注意每次修改配置文件后必须项目重启
Structs2=structs1+xwork
Struct2框架预先实现了一些功能:
1.请求数据的封装;2.文件上传的功能3.对国际化功能的简化4.文件效验功能
1.开发Structs框架的步骤:
1)引入8大jar包
commons-fileupload-1.2.2.jar 【文件上传相关包】
commons-io-2.0.1.jar
struts2-core-2.3.4.1.jar 【struts2核心功能包】
xwork-core-2.3.4.1.jar 【Xwork核心包】
ognl-3.0.5.jar 【Ognl表达式功能支持表】
commons-lang3-3.1.jar 【struts对java.lang包的扩展】
freemarker-2.3.19.jar 【struts的标签模板库jar文件】
javassist-3.11.0.GA.jar 【struts对字节码的处理相关jar】
2)配置web.xml
主要配置filter Struct过滤器,StructsPrepareAndExecuteFilter核心过滤器
//引入struct核心过滤器 <filter> <filter-name>struct2</filter-name> <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struct2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
3)开发Action
方法满足:无参数,放回值为String,public修饰
编写普通类1.继承ActionSupport有数据效验时必须继承;2.或者实现action接口
3.什么都不写,直接return ”success”再从structs.xml中找到对应的返回页面
例如:
public String register() {
System.out.println("register()" + userName);
return "register";
}
再配置文件中配置
<action name="register" class="cn.itcast.a_config.UserAction" method="register">
<result name="success">/index.jsp</result>
</action>
可以使用通配符优化配置
<!-- 使用通配符优化上面的步骤 -->
<!-- http://localhost:8080/struts02/user_login -->
<action name="user_*" class="cn.itcast.a_config.UserAction" method="{1}">
<result name="{1}">/{1}.jsp</result>
</action>
public class HelloAction extends ActionSupport {
// 处理请求
public String execute() throws Exception {}
}
4)配置struct.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"> <struts> <!-- package 定义一个包。 包作用,管理action。 (通常,一个业务模板用一个包) name 包的名字; 包名不能重复; extends 当前包继承自哪个包 在struts中,包一定要继承struts-default struts-default在struts-default.xml中定的包 abstract 表示当前包为抽象包; 抽象包中不能有action的定义,否则运行时期报错 abstract=true 只有当当前的包被其他包继承时候才用! 如: <package name="basePackage" extends="struts-default" abstract="true"></package> <package name="user" extends="basePackage"> namespace 名称空间,默认为"/" 作为路径的一部分 访问路径= http://localhost:8080/项目/名称空间/ActionName action 配置请求路径与Action类的映射关系 name 请求路径名称 class 请求处理的aciton类的全名 method 请求处理方法 result name action处理方法返回值 type 跳转的结果类型 标签体中指定跳转的页面 --> <package name="user" extends="struts-default" namespace="/"> <action name="login" class="cn.itcast.b_execute.UserAction" method="login"> <result name="login">/index.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
2.访问流程:
tomcat服务器启动-》读取web,xml-》读取struct2核心过滤器-》初始化过滤器-》init方法(这里分别读取了struct-default.xml核心功能初始化有拦截器等;struct-plugin.xml:struct相关插件;struct.xml用户编写的xml)-》读取到struct.xml后找到action类-》读取structs.properties用户自定义配置文件会覆盖Structs.xml中的常量设置-》加载到内存中等待访问再实例化action类
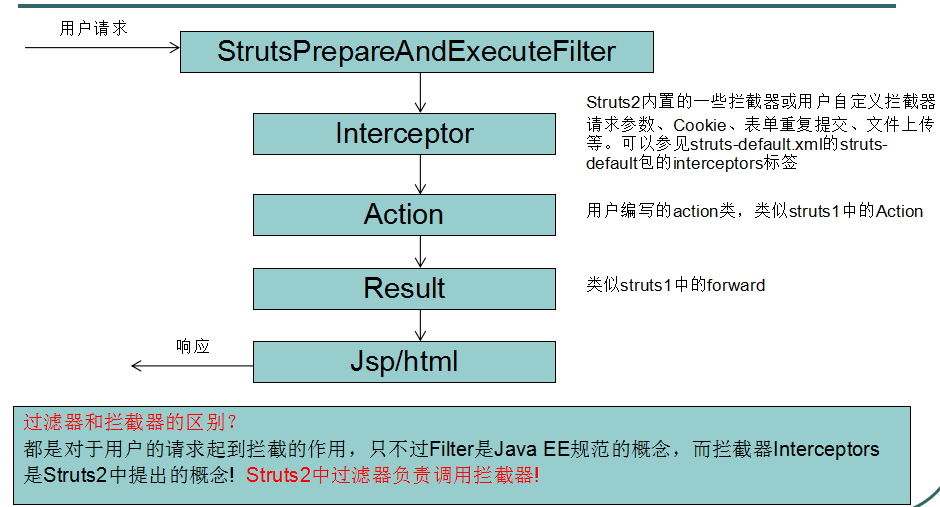
3.一些配置文件详解
struct-default.xml

目录:struts2-core-2.3.4.1.jar/ struts-default.xml 内容: 1. bean节点指定struts在运行的时候创建的对象类型 2.指定struts-default包 【用户写的package(struts.xml)一样要继承此包 】 package struts-default 包中定义了: a. 跳转的结果类型 dispatcher 转发,不指定默认为转发 redirect 重定向 redirectAction 重定向到action资源 stream (文件下载的时候用) b. 定义了所有的拦截器 定义了32个拦截器! 为了拦截器引用方便,可以通过定义栈的方式引用拦截器, 此时如果引用了栈,栈中的拦截器都会被引用! defaultStack 默认的栈,其中定义默认要执行的18个拦截器! c. 默认执行的拦截器栈、默认执行的action <default-interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/> <default-class-ref class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport" /> <interceptor name="prepare" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.PrepareInterceptor"/> <interceptor name="params" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ParametersInterceptor"/>
自己的struct。xml配置
1)两种方便访问action的方法“通配符”“动态配置”
通配符:可以使用* 和{1}来优化配置
动态配置:这个访问方式action名字!action类中的需要访问的方法名例如:hello!add.action
/struct2/hello!add.action:用这个只有在常量设置中设置
<constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="false"/>
<action name="user_*_*" class="" method="{1}{2}"> <result name="{1}">/{1}.jsp</result> </action>
2)路径匹配原则
/Struts2_01/hello_a/a/b/helloWorld.action
/Struts2_01/hello_a/a/b找package->没找到/Struts2_01/hello_a/a-》没找到/Struts2_01/hello_a没找到/Struts2_01/-报404错
3)常量
所有的初始化全局变量配置都在Structs-core-2.3.4-1.jar/org.apache.structs/default.properities

