1.1 vuex简介
官网:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/first-time/p/6815036.html
1、什么是Vuex?
1. 官方说法:Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式。
2. 它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
3. 个人理解:Vuex是用来管理组件之间通信的一个插件
2、vuex作用
1. 我们知道组件之间是独立的,组件之间想要实现通信,我目前知道的就只有props选项,但这也仅限于父组件和子组件之间的通信。
2. 如果兄弟组件之间想要实现通信呢?当做中大型项目时,面对一大堆组件之间的通信,还有一大堆的逻辑代码,会不会很抓狂??
3. 那为何不把组件之间共享的数据给“拎”出来,在一定的规则下管理这些数据呢? 这就是Vuex的基本思想了。
总结:使用vuex作用就是实现组件间数据共享
3、vuex原理
1. vue团队为了简化组件间的通信,将state抽象成一个单例模式,将其放到全局,让各个组件都能共享使用
2. vuex数据传递是单向的:action ---> mutation ---> state ---> component ---> action
vue component指的就是我门定义的组件
action 交互中产生的动作
mutations 动作产生的修改数据的行为
state 共享数据
3. vuex设计的时候相对修改的行为做单测(测试),开发了devtools来做测试,只能检测同步的操作
4. 规范定义:只能在mutations中做同步操作,所以增加了action来异步处理数据
5. 将mutations中的异步操作转移到actions中了,这样就可以测试同步的操作了
4、vuex使用场景
1. 如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
2. 如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。
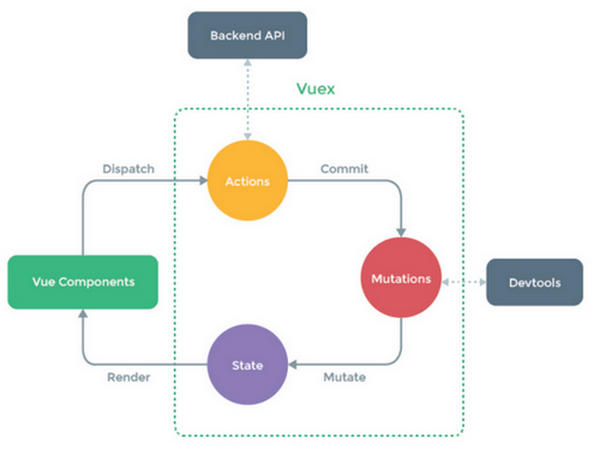
5、vuex流程图
1、vue组件(Vue Components)会 发出(Dispatch)一些动作(Actions)
2、动作会 提交(Commit)一个对数据的改变(Mutations)
3、提交的改变数据存放在 状态(State) 中的
4、最后 State将改变的数据再 渲染(Render)到组件(Vue Components),展示被改变后的数据
1.2 vuex使用(vuex使用分为以下两步)
1、第一步:实例化一个store
注:vuex.store用来创建store,参数对象中,可以定义各个模块
1. state定义状态模块(存储数据的),存放组件之间共享的数据
2. getters定义动态的数据,类似组件中的computed动态数据
3. mutations:定义改动states的动作行为,类似观察者模式中的订阅事件on
4. action:定义这些交互动作(异步),类似观察者模式中的订阅事件方法on(只不过是用来处理异步的)
2、第二步:在vue实例化对象中,注册store
1. 将第一步的实例化对象注册进来,注册路由后,组件实例化对象有了$route属性对象
2. 注册store,组件实例化对象有了$store属性对象,这个store对象有下面这些方法
$.store.commit用来触发mutations订阅的消息
$.store.dispatch用来触发action订阅的消息的
$.store.state使用状态中的数据

