SIGNAL-SLOT是Qt的一大特色,使用起来十分方便。在传统的AWT和Swing编程中,我们都是为要在
监听的对象上添加Listener监听器。被监听对象中保存有Listener的列表,当相关事件发生时,被监听
对象会通知所有Listener。而在Qt中,我们只需通过connect方法连接两个对象上的方法就可以了,非常
方便、优雅地实现了传统的观察者Observer模式。
Qt是如何办到的呢?对于发出SIGNAL的对象,我们需要在其头文件定义中声明Q_Object宏,之后Qt的
预处理器MOC会为我们自动添加上相应的代码来实现SIGNAL-SLOT机制。这与AspectJ自定义了Javac
编译器很类似,都是通过增强编译器来自动添加相应的代码。
增强编译或增加预处理太复杂,怎样能够简单的实现这种机制呢?首先我们实现一个类似的QObject类,
需要发射SIGNAL的类都要继承它。在QObject类中,我们自动为其子类提供监听器列表,查找SLOT方法,
信号发射等功能。
QObject.java
1.在连接方法中,我们将信号和新建的ReceiverSlot类保存到Map中,从而将它们关联起来。
public static void connect(QObject sender, String signal, Object receiver, String slot) {
if (sender.signalSlotMap == null)
sender.signalSlotMap = new HashMap<String, List<ReceiverSlot>>();
List<ReceiverSlot> slotList = sender.signalSlotMap.get(signal);
if (slotList == null) {
slotList = new LinkedList<ReceiverSlot>();
sender.signalSlotMap.put(signal, slotList);
}
slotList.add(createReceiverSlot(receiver, slot));
} static class ReceiverSlot {
Object receiver;
Method slot;
Object[] args;
}2.在创建ReceiverSlot时,我们解析SLOT方法名,如将slot(String,String)解析为方法slot,参数两个String。
如果解析失败我们就认为该SLOT仍是一个信号,也就是SIGNAL-SIGNAL的连接。这种情况下,我们需要
传递调用的不是receiver的SLOT方法,而是emit方法继续发射信号。
private static ReceiverSlot createReceiverSlot(Object receiver, String slot) {
ReceiverSlot receiverSlot = new ReceiverSlot();
receiverSlot.receiver = receiver;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)\\(([\\w+,]*)\\)");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(slot);
if (matcher.matches() && matcher.groupCount() == 2) {
// 1.Connect SIGNAL to SLOT
try {
String methodName = matcher.group(1);
String argStr = matcher.group(2);
ArrayList<String> argList = new ArrayList<String>();
pattern = Pattern.compile("\\w+");
matcher = pattern.matcher(argStr);
while (matcher.find())
argList.add(matcher.group());
String[] arguments = argList.toArray(new String[0]);
receiverSlot.slot = findMethod(receiver, methodName, arguments);
receiverSlot.args = new Object[0];
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else {
// 2.Connect SIGNAL to SIGNAL
if (receiver instanceof QObject) {
receiverSlot.slot = emitMethod;
receiverSlot.args = new Object[] { slot };
}
}
return receiverSlot;
}
private static Method emitMethod;
protected Map<String, List<ReceiverSlot>> signalSlotMap;
static {
try {
emitMethod = QObject.class.getDeclaredMethod("emit", String.class, Object[].class);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3.解析后,如果是SIGNAL-SLOT的连接,那我我们根据方法名和参数找到该方法,准备反射调用。
private static Method findMethod(Object receiver, String methodName, String[] arguments)
throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method slotMethod = null;
if (arguments.length == 0)
slotMethod = receiver.getClass().getMethod(methodName, new Class[0]);
else {
for (Method method : receiver.getClass().getMethods()) {
// 1.Check method name
if (!method.getName().equals(methodName))
continue;
// 2.Check parameter number
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (paramTypes.length != arguments.length)
continue;
// 3.Check parameter type
boolean isMatch = true;
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.length; i++) {
if (!paramTypes[i].getSimpleName().equals(arguments[i])) {
isMatch = false;
break;
}
}
if (isMatch) {
slotMethod = method;
break;
}
}
if (slotMethod == null)
throw new NoSuchMethodException("Cannot find method[" + methodName +
"] with parameters: " + Arrays.toString(arguments));
}
return slotMethod;
}
4.发射信号时,我们取到所有与该SIGNAL关联的ReceiverSlot类,逐个发射信号。
protected void emit(String signal, Object... args) {
System.out.println(getClass().getSimpleName() + " emit signal " + signal);
if (signalSlotMap == null)
return;
List<ReceiverSlot> slotList = signalSlotMap.get(signal);
if (slotList == null || slotList.isEmpty())
return;
for (ReceiverSlot objSlot : slotList) {
try {
if (objSlot.slot == emitMethod)
objSlot.slot.invoke(objSlot.receiver, objSlot.args[0], args);
else
objSlot.slot.invoke(objSlot.receiver, args);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
之后,我们实现一个它的子类QWidget,将常用的Swing控件都封装在QWidget的子类中,为这些控件提供
常见的预定义的SIGNAL,像Qt中的clicked和returnPressed。