# # $Id: default.properties 1132110 2011-06-05 08:45:32Z lukaszlenart $ # # Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one # or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file # distributed with this work for additional information # regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file # to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the # "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance # with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at # # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 # # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, # software distributed under the License is distributed on an # "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY # KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the # specific language governing permissions and limitations # under the License. # ### START SNIPPET: complete_file ### Struts default properties ###(can be overridden by a struts.properties file in the root of the classpath) ### ### Specifies the Configuration used to configure Struts ### one could extend org.apache.struts2.config.Configuration ### to build one's customize way of getting the configurations parameters into Struts # struts.configuration=org.apache.struts2.config.DefaultConfiguration ### This can be used to set your default locale and encoding scheme # struts.locale=en_US struts.i18n.encoding=UTF-8 ### if specified, the default object factory can be overridden here ### Note: short-hand notation is supported in some cases, such as "spring" ### Alternatively, you can provide a com.opensymphony.xwork2.ObjectFactory subclass name here # struts.objectFactory = spring ### specifies the autoWiring logic when using the SpringObjectFactory. ### valid values are: name, type, auto, and constructor (name is the default) struts.objectFactory.spring.autoWire = name ### indicates to the struts-spring integration if Class instances should be cached ### this should, until a future Spring release makes it possible, be left as true ### unless you know exactly what you are doing! ### valid values are: true, false (true is the default) struts.objectFactory.spring.useClassCache = true ### ensures the autowire strategy is always respected. ### valid values are: true, false (false is the default) struts.objectFactory.spring.autoWire.alwaysRespect = false ### if specified, the default object type determiner can be overridden here ### Note: short-hand notation is supported in some cases, such as "tiger" or "notiger" ### Alternatively, you can provide a com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ObjectTypeDeterminer implementation name here ### Note: By default, com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.DefaultObjectTypeDeterminer is used which handles type detection ### using generics. com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.GenericsObjectTypeDeterminer was deprecated since XWork 2, it's ### functions are integrated in DefaultObjectTypeDeterminer now. ### To disable tiger support use the "notiger" property value here. #struts.objectTypeDeterminer = tiger #struts.objectTypeDeterminer = notiger ### Parser to handle HTTP POST requests, encoded using the MIME-type multipart/form-data # struts.multipart.parser=cos # struts.multipart.parser=pell struts.multipart.parser=jakarta # uses javax.servlet.context.tempdir by default struts.multipart.saveDir= struts.multipart.maxSize=2097152 ### Load custom property files (does not override struts.properties!) # struts.custom.properties=application,org/apache/struts2/extension/custom ### How request URLs are mapped to and from actions #struts.mapper.class=org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.mapper.DefaultActionMapper ### Used by the DefaultActionMapper ### You may provide a comma separated list, e.g. struts.action.extension=action,jnlp,do ### The blank extension allows you to match directory listings as well as pure action names ### without interfering with static resources, which can be specified as an empty string ### prior to a comma e.g. struts.action.extension=, or struts.action.extension=x,y,z,, struts.action.extension=action,, ### Used by FilterDispatcher ### If true then Struts serves static content from inside its jar. ### If false then the static content must be available at <context_path>/struts struts.serve.static=true ### Used by FilterDispatcher ### This is good for development where one wants changes to the static content be ### fetch on each request. ### NOTE: This will only have effect if struts.serve.static=true ### If true -> Struts will write out header for static contents such that they will ### be cached by web browsers (using Date, Cache-Content, Pragma, Expires) ### headers). ### If false -> Struts will write out header for static contents such that they are ### NOT to be cached by web browser (using Cache-Content, Pragma, Expires ### headers) struts.serve.static.browserCache=true ### Set this to false if you wish to disable implicit dynamic method invocation ### via the URL request. This includes URLs like foo!bar.action, as well as params ### like method:bar (but not action:foo). ### An alternative to implicit dynamic method invocation is to use wildcard ### mappings, such as <action name="*/*" method="{2}" class="actions.{1}"> struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation = true ### Set this to true if you wish to allow slashes in your action names. If false, ### Actions names cannot have slashes, and will be accessible via any directory ### prefix. This is the traditional behavior expected of WebWork applications. ### Setting to true is useful when you want to use wildcards and store values ### in the URL, to be extracted by wildcard patterns, such as ### <action name="*/*" method="{2}" class="actions.{1}"> to match "/foo/edit" or ### "/foo/save". struts.enable.SlashesInActionNames = false ### use alternative syntax that requires %{} in most places ### to evaluate expressions for String attributes for tags struts.tag.altSyntax=true ### when set to true, Struts will act much more friendly for developers. This ### includes: ### - struts.i18n.reload = true ### - struts.configuration.xml.reload = true ### - raising various debug or ignorable problems to errors ### For example: normally a request to foo.action?someUnknownField=true should ### be ignored (given that any value can come from the web and it ### should not be trusted). However, during development, it may be ### useful to know when these errors are happening and be told of ### them right away. struts.devMode = false ### when set to true, resource bundles will be reloaded on _every_ request. ### this is good during development, but should never be used in production struts.i18n.reload=false ### Standard UI theme ### Change this to reflect which path should be used for JSP control tag templates by default struts.ui.theme=xhtml struts.ui.templateDir=template #sets the default template type. Either ftl, vm, or jsp struts.ui.templateSuffix=ftl ### Configuration reloading ### This will cause the configuration to reload struts.xml when it is changed struts.configuration.xml.reload=false ### Location of velocity.properties file. defaults to velocity.properties struts.velocity.configfile = velocity.properties ### Comma separated list of VelocityContext classnames to chain to the StrutsVelocityContext struts.velocity.contexts = ### Location of the velocity toolbox struts.velocity.toolboxlocation= ### used to build URLs, such as the UrlTag struts.url.http.port = 80 struts.url.https.port = 443 ### possible values are: none, get or all struts.url.includeParams = none ### Load custom default resource bundles # struts.custom.i18n.resources=testmessages,testmessages2 ### workaround for some app servers that don't handle HttpServletRequest.getParameterMap() ### often used for WebLogic, Orion, and OC4J struts.dispatcher.parametersWorkaround = false ### configure the Freemarker Manager class to be used ### Allows user to plug-in customised Freemarker Manager if necessary ### MUST extends off org.apache.struts2.views.freemarker.FreemarkerManager #struts.freemarker.manager.classname=org.apache.struts2.views.freemarker.FreemarkerManager ### Enables caching of FreeMarker templates ### Has the same effect as copying the templates under WEB_APP/templates struts.freemarker.templatesCache=false ### Enables caching of models on the BeanWrapper struts.freemarker.beanwrapperCache=false ### See the StrutsBeanWrapper javadocs for more information struts.freemarker.wrapper.altMap=true ### maxStrongSize for MruCacheStorage for freemarker struts.freemarker.mru.max.strong.size=100 ### configure the XSLTResult class to use stylesheet caching. ### Set to true for developers and false for production. struts.xslt.nocache=false ### Whether to always select the namespace to be everything before the last slash or not struts.mapper.alwaysSelectFullNamespace=false ### Whether to allow static method access in OGNL expressions or not struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess=false ### Whether to throw a RuntimeException when a property is not found ### in an expression, or when the expression evaluation fails struts.el.throwExceptionOnFailure=false ### Logs as Warnings properties that are not found (very verbose) struts.ognl.logMissingProperties=false ### Caches parsed OGNL expressions, but can lead to memory leaks ### if the application generates a lot of different expressions struts.ognl.enableExpressionCache=true ### END SNIPPET: complete_file
1.Struct中默认访问后缀
Struct1:.do;Struct2:.action
2.在Struct.xml通过常量修改
<constant name="struct.action.extension" value="action,do,"></constant>
指定访问后缀为action/do/没有访问后缀都可以
value="action,do,"不带后缀
value="action,do"访问后缀action或do
value="action" 后缀只能是action
3.常量在struct.xml中配置
<!-- 1.常量 --> <!-- 指定默认编码集,作用于HttpServletRequest的setCharacterEncoding方法 和freemarker 、velocity的输出 --> <constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="UTF-8"/> <!-- 自定义后缀修改常量 --> <constant name="struts.action.extension" value="do"/> <!-- 设置浏览器是否缓存静态内容,默认值为true(生产环境下使用),开发阶段最好关闭 --> <constant name="struts.serve.static.browserCache" value="false"/> <!-- 当struts的配置文件修改后,系统是否自动重新加载该文件,默认值为false(生产环境下使用),开发阶段最好打开 --> <constant name="struts.configuration.xml.reload" value="true"/> <!-- 开发模式下使用,这样可以打印出更详细的错误信息 --> <constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" /> <!-- 默认的视图主题 --> <constant name="struts.ui.theme" value="simple" /> <!-- 与spring集成时,指定由spring负责action对象的创建 --> <constant name="struts.objectFactory" value="spring" /> <!-- 该属性设置Struts 2是否支持动态方法调用,该属性的默认值是true。如果需要关闭动态方法调用,则可设置该属性 为 false --> <constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="false"/> <!-- 上传文件的大小限制 --> <constant name="struts.multipart.maxSize" value="10701096"/>
4)resultType
1.在action中想要获得request对象:
ServletActionContext.getRequest();ServletActionContext是action重要对象