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h1 @click="$store.commit('reduce', 20);">vue实例化对象:点击减20</h1> <h2 @click="$store.dispatch('dealNum', 10, 20, 30)">更新数据:将num两秒后重置为:10</h2> <h1>state中的数据 {{$store.state.num}}</h1> <h2>双倍num {{$store.getters.doubleNum}}</h2> <router-view></router-view> <!-- 定义渲染的容器 --> </div> <template id="home"> <div> <h1 @click="$store.commit('add', 10, 'hello')">home:点击加10</h1> <h2>home组件中 {{$store.state.num}}</h2> <router-view></router-view> <!-- 第一步 定义子路由渲染的容器 --> </div> </template> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue-router.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="vuex.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> // 定义组件 var Home = { template: '#home' }; // 第一步 定义路由规则 var routes = [ { path: '/home', name: 'home', component: Home } ]; // 定义store第一步 定义store实例化对象 var store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { // 定义状态 num: 0 }, getters: { // 定义动态绑定的数据 doubleNum: function(state) { return state.num * 2; } }, mutations: { // 修改的消息 add: function(state, num) { // 增加num值 state.num += num; }, reduce: function(state, num) { // 减少num值 state.num -= num; }, resetNum: function(state, num) { state.num = num; } }, actions: { // 定义actions dealNum: function(context, num) { setTimeout(function() { // 我们可以异步提交 context.commit('resetNum', num) }, 2000) } } }); // 第二步 实例化路由对象 var router = new VueRouter({ routes: routes // 定义路由规则 }); // 第三步 注册路由 和 store对象 var app = new Vue({ el: '#app', // 注册路由 router: router, store: store // 使用vuex第二步 注册store }) </script> </body> </html>
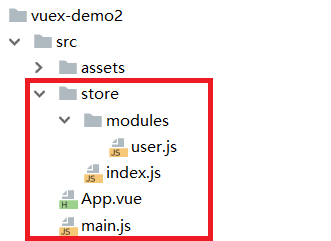
1.3 vuex基本用法
1、初始化环境
vue init webpack-simple vuex-demo
cd vuex-demo
npm install
cnpm install vuex -S # 安装vuex
npm run dev
2、在main.js中导入并配置store.选项(创建 sre/store.js文件,可以是一个空文件)
1. 在main.js中导入 store对象: import store from './store'
2. 配置store选项后,vue就会自动将store对象注入到所有子组件中,在子组件中通过this.$store 访问store对象

import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import store from './store' // 导入store对象 new Vue({ store, // 配置store选项后,指定为store对象,vue就会自动将store对象注入到所有子组件中 // 在子组件中通过this.$store 访问store对象 el: '#app', render: h => h(App) });
3、编辑store.js文件
注1:Vuex的核心是Store(仓库),相当于是一个容器,一个store实例中包含以下属性的方法:
注2:不能直接修改数据,必须显式提交变化,目的是为了追踪到状态的变化
1) state 定义属性(状态、数据)
2) getters 用来获取属性
3) actions 定义方法(动作)
4) commit 提交变化,修改数据的唯一方式就是显式的提交mutations
5) mutations 定义变化

/** * vuex配置:store.js **/ import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); //1、定义属性(数据) var state = { count:6 }; //2、定义gettters获取属性:在App.vue中使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据调用此函数 var getters={ count(state){ return state.count; } }; //3、定义actions提交变化:其他组件中调用的方法() const actions = { increment({commit,state}){ // context包含属性(函数):commit,dispatch,state if(state.count<10){ // 当count数值小于10才会提交改变(大于10就不增加了) commit('increment'); } // 1、commit提交改变(不能直接修改数据) // 2、commit中的参数 'increment' 是自定义的,可以认为是类型名 // 3、commit提交的改变会给 mutations } }; //4、定义mutations定义变化,处理状态(数据的改变) const mutations={ increment(state){ state.count++; } }; // 创建一个store对象(对象里定义需要导出的变量) const store=new Vuex.Store({ state, getters, actions, mutations, }); // 导出store对象 export default store;
4、 编辑App.vue
1. 在子组件中访问store对象的两种方式
方式1:通过this.$store访问
方式2:通过辅助函数:mapState、mapGetters、mapActions 访问,vuex提供了两个方法
mapState 获取state
mapGetters 获取getters(获取属性:数据)
mapActions 获取actions(获取方法:动作)

