提供声明式事务; 允许用户自定义切面
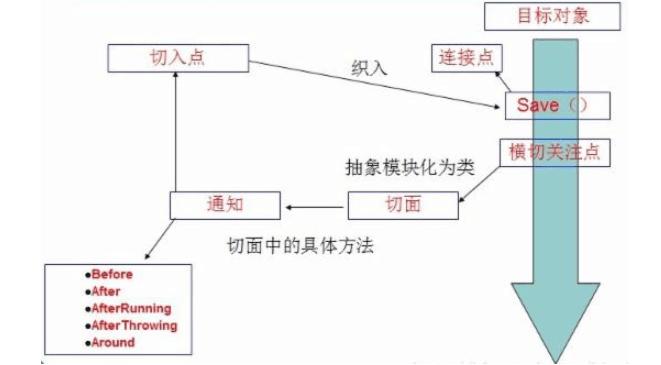
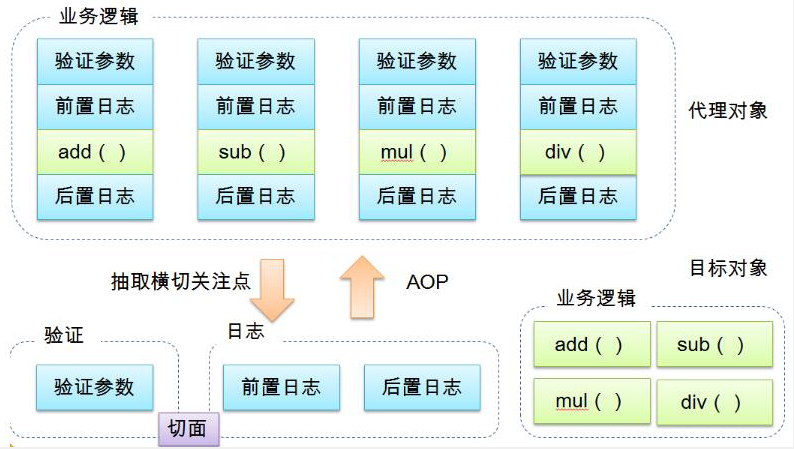
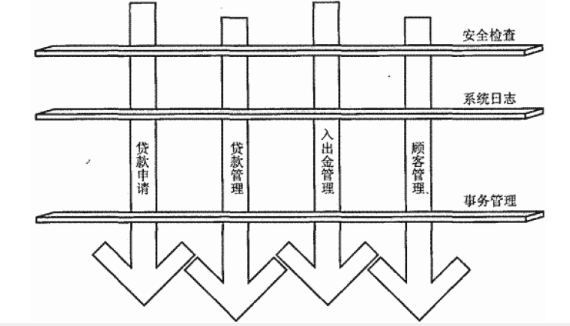
横切关注点
切面(ASPECT):横切关注点 被模块化 的特殊对象。即,它是一个类。
通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的工作。即,它是类中的一个方法。
目标(Target):被通知对象。
代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
切入点(PointCut):切面通知 执行的 “地点”的定义。
连接点(JointPoint):与切入点匹配的执行点。
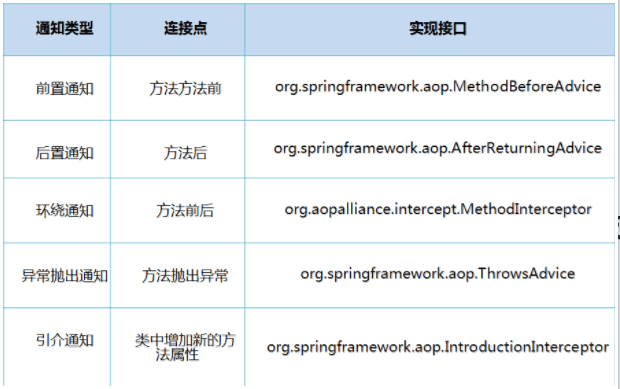
SpringAOP中,通过Advice定义横切逻辑,Spring中支持5种类型的Advice:
即 aop 在不改变原有代码的情况下 , 去增加新的功能 .
编写业务类
public interface UserService { void add(); void delete(); void update(); void query(); }
业务类的实现类
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ public void add() { System.out.println("增加了一个用户"); } public void delete() { System.out.println("删除了一个用户"); } public void update() { System.out.println("更新了一个用户"); } public void query() { System.out.println("查询了一个用户"); } }
定义日志增加类实现
package org.west.advicemethod; import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class BeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice { // method:要被执行目标对象的方法 //object :要被调用的方法的参数 //o: 目标对象 public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable { System.out.println(o.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"的方法被执行了"); } }
定义日志增加类实现
package org.west.advicemethod; import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class AfterAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice { //value:返回值 //method:被调用的方法 //args:被调用方法的参数 //target:目标对象 public void afterReturning(Object value, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的" +method.getName()+"的方法被调用了"+ "返回值是"+value); } }
编写Spring核心配置文件
注意:
写入AOP的约束:
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
用meavn导入AOP的织入包
<dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.8.9</version> </dependency>
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--注册bean--> <bean id="userService" class="org.west.service.UserServiceImpl"/> <!--注册advice类的bean--> <bean id="beforeAdvice" class="org.west.advicemethod.BeforeAdvice"/> <bean id="afterAdvice" class="org.west.advicemethod.AfterAdvice"/> <!-- 使用spring AOP切入 注意导入约束文件: xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd --> <aop:config> <!--pointcut:切入点 expression:表达式要切入的点 语法execution([类的修饰符] [类的全路径] [方法] [参数]) --> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* org.west.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <!--执行通知 增强 pointcut-ref:在那个切入点执行增强--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="afterAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:config> </beans>
编写测试类:
public class TestDemo { @Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); userService.add(); } }
spring调用的是真实对象userService
暗箱中: 动态的修改userService,在方法的前后或者其他通知的地方增加了我们的切入代码。
我们就可以实现依旧调用原来的对象,产生增加新的业务的功能;