2.其中type的设置有

3.result全局结果
当多个action中使用了相同的result,为了避免result的重复,我们可以设置全局结果;但是局部权限大于全局
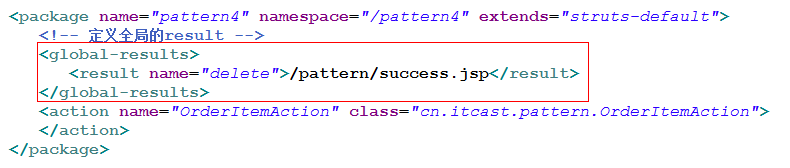
4.数据封装
1)struts对数据封装,当访问action时,参与核心过滤器,访问default-struts.xml->strut.xml,在default-struts.xml中有32个拦截器,其中Parameters拦截器对数据进行封装
2)String-》基本数据类型转换是自动的
String-》Date日期类型的转换是有条件的
3)转换原理过程
1.表单中的name值自动映射到Action中的一个属性;2.还可以映射到一个集合
3.Struts对HttpServetRequest,HttpSession,ServletContext进行了封装,构造了三个Map对象,可通过ServletActionContext来访问三个对象
4)在action中两种获得数据的方法
1.ServletApi 2.通过ServletActionContext获得ActionContext对象得到三个封装好的Map对象3.实现三个接口RequestAware, SessionAware, ApplicationAwar也可以
方式一:通过Servlet Api
HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); HttpSession session = request.getSession(); ServletContext application = ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); // 操作 request.setAttribute("request_data", "request_data1"); session.setAttribute("session_data", "session_data1"); application.setAttribute("application_data", "application_data1");
方式二:推荐这个方法
// Struts中对数据操作,方式2: 通过ActionContext类 ActionContext ac = ActionContext.getContext(); // 得到Struts对HttpServletRequest对象进行了封装,封装为一个map // 拿到表示request对象的map Map<String,Object> request = ac.getContextMap(); // 拿到表示session对象的map Map<String, Object> session = ac.getSession(); // 拿到表示servletContext对象的map Map<String, Object> application = ac.getApplication(); // 数据 request.put("request_data", "request_data1_actionContext"); session.put("session_data", "session_data1_actionContext"); application.put("application_data", "application_data1_actionContext");