<template> <div id="app"> <button @click="increment">增加</button> <button>减小</button> <p>当前数字为:{{count}}</p> </div> </template> <script> import {mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex' export default { name: 'app', data () { return { msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App' } }, // 方式二:使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据 computed:mapGetters([ // 这里定义一个数组,数组中指定要从vuex中获取的属性 'count', // 这里的count就是 store.js中getters定义的属性 ]), methods:mapActions([ // 这里定义一个数组,数组中指定要从vuex中获取的方法 'increment' // 这里的increment就是 store.js中actions定义的函数 ]) // // 方式一:通过this.$store访问vuex组件中的数据 // computed:{ // count(){ // return this.$store.state.count; // } // } } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } h1, h2 { font-weight: normal; } ul { list-style-type: none; padding: 0; } li { display: inline-block; margin: 0 10px; } a { color: #42b983; } </style>
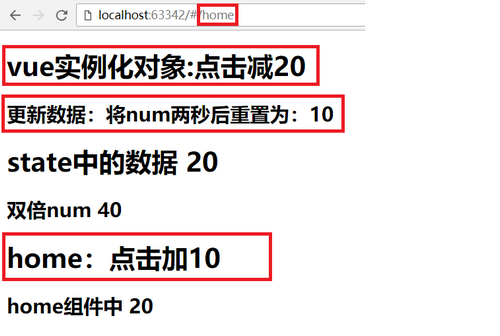
5、效果图

6、异步操作

import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import store from './store' // 导入store对象 new Vue({ store, // 配置store选项后,指定为store对象,vue就会自动将store对象注入到所有子组件中 // 在子组件中通过this.$store 访问store对象 el: '#app', render: h => h(App) });

/** * vuex配置:store.js **/ import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); //1、定义属性(数据) var state = { count:6 }; //2、定义gettters获取属性:在App.vue中使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据调用此函数 var getters={ count(state){ return state.count; } }; //3、定义actions提交变化:其他组件中调用的方法() const actions = { increment({commit,state}){ // context包含属性(函数):commit,dispatch,state if(state.count<10){ // 当count数值小于10才会提交改变(大于10就不增加了) commit('increment'); } // 1、commit提交改变(不能直接修改数据) // 2、commit中的参数 'increment' 是自定义的,可以认为是类型名 // 3、commit提交的改变会给 mutations }, /** 定义异步操作 **/ incrementAsyn({commit,state}){ var p=new Promise((resolve,reject) => { // 异步操作 setTimeout(() => { resolve() },3000) }); p.then(() => { // 上面执行完成后才执行 p.then() commit('increment'); }).catch(() => { // 异常处理 console.log('异步操作失败') }) } }; //4、定义mutations定义变化,处理状态(数据的改变) const mutations={ increment(state){ state.count++; } }; // 创建一个store对象(对象里定义需要导出的变量) const store=new Vuex.Store({ state, getters, actions, mutations, }); // 导出store对象 export default store;

<template> <div id="app"> <button @click="increment">增加</button> <button @click="incrementAsyn">异步增加</button> <p>当前数字为:{{count}}</p> </div> </template> <script> import {mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex' export default { name: 'app', data () { return { msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App' } }, // 方式二:使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据 computed:mapGetters([ // 这里定义一个数组,数组中指定要从vuex中获取的属性 'count', // 这里的count就是 store.js中getters定义的属性 ]), methods:mapActions([ // 这里定义一个数组,数组中指定要从vuex中获取的方法 'increment', // 这里的increment就是 store.js中actions定义的函数 'incrementAsyn' // 异步提交 ]) } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } h1, h2 { font-weight: normal; } ul { list-style-type: none; padding: 0; } li { display: inline-block; margin: 0 10px; } a { color: #42b983; } </style>

