreadLocalMap.get(); final int stackDepth = threadLocals.futureListenerStackDepth(); if (stackDepth < MAX_LISTENER_STACK_DEPTH) {//小监听器栈的最大深度 threadLocals.setFutureListenerStackDepth(stackDepth + 1);//深度+1 try { notifyListenersNow();//立刻通知 } finally { threadLocals.setFutureListenerStackDepth(stackDepth);//通知完深度设置回来 } return; } } //非IO线程,提交任务 safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { notifyListenersNow(); } }); }
DefaultPromise的notifyListenersNow
这里就要进行真正的回调啦。为了线程安全,用了同步代码块,然后循环通知所有监听器,因为同步代码块的粒度还是比较细的,所以可能通知完了之后又有新的添加到this.listeners,所以还要循环处理,直到没有监听器位置才返回。
private void notifyListenersNow() { Object listeners; synchronized (this) { // Only proceed if there are listeners to notify and we are not already notifying listeners. if (notifyingListeners || this.listeners == null) { return; } notifyingListeners = true;//设置已经通知 listeners = this.listeners; this.listeners = null; } for (;;) {//循环通知 if (listeners instanceof DefaultFutureListeners) { notifyListeners0((DefaultFutureListeners) listeners); } else { notifyListener0(this, (GenericFutureListener<?>) listeners); } synchronized (this) { if (this.listeners == null) {//处理完了 // Nothing can throw from within this method, so setting notifyingListeners back to false does not // need to be in a finally block. notifyingListeners = false;//设置回来,返回 return; } listeners = this.listeners;//还有新的加进来了继续处理 this.listeners = null; } } }
DefaultPromise的notifyListeners0
调用我们的操作完成回调,结果编号1554没变。
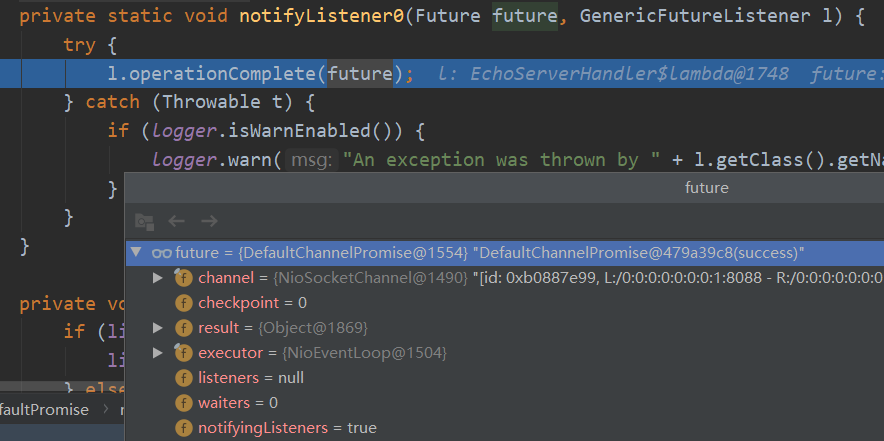
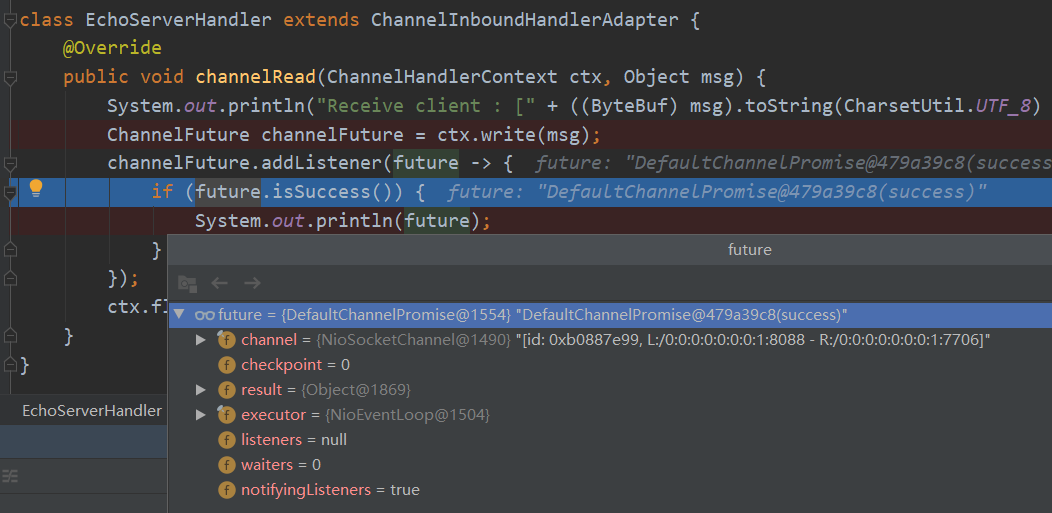
至此,我们的异步回调终于完成了,我们现在知道,原来我们write的时候是不回调成功的,除非出了什么异常,否则只有当flush的完成了才回调成功。
sysn同步
调用链路
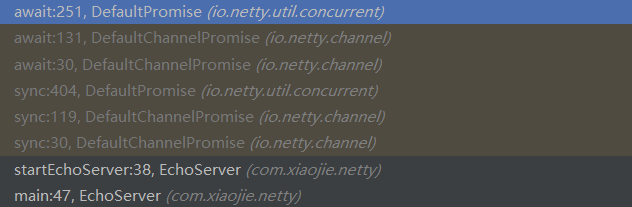
DefaultPromise的await
会先检查是否完成,完成了就不需要等了,然后看是否有中断,再检查死锁,最后再判断是否完成,没完成就进行wait,等待通知唤醒,唤醒了后还是要继续循环看是否完成了,只有完成了才可以返回。现在我们知道同步原理是内部用了一个无限循环来判断是否是否完成,如果完成了才会返回,否则就一直wait。
public Promise<V> await() throws InterruptedException { if (isDone()) { return this; } if (Thread.interrupted()) { throw new InterruptedException(toString()); } checkDeadLock(); synchronized (this) { while (!isDone()) { incWaiters(); try { wait(); } finally { decWaiters(); } } } return this; }
DefaultChannelPromise的checkDeadLock
检查死锁
protected void checkDeadLock() { if (channel().isRegistered()) { super.checkDeadLock(); } }
DefaultPromise的checkDeadLock
具体会看是不是当前线程是不是DefaultPromise的执行器的线程是IO线程,如果是IO线程,当然报阻塞IO线程的异常啦。
protected void checkDeadLock() { EventExecutor e = executor(); if (e != null && e.inEventLoop()) { throw new BlockingOperationException(toString()); } }
看看不报异常的情况,就是我们主线程在bind后的同步阻塞,因为调用这个方法的当前线程是主线程,不是事件循环的IO线程,所以不会报死锁的异常:

DefaultPromise的incWaiters
这个就是如果wait前会增加等待的记录。
private void incWaiters() { if (waiters == Short.MAX_VALUE) { throw new IllegalStateException("too many waiters: " + this); } ++waiters; }
用于在通知前,会checkNotifyWaiters判断。如果有等着的,就需要唤醒notifyAll所有的,因为完成了嘛,这样wait的才可以返回,不阻塞了。
cancel取消
我们再来研究下取消的情况:
DefaultPromise的cancel
会设置一个取消异常,然后直接通知监听器:
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { if (RESULT_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, null, CANCELLATION_CAUSE_HOLDER)) { if (checkNotifyWaiters()) { notifyListeners(); } return true; } return false; }