/** * 数据处理, 方式3: 实现接口的方法 * @author Jie.Yuan * */ public class DataAction extends ActionSupport implements RequestAware, SessionAware, ApplicationAware{ private Map<String, Object> request; private Map<String, Object> session; private Map<String, Object> application; // struts运行时候,会把代表request的map对象注入 public void setRequest(Map<String, Object> request) { this.request = request; } // 注入session public void setSession(Map<String, Object> session) { this.session = session; } // 注入application public void setApplication(Map<String, Object> application) { this.application = application; } public String execute() throws Exception { // 数据 /* * // Struts中对数据操作,方式1: 直接拿到ServletApi, 执行操作 HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); HttpSession session = request.getSession(); ServletContext application = ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); // 操作 request.setAttribute("request_data", "request_data1"); session.setAttribute("session_data", "session_data1"); application.setAttribute("application_data", "application_data1"); */ // 【推荐:解耦的方式实现对数据的操作】 // Struts中对数据操作,方式2: 通过ActionContext类 ActionContext ac = ActionContext.getContext(); // 得到Struts对HttpServletRequest对象进行了封装,封装为一个map // 拿到表示request对象的map Map<String,Object> request = ac.getContextMap(); // 拿到表示session对象的map Map<String, Object> session = ac.getSession(); // 拿到表示servletContext对象的map Map<String, Object> application = ac.getApplication(); // 数据 request.put("request_data", "request_data1_actionContext"); session.put("session_data", "session_data1_actionContext"); application.put("application_data", "application_data1_actionContext"); // return SUCCESS; } }
5.类型转换
前面说了数据转换String->基本类型类型自动的,日期需要条件
1)是Parameters拦截器做的类似于: Beanutils工具
2)自定义类型转换器
1.继承StrutsTypeConverter
2.全局转换,局部转换配置
例子:

/** * 自定义类型转换器类 * * @author Jie.Yuan * */ public class MyConverter extends StrutsTypeConverter { // 新需求: 要求项目中要支持的格式,如: yyyy-MM-dd/yyyyMMdd/yyyy年MM月dd日.. // 先定义项目中支持的转换的格式 DateFormat[] df = { new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"), new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd"), new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日") }; /** * 把String转换为指定的类型 【String To Date】 * * @param context * 当前上下文环境 * @param values * jsp表单提交的字符串的值 * @param toClass * 要转换为的目标类型 */ @Override public Object convertFromString(Map context, String[] values, Class toClass) { // 判断: 内容不能为空 if (values == null || values.length == 0) { return null; } // 判断类型必须为Date if (Date.class != toClass) { return null; } // 迭代:转换失败继续下一个格式的转换; 转换成功就直接返回 for (int i=0; i<df.length; i++) { try { return df[i].parse(values[0]); } catch (ParseException e) { continue; } } return null; } @Override public String convertToString(Map context, Object o) { return null; } }
局部配置:在自定义转化器添加(自定义转换器名字-conversion.properties):MyConverter-conversion.properties
在其中写:需要转换的字段名=自定义转换器类的权限定名birth=type.MyConverter
全局配置:在项目src目录下建立固定文件xwork-conversion.properties
在其中写:需要转换的类类型=转换器类的权限定名 :java.util.Date=type.MyConverter(java.util.Date是birth的类型)
3)struts-default.xml <interceptor name="conversionError" class="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.StrutsConversionErrorInterceptor"/>
该拦截器负责对错误信息处理
6.文件支持
1)文件上传
1.核心类:FileItemFactory;ServletFileUpload;FileItem
2.struts处理上传文件:
获得上传文件的file,对应的fileName,fileContextType,之后再execute中执行对上传文件的处理;
上传文件默认都是被缓存到.me_tcatworkCatalinalocalhoststruts02upload_5bd0b60c_15c3369eeb3__8000_00000005.tmp中
我们要做的是把文件得到存到我们指定的位置
3.配置action:在action子栏中添加。。。等信息
在default-struts中有拦截器fileUpload,而在ServletFileUpload类中文件属性我们都可以在自己写的拦截器中添加
<!-- 限制运行上传的文件的类型 -->
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack">
<!-- 限制运行的文件的扩展名 -->
<param name="fileUpload.allowedExtensions">txt,jpg,jar</param>
<param name="fileUpload.maximumSize">1024</param>
<!-- 限制运行的类型 【与上面同时使用,取交集】
<param name="fileUpload.allowedTypes">text/plain</param>
-->
</interceptor-ref>
当文件上传错误时,会自动放回字符串input,我们可以在action中配置跳转到指定页面,这个页面想要显示错误信息可以通过引用struts标签,显示
4.上传例子

1.jsp <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/fileUploadAction" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="userName"><br/> 文件:<input type="file" name="file1"><br/> <input type="submit" value="上传"> </form> 2.action public class FileUpload extends ActionSupport { /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // 对应表单:<input type="file" name="file1"> private File file1; // 文件名 private String file1FileName; // 文件的类型(MIME) private String file1ContentType; public void setFile1(File file1) { this.file1 = file1; } public void setFile1FileName(String file1FileName) { this.file1FileName = file1FileName; } public void setFile1ContentType(String file1ContentType) { this.file1ContentType = file1ContentType; } //上面的代码是通过拦截器对数据自动封装到这三个属性中的 @Override public String execute() throws Exception { /******拿到上传的文件,进行处理******/ // 把文件上传到upload目录 System.out.println(file1FileName); System.out.println(file1ContentType); // 获取上传的目录路径 String path = ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload"); System.out.println(path); // 创建目标文件对象 File destFile = new File(path,file1FileName); // 把上传的文件,拷贝到目标文件中 FileUtils.copyFile(file1, destFile); return SUCCESS; } }
2)文件下载
访问连接down_down.action就是到down_list的action中找到类,对应的list方法,下面的例子是list方法返回list字符串在action中就找到对于的result放回到list.jsp中,在这里通过点击下载-》又发送连接down_down?fileName=文件名.txt-》找到down_down的action找到对应的类里面的down方法开始下载-》随后在对应的action中找到result,这个result的为属于下载业务功能,需要特殊设置:
type="stream";之后在子项中添加四个param子标签
<!-- 下载操作 -->
<result name="download" type="stream">
<!-- 运行下载的文件的类型:指定为所有的二进制文件类型 -->
<param name="contentType">application/octet-stream</param>
<!-- 对应的是Action中属性: 返回流的属性【其实就是getAttrInputStream()】 -->
<param name="inputName">attrInputStream</param>
<!-- 下载头,包括:浏览器显示的文件名 -->
<param name="contentDisposition">attachment;filename=${downFileName}</param>
<!-- 缓冲区大小设置 -->
<param name="bufferSize">1024</param>
</result>
之后我们需要在action类中再写 1.放回流属性的getAttrInputStream()方法放回要下载文件的流;
2.返回下载头包含浏览器显示的文件名:getDownFileName()
上传下载的整体例子
上传