1.4 分模块组织Vuex
1、初始化环境
vue init webpack-simple vuex-demo2
cd vuex-demo2
npm install
cnpm install vuex -S # 安装vuex
npm run dev
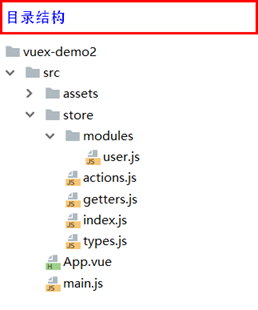
2、Vuex模块化结构

|-src |-main.js // 项目入口文件 |-App.vue |-store |-index.js // 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方 |-getters.js // 公共的 getters (用来获取公共属性) |-actions.js // 根级别的 action (提交公共改变) |-mutations.js // 根级别的 mutation (处理状态,数据的改变) |-types.js // 定义类型常量(commit中提交的常量) |-modules //分为多个模块,每个模块都可以拥有自己的state、getters、actions、mutations |-user.js // 用户模块(这里仅以user模块作为事例)
3、代码事例

import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import store from './store/index.js' new Vue({ store, el: '#app', render: h => h(App) });

<template> <div id="app"> <button @click="increment">增加</button> <button @click="decrement">减小</button> <button @click="incrementAsync">增加</button> <p>当前数字为:{{count}}</p> <p>{{isEvenOrOdd}}</p> </div> </template> <script> import {mapState,mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex' export default { name: 'app', data () { return { msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App' } }, computed:mapGetters([ 'count', 'isEvenOrOdd' ]), methods:mapActions([ 'increment', 'decrement', 'incrementAsync' ]) } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } h1, h2 { font-weight: normal; } ul { list-style-type: none; padding: 0; } li { display: inline-block; margin: 0 10px; } a { color: #42b983; } </style>

import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); import getters from './getters.js' import actions from './actions.js' import user from './modules/user.js' export default new Vuex.Store({ getters, actions, modules:{ user } });

const getters={ isEvenOrOdd(state){ return state.user.count%2==0?'偶数':'奇数'; // user模块中的count } }; export default getters;

import types from './types.js' const actions={ incrementAsync({commit,state}){ //异步操作 var p=new Promise((resolve,reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve(); },3000); }); p.then(() => { commit(types.INCREMENT); }).catch(() => { console.log('异步操作'); }); } }; export default actions;

/** * 定义类型常量 */ const INCREMENT='INCREMENT'; const DECREMENT='DECREMENT'; export default { INCREMENT, DECREMENT }

/** * 用户模块 */ import types from '../types.js' const state={ count:6 }; var getters={ count(state){ return state.count; } }; const actions = { increment({commit,state}){ commit(types.INCREMENT); //提交一个名为increment的变化,名称可自定义,可以认为是类型名 }, decrement({commit,state}){ if(state.count>10){ commit(types.DECREMENT); } } }; const mutations={ [types.INCREMENT](state){ // ES6中中括号里表示 变量 state.count++; }, [types.DECREMENT](state){ state.count--; } }; export default { state, getters, actions, mutations }
4、项目结构

5、简化版

import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import store from './store/index' new Vue({ store, el: '#app', render: h => h(App) })

<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>app</h1>
<p>数据:{{count}}</p>
<p @click="increment">增加</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapGetters, mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'app',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App'
}
},
computed:mapGetters([
'count',
]),
methods:mapActions([
'increment'
])
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1, h2 {
font-weight: normal;
}
ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
}
li {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 10px;
}
a {
color: #42b983;
}
</style>

import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); // import getters from './getters.js' // import actions from './actions.js' import user from './modules/user.js' export default new Vuex.Store({ // getters, // actions, modules:{ user } });

//1、定义属性(数据) var state = { count:6 }; //2、定义gettters获取属性:在App.vue中使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据调用此函数 var getters = { count(state){ return state.count } }; //3、定义actions提交变化:其他组件中调用的方法() var actions = { increment({commit,state}){ commit('increment') } }; //4、定义mutations定义变化,处理状态(数据的改变) var mutations = { increment(state){ state.count++ } }; //5、导出store对象 export default { state, getters, actions, mutations }