QWidget.java
public class QWidget<T extends JComponent> extends QObject implements QSwing<T> {
protected T widget;
public QWidget(Class<T> clazz) {
try {
widget = clazz.newInstance();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public T getSwingWidget() {
return this.widget;
}
}
以下是封装了JButton和JTextField的QWidget子类。
QPushButton.java
public class QPushButton extends QWidget<JButton> {
public static final String CLICKED = "clicked";
public QPushButton(String text) {
super(JButton.class);
widget.setText(text);
widget.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
emit(CLICKED);
}
});
}
}QLineEdit.java
public class QLineEdit extends QWidget<JTextField> {
public static final String RETURN_PRESSED = "returnPressed";
public QLineEdit() {
super(JTextField.class);
widget.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
emit(RETURN_PRESSED);
}
});
}
}下面我们来写个测试类实验下Java版的SIGNAL-SLOT机制,依旧是之前的浏览器的例子。
AddressBar.java
public class AddressBar extends QWidget<JPanel> {
/**
* SIGNAL
*/
public static final String NEW_BUTTON_CLICKED = "newButtonClicked";
public static final String GO_TO_ADDRESS = "goToAddress(String,String)";
/**
* SLOT
*/
public static final String HANDLE_GO_TO_ADDRESS = "handleGoToAddress()";
private QPushButton newButton;
private QLineEdit addressEdit;
private QPushButton goButton;
public AddressBar() {
super(JPanel.class);
// 1.Create widget
newButton = new QPushButton("New");
addressEdit = new QLineEdit();
goButton = new QPushButton("Go");
// 2.Set property
addressEdit.getSwingWidget().setColumns(10);
// 3.Connect signal-slot
connect(newButton, QPushButton.CLICKED, this, NEW_BUTTON_CLICKED);
connect(addressEdit, QLineEdit.RETURN_PRESSED, this, HANDLE_GO_TO_ADDRESS);
connect(goButton, QPushButton.CLICKED, this, HANDLE_GO_TO_ADDRESS);
// 4.Add to layout
getSwingWidget().add(newButton.getSwingWidget());
getSwingWidget().add(addressEdit.getSwingWidget());
getSwingWidget().add(goButton.getSwingWidget());
}
public void handleGoToAddress() {
emit(GO_TO_ADDRESS, addressEdit.getSwingWidget().getText(), "test string");
}
}TabBar.java
public class TabBar extends JTabbedPane {
/**
* SLOT
*/
public static final String HANDLE_NEW_TAB = "handleNewTab()";
public static final String HANDLE_GO_TO_SITE = "goToSite(String,String)";
public TabBar() {
handleNewTab();
}
public void handleNewTab() {
WebView tab = new WebView();
add("blank", tab);
}
public void goToSite(String url, String testStr) {
System.out.println("Receive url: " + url + ", " + testStr);
WebView tab = (WebView) getSelectedComponent();
tab.load(url);
}
}MainWindow.java
public class MainWindow extends JFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame window = new MainWindow();
window.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
window.setSize(320, 340);
window.setVisible(true);
}
public MainWindow() {
// 1.Create widget
AddressBar addressBar = new AddressBar();
TabBar tabBar = new TabBar();
// 2.Set property
// 3.Connect signal-slot
QObject.connect(addressBar, AddressBar.NEW_BUTTON_CLICKED, tabBar, TabBar.HANDLE_NEW_TAB);
QObject.connect(addressBar, AddressBar.GO_TO_ADDRESS, tabBar, TabBar.HANDLE_GO_TO_SITE);
// 4.Add to layout
GridBagLayout layout = new GridBagLayout();
setLayout(layout);
GridBagConstraints grid = new GridBagConstraints();
grid.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH;
grid.gridx = grid.gridy = 0;
grid.weightx = 1.0;
grid.weighty = 0.1;
add(addressBar.getSwingWidget(), grid);
grid.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH;
grid.gridx = 0;
grid.gridy = 1;
grid.weightx = 1.0;
grid.weighty = 0.9;
add(tabBar, grid);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
class WebView extends JEditorPane {
public WebView() {
setEditable(false);
}
public void load(final String url) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
WebView.this.setPage(url);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
测试一下吧,运行起来的效果就是这样。
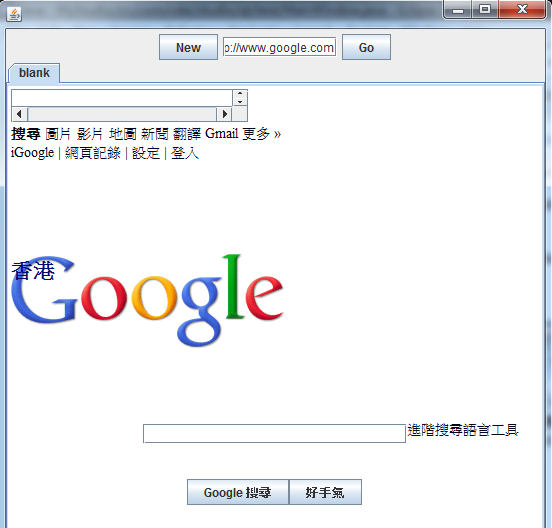
新建Tab页和前往该地址事件都可以成功地从AddressBar传递到TabBar。怎么样,这种Java版的
SIGNAL-SLOT是不是很方便。多开拓自己的视野,借鉴优秀的思想,我们才能做出更好的设计!
希望你喜欢本文。