1.file.xml中的配置 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"> <struts> <package name="file" extends="struts-default" namespace="/"> <action name="FileUploadAction" class="fileupload.FileUpload"> <!-- 文件上传有拦截器我们自己定义下,在defaultStrack中的一些定义好的元素会别创建我们可以对他们属性设置 --> <interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"> <param name="fileUpload.allowedExtension">txt,jpg,jar</param> <param name="fileUpload.maximumSize">2097152</param> </interceptor-ref> <result name="success">/e/success.jsp</result> <result name="input">/e/error.jsp</result> </action> <action name="down_*" class="fileupload.DownAction" method="{1}"> <!-- 列表显示 --> <result name="list">e/list.jsp</result> <!-- 下载操作 --> <result name="download" type="stream"> <!-- 运行下载的文件的类型:指定为所有的二进制文件类型 --> <param name="contentType">application/octet-stream</param> <!-- 对应的是Action中属性: 返回流的属性【其实就是getAttrInputStream()】 --> <param name="inputName">attrInputStream</param> <!-- 下载头,包括:浏览器显示的文件名 --> <param name="contentDisposition">attachment;filename=${downFileName}</param> <!-- 缓冲区大小设置 --> <param name="bufferSize">1024</param> </result> </action> </package> </struts> 2.FileUpload.java代码 package fileupload; import java.io.File; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; /** * 文件上传 * @author Administrator * */ public class FileUpload extends ActionSupport{ /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private File file1; private String file1FileName; //上面的代码是通过拦截器对数据自动封装到这三个属性中的 public void setFile1(File file1) { this.file1 = file1; } public void setFile1FileName(String file1FileName) { this.file1FileName = file1FileName; } @Override public String execute() throws Exception { String path=ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload"); File destDir=new File(path,file1FileName); FileUtils.copyDirectory(file1, destDir); System.out.println("上传成功"); return SUCCESS; } } 3.提交上传的表单jsp <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="/structs/FileUploadAction" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 文件:<input type="file" name="file1"/> <input type="submit" value="上传"/> </form> </body> </html>
下载

1.DownAction.java package fileupload; import java.io.File; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.net.URLEncoder; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; public class DownAction extends ActionSupport{ /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /************显示所有需要下载的文件*************/ public String list(){ String path=ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload"); File file=new File(path); String[] fileNames = file.list();//得到所有下载的文件名 //保存 ActionContext ac=ServletActionContext.getContext(); Map<String,Object> request=(Map<String, Object>) ac.get("request"); request.put("fileNames", fileNames); return "list"; } /***************2.文件下载****************/ /*1。获得要下载的文件名字*/ private String fileName; public void setFileName(String fileName){ //这里提交时get提交存在乱码问题需要解决下 try { fileName=new String(fileName.getBytes("ISO8859-1"),"UTF-8"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } this.fileName=fileName; } /*2.下载提交业务*/ public String down(){ return "download"; } /*3.返回文件流的方法*/ public InputStream getAttrInputStream(){ return ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/upload"+fileName); } /*4.下载显示的文件名*/ public String getDownFileName(){ //需要中文编码 try { fileName=URLEncoder.encode(fileName,"UTF-8"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return fileName; } } 2.显示所有下载文件的list.jsp <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>下载列表</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> </head> <body> list列表 <table border="1" align="center" > <tr> <td>编号</td> <td>文件名</td> <td>操作</td> </tr> <%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <c:forEach items="${fileNames }" varStatus="vs" var="fileName"> <tr> <td>${vs.count}</td> <td>${fileName}</td> <td> <!-- 创建一个url --> <c:url var="url" value="down_down"> <c:param name="fileName" value="${fileName }"></c:param> </c:url> <a href="${url }">下载</a> </td> </tr> </c:forEach> </table> </body> </html> 3。访问方式:先访问list,再下载
6.拦截器
a) 想出拦截器原因
用户想要给action什么功能的时候可以通过拦截器自由组装,基于组件的设计
b) 知识点:拦截器在struts-default中定义了32种拦截器,18中默认拦截器
拦截器栈:组合多个拦截器,默认使用strut-default的18个默认拦截器defaultStack
一旦用户指定哪个拦截器,默认拦截器就不起作用了
c) 拦截器的配置
在struts-default中定义所有的拦截器其中默认拦截器

<interceptor-stack name="defaultStack"> <interceptor-ref name="exception"/> <interceptor-ref name="alias"/> <interceptor-ref name="servletConfig"/> <interceptor-ref name="i18n"/> <interceptor-ref name="prepare"/> <interceptor-ref name="chain"/> <interceptor-ref name="scopedModelDriven"/> <interceptor-ref name="modelDriven"/> <interceptor-ref name="fileUpload"/> <interceptor-ref name="checkbox"/> <interceptor-ref name="multiselect"/> <interceptor-ref name="staticParams"/> <interceptor-ref name="actionMappingParams"/> <interceptor-ref name="params"> <param name="excludeParams">dojo..*,^struts..*,^session..*,^request..*,^application..*,^servlet(Request|Response)..*,parameters...*</param> </interceptor-ref> <interceptor-ref name="conversionError"/> <interceptor-ref name="validation"> <param name="excludeMethods">input,back,cancel,browse</param> </interceptor-ref> <interceptor-ref name="workflow"> <param name="excludeMethods">input,back,cancel,browse</param> </interceptor-ref> <interceptor-ref name="debugging"/> </interceptor-stack>
自己在struts中定义拦截器
1.定义拦截器和拦截器栈
1.1定义拦截器
<interceptors name=”” class=””></interceptors>
1.2定义拦截器栈
<interceptors-stack name=””>
引用上面的或其他的拦截器
</interceptors-stack>
2.默认执行拦截器(栈)
<default-interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/>
e) 拦截器核心api
Interceptor接口
AbstractInterceptor 拦截器默认实现的抽象类,一般自定义开发继承它就行了
ActionInvacation 拦截器的执行状态,调用下一个拦截器或者action
f) 拦截器和过滤器的区别
g) 拦截器的生命周期
服务器启动-》过滤器创建-》初始化init()创建所有拦截器对象-》客户端访问-》创建action实例-》拦截器interceptor方法拦截-》下一个拦截-》。。。》到达action执行execute()->返回给用户结果
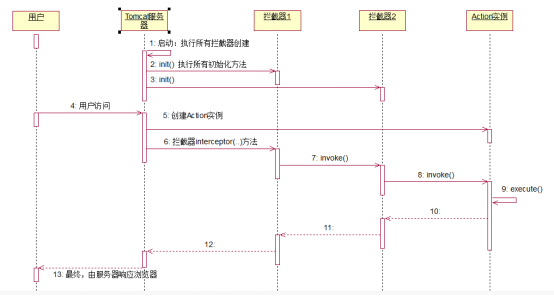
h) 自定义拦截器例子
1.写一个拦截器类

package interceptor; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionInvocation; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.Interceptor; /** * 拦截器定义 * @author Administrator * */ public class HelloInterceptor implements Interceptor{ /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Override public void destroy() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("销毁。。。。。"); } @Override public void init() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("自定义拦截器初始化成功"); } /** * 拦截器业务处理:在访问action时执行,在excute之前执行 */ @Override public String intercept(ActionInvocation arg0) throws Exception { System.out.println("拦截器开始执行"); //执行业务逻辑 //执行下一个拦截器 String aa=arg0.invoke(); //拦截器结束 System.out.println("拦截器结束"); return aa; } }
2.配置struts配置拦截器分3步
a) 定义自定义拦截器<interceptor>
b) 定义我们的拦截器栈<interceptor-stack>:其中引用默认拦截器栈要放在第一位
c) 执行拦截器:<default-interceptor-ref>

<!-- 拦截器配置 -->
<interceptors>
<interceptor name="helloInterceptor" class="interceptor.HelloInterceptor"></interceptor>
<interceptor-stack name="helloStack">
<!-- 引用默认栈 (一定要放到第一行)-->
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"></interceptor-ref>
<!-- 引用自定义拦截器 -->
<interceptor-ref name="helloInterceptor"></interceptor-ref>
</interceptor-stack>
</interceptors>
<!-- 执行拦截器 -->
<default-interceptor-ref name="helloStack"></default-interceptor-ref>
<action name="hello" class="interceptor.HelloAction">
<result name="success">/index.jsp</result>
</action>
7.国际化
a) Serlvelt中的国际化
- 写资源文件
基础名.properties【默认的语言环境设置】
基础名_语言简称_国家简称.properties
- 读取资源文件再使用
程序:ResourceBundle
Jsp: jstl提供的格式化与国际化标签库。
b) Struts中的国际化
- 写资源文件(同servlet)
- 读取资源文件再使用
程序:ResourceBundle
Jsp: 1)jstl表亲啊 (同servlet)
2)struts标签获取资源文件内容
c) 注意
还可以在页面加载
<s:i18n name="cn.itcast.config.msg">
<s:text> 标签必须放到标签体中。
</s:i18n>
d) 区别
Struts2加载资源文件更加简单!通过常量加载即可!再在jsp页面直接使用
|
à1. 写资源文件 |
|
Msg.properties 默认的语言环境; 找不到配置就找它 |
|
Msg_en_US.properties 美国 |
|
-à2. 加载 |
|
<constant name="struts.custom.i18n.resources" value="cn.itcast.config.msg"></constant> |
|
à3. 使用: 标签name值直接写配置文件中的key |
|
<s:text name="title"></s:text> |
8.Ognl表达式语言与Struts标签
深刻理解Ognl,Struct2传输模式
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7ffb8dd5010141pd.html
1.ActionContext装饰OgnlContext 2.OgnlValueStack值栈对象包含了OgnlContext,root对象 3.OgnlContext中包含了所有域对象,全局属性,action对象等等 4.Struts2数据传输DataTransfer的核心对象是OgnlValueStack、 OgnlContext
这里主要需要知道的是“值栈对象”生成过程和内部成员,调用方式
a) Ognl表达式:Object Graphic Navigation Language(对象图导航语言)的缩写是一个开源项
b) 优势:
- 支持对象方法调用,如xxx.doSomeSpecial();
支持类静态的方法调用和值访问,表达式的格式:@[类全名(包括包路径)]@[方法名 | 值名]例如:@java.lang.String@format('foo %s', 'bar')
- 支持赋值操作和表达式串联,如price=100, discount=0.8,calculatePrice(),这个表达式会返回80
- 访问OGNL上下文(OGNL context)和ActionContext;
- 操作集合对象
c) OgnlContext对象
是Ognl表达式的核心
访问Ognl表达式中值Ognl.getValue(ognl表达式,ActionContext ac,ognl的root)
例子:主要看我们对ActionContext上下文对象如何处理,ac中直接添加键值对,创建ognl表达式时要加#,ac添加root时,创建表达式就不需要了
当我们调用工具类的一个方法时,创建ognl表达式:Ognl.parseExpression("@[类名]@[方法调用]")如:@Math@floor(10.9)
1. Ognl表达式语言语言取值,取非根元素的值,必须用#号

public void testOgnl() throws Exception { // 创建一个Ognl上下文对象 OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); // 放入数据 User user = new User(); user.setId(100); user.setName("Jack"); // 【往非根元素放入数据, 取值的时候表达式要用"#"】 context.put("user", user); // 获取数据(map) // 先构建一个Ognl表达式, 再解析表达式 Object ognl = Ognl.parseExpression("#user.name"); Object value = Ognl.getValue(ognl, context, context.getRoot()); System.out.println(value); }
2. Ognl表达式语言语言取值,取根元素的值,不用带#号

public void testOgn2() throws Exception { // 创建一个Ognl上下文对象 OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); // 放入数据 User user = new User(); user.setId(100); user.setName("Jack"); // 【往根元素放入数据】 context.setRoot(user); // 获取数据(map) // 先构建一个Ognl表达式, 再解析表达式 Object ognl = Ognl.parseExpression("address.province"); Object value = Ognl.getValue(ognl, context, context.getRoot()); System.out.println(value); }
3.Ognl对 静态方法调用的支持

public void testOgn3() throws Exception { // 创建一个Ognl上下文对象 OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); // Ognl表单式语言,调用类的静态方法 //Object ognl = Ognl.parseExpression("@Math@floor(10.9)"); // 由于Math类在开发中比较常用,所以也可以这样写 Object ognl = Ognl.parseExpression("@@floor(10.9)"); Object value = Ognl.getValue(ognl, context, context.getRoot()); System.out.println(value); }
4.Ognl运用在jsp页面:数据存到request中后自然就存到OgnlContext中了,在jsp页面通过#request.list就能访问到OgnlContext中的list对象和里面的值,OgnlContext就相当于一个容器,存放了所有的域对象和自己存进去的键值对

map迭代 <s:iterator var="en" value="#request.map" status="st"> <tr> <td><s:property value="#en.key"/></td> <td><s:property value="#en.value.name"/></td> </tr> </s:iterator>
不是根Obnl的根对象都是用#开头才能访问到
d) ValueStack对象
用户访问action时,创建action对象,之后再将很多信息,action对象、全局属性、域对象、等等存入值栈对象中,之后值栈对象就有了很多内容,我们取值都可以从这里取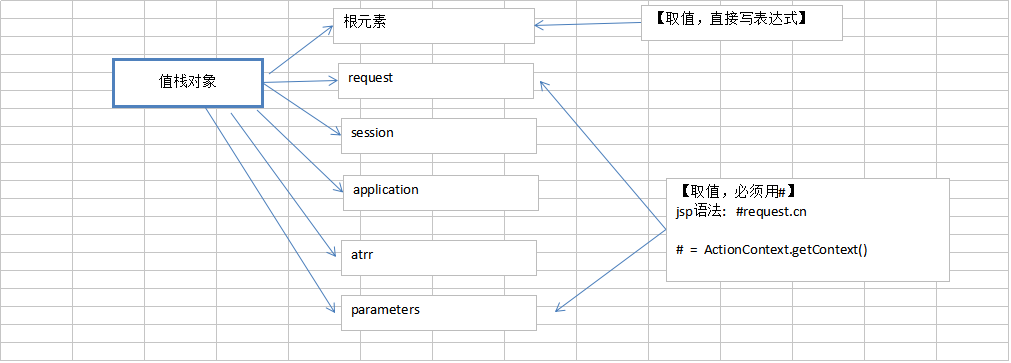

值栈对象,是struts数据存储中心,或者说是中转站
访问action时,创建了action对象、值栈对象、ActionContext对象;将action对象放入值栈对象,再将值栈对象存入request中传到jsp中
ActionContext类装饰OgnlContext类
获取值栈对象2种方式:
1.因为action对象放入值栈对象,值栈对象又存入request对象,所有想要获得ValueStack对象可以从request对象中获得
ValueStack vs1 = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute("struts.valueStack");
2.直接从ActionContext对中获得
ac..getValueStack();
e) Struts标签
Struct标签就是用了Ognl表达式语言
9.验证
代码验证

package validation; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; /** * 验证需要实现接口或者继承ActionSupport * @author Administrator * */ public class UserAction extends ActionSupport{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; //封装数据的请求 private User user; public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } //重写数据验证的方法 /*public void validateRegister() { if(user.getUserName()==null||"".equals(user.getUserName())){ //保存错误信息 super.addFieldError("userName","用户名必须重写"); } // 密码 if (user.getPwd() == null || "".equals(user.getPwd())) { super.addFieldError("pwd", "密码必填"); } }*/ //业务方法 public String register(){ System.out.println(user); System.out.println(1); return SUCCESS; } //列表展示 public String list(){ return SUCCESS; } }
xml验证

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE validators PUBLIC "-//Apache Struts//XWork Validator 1.0.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/xwork-validator-1.0.3.dtd"> <validators> <!-- 验证每一个字段用field表示 --> <field name="user.userName"> <field-validator type="requiredstring"> <!-- 验证失败的错误提示信息 --> <message>用户名不能为空</message> </field-validator> </field> <!-- 密码不能为空 --> <field name="user.pwd"> <!-- 非空 --> <field-validator type="requiredstring"> <message>密码不能为空!</message> </field-validator> <!-- 长度 --> <field-validator type="stringlength"> <param name="minLength">6</param> <param name="maxLength">8</param> <message>密码必须为6-8位!</message> </field-validator> </field> <!-- 验证日期 --> <field name="user.birth"> <field-validator type="date"> <message>日期格式不对!</message> </field-validator> </field> <!-- 验证emil --> <field name="user.emil"> <field-validator type="email"> <message>邮件格式不对</message> </field-validator> </field> </validators>
1)验证原理
通过拦截器验证
<interceptor name="validation" class="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.validation.AnnotationValidationInterceptor"/>
2)配置验证步骤
写一个类继承ActionSuppert或者实现Validate接口重写validate()方法即可
要注意的是:想要验证指定的方法只需只需验证名称规则:validate+要验证的方法名(public void validateRegister())
3)验证action的方法
1)代码验证
重写验证方法,注意命名规则可以指定特定的方法验证
validate+要验证的方法名
public void validateRegister() {
只会验证当前action的register方法!
2)XML方式验证
1.将错误信息显示在jsp页面:<s:fielderror fieldName="user.userName"></s:fielderror>
2.代码验证缺点:设计很多重复的验证逻辑!例如:非空验证、数值验证、email、日期等。
3.Struts对于常用的验证进行了封装
Struts提供的所有的验证器:xwork-core-2.3.4.1.jar/com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators/default.xml
都在这里了

<!-- START SNIPPET: validators-default --> <validators> <validator name="required" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RequiredFieldValidator"/> <validator name="requiredstring" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RequiredStringValidator"/> <validator name="int" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.IntRangeFieldValidator"/> <validator name="long" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.LongRangeFieldValidator"/> <validator name="short" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ShortRangeFieldValidator"/> <validator name="double" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.DoubleRangeFieldValidator"/> <validator name="date" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.DateRangeFieldValidator"/> <validator name="expression" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ExpressionValidator"/> <validator name="fieldexpression" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.FieldExpressionValidator"/> <validator name="email" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.EmailValidator"/> <validator name="url" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.URLValidator"/> <validator name="visitor" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.VisitorFieldValidator"/> <validator name="conversion" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ConversionErrorFieldValidator"/> <validator name="stringlength" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.StringLengthFieldValidator"/> <validator name="regex" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RegexFieldValidator"/> <validator name="conditionalvisitor" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ConditionalVisitorFieldValidator"/> </validators> <!-- END SNIPPET: validators-default -->
XML文件名称语法:
指定的是所有验证:ActionClassName-validation.xml;
指定特定的方法命名规则:ActionClassName-ActionName-validation.xml
注意:此XML需要与当前要验证的acton同在一个目录
举例:UserAction-validation.xml/UserAction-register-validation.xml
例如:xml中的规则在dtd文件在xwork-core-2.3.4.1.jar下慢慢找吧dtd文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE validators PUBLIC "-//Apache Struts//XWork Validator 1.0.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/xwork-validator-1.0.3.dtd"> <validators> <!-- 验证每一个字段用field表示 --> <field name="user.userName"> <field-validator type="requiredstring"> <!-- 验证失败的错误提示信息 --> <message>用户名不能为空</message> </field-validator> </field> <!-- 密码不能为空 --> <field name="user.pwd"> <!-- 非空 --> <field-validator type="requiredstring"> <message>密码不能为空!</message> </field-validator> <!-- 长度 --> <field-validator type="stringlength"> <param name="minLength">6</param> <param name="maxLength">8</param> <message>密码必须为6-8位!</message> </field-validator> </field> <!-- 验证日期 --> <field name="user.birth"> <field-validator type="date"> <message>日期格式不对!</message> </field-validator> </field> <!-- 验证emil --> <field name="user.emil"> <field-validator type="email"> <message>邮件格式不对</message> </field-validator> </field> </validators>
3)验证总结
代码:
重写validate() , 验证action所有方法
Validate方法名(), 验证指定“方法名”的方法
Xml:
验证所有方法: ActionClassName-validation.xml
验证指定方法: ActionClassName-actionName-validation.xml
代码验证,
比较灵活,可以满足所有的需求.
比较繁琐,要写重复的验证判断逻辑!
适合: 表单字段较少的情况用!
XML验证:
通用,但不够灵活; 可以验证特定简单的业务。
适合: 验证表单字段较多,可以大大简化代码!
(配置文件过多)
4)显示错误信息:

1.方式一: <%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %> <!-- 显示的是struts在运行时期产生的所有错误 --> <s:fielderror></s:fielderror> 2.方式二: <!-- 修改struts标签默认的样式: 不让换行 --> 这样弄因为显示错写信息时会自动生成ui,ul标签 <style type="text/css"> ul{display: inline;} ul li{display: inline;color: red;} </style> 3.修改标签定义的模板 找到fielderror标签定义的模板文件:Struts-core.jar emplatesimple fielderror.ftl 把修改后的文件放到src/ template/ simple/ fielderror.ftl 这样样式就修改好了
10.struts简单的UI标签
<!-- 服务器标签 : 最终别解析为html标签-->
<s:form action="/user_login" method="post" name="frmLogin" id="frmLogin" theme="simple">
用户名:<s:textfield name="user.name"></s:textfield>
密码:<s:textfield name="user.pwd"></s:textfield>
<s:submit value="登陆"></s:submit>
</s:form>
<!-- 修改主题 (当前项目所有的标签都用此主题)-->
<constant
name="struts.ui.theme" value="simple"></constant>
11.Struts中几种特殊符号(jsp页面)
#:获取非根元素值、map集合
$:配置文件取值
%:提供一个ognl表示的运行环境
例子:

<body>
<br/>获取request域数据<br/>
<!-- property 标签是对象类型的标签,默认支持ognl表达式, 会从根元素去China名称对应的值 -->
<s:property value="China"/> <br/>
<!-- 如果直接赋值,需要用单引号 -->
<s:property value="'China'"/> <br/>
<s:property value="%{#request.cn}"/> <br/>
<!-- 值类型的标签,value值默认就是值类型,不支持ognl表达式 -->
国家:<s:textfield name="txtCountry" value="%{#request.cn}"></s:textfield>
</body>
12.Struts中常用的几个技术
1)数据回显
必须使用struts标签:
进入修改页面时-》将数据信息存入request域Map中,或者存入栈值对中,在jsp页面,通过struts标签就能获得obnl标签值
两种数据存入方式
1.通过request域Map
2.通过ValueStack存入头对象,能直接访问
例子:

Action中: // 进入修改页面 public String viewUpdate() { // 模拟一个对象(先获取一个id,再根据id调用service查询,把查到的结果保存到域) User userInfo = new User(); userInfo.setUserName("Jack"); userInfo.setEmail("yuanjie@itcast.cn"); ActionContext ac = ActionContext.getContext(); // Map<String,Object> request = (Map<String, Object>) ac.get("request"); // request.put("userInfo", userInfo); /************* 数据回显***************/ // 获取值栈 ValueStack vs = ac.getValueStack(); vs.pop();// 移除栈顶元素 vs.push(userInfo); // 入栈 // 进入修改页面 return "viewUpdate"; } JSP页面: <body> <%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %> <br/> <!-- 在页面文本框内,显示要修改记录的数据 --> <!-- 手动通过value设置显示的值 <s:form action="#"> 用户名: <s:textfield name="user.userName" value="%{#request.userInfo.userName}"></s:textfield> <br/> 邮箱: <s:textfield name="user.email" value="%{#request.userInfo.email}"></s:textfield> <br/> </s:form> --> <!-- 数据回显技术:s:textfield会自动查找根元素数据(Ognl表达式语言取值) --> <s:form action="#"> 用户名: <s:textfield name="userName"></s:textfield> <br/> 邮箱: <s:textfield name="email"></s:textfield> <br/> </s:form> <s:debug></s:debug> </body>
2)模型驱动,属性驱动
模型驱动就是直接将对象封装,属性驱动就是将属性赋值给对象的属性
<interceptor name="modelDriven" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ModelDrivenInterceptor"/>

@Override public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { Object action = invocation.getAction(); if (action instanceof ModelDriven) { ModelDriven modelDriven = (ModelDriven) action; ValueStack stack = invocation.getStack(); Object model = modelDriven.getModel(); if (model != null) { stack.push(model); } if (refreshModelBeforeResult) { invocation.addPreResultListener(new RefreshModelBeforeResult(modelDriven, model)); } } return invocation.invoke(); }
prams拦截器,可以把请求数据自动填充的action的属性中
就是数据封装的关键拦截器
4.表单重复提交拦截器
<interceptor name="token" class="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.TokenInterceptor"/>
Struts2知识进阶
1.继承了ActionSupport的类,想要给前台页面发送信息处了可以通过域对象发送;还可以通过以下三种方式提交信息
this.addActionMessage("message");
this.addActionError(anErrorMessage);
this.addFieldError(fieldName, errorMessage)
之后在前台界面使用<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%>
<s:actionmessage/>;<s:actionerror/>来显示数据信息
