四、操作BLOB类型字段
4.1 MySQL BLOB类型
-
MySQL中,BLOB是一个二进制大型对象,是一个可以存储大量数据的容器,它能容纳不同大小的数据。
-
插入BLOB类型的数据必须使用PreparedStatement,因为BLOB类型的数据无法使用字符串拼接写的。
-
MySQL的四种BLOB类型(除了在存储的最大信息量上不同外,他们是等同的)
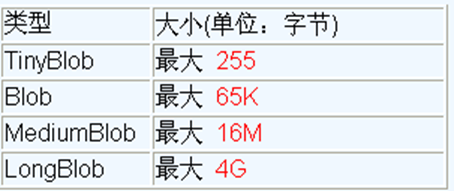
- 实际使用中根据需要存入的数据大小定义不同的BLOB类型。
- 需要注意的是:如果存储的文件过大,数据库的性能会下降。
- 如果在指定了相关的Blob类型以后,还报错:xxx too large,那么在mysql的安装目录下,找my.ini文件加上如下的配置参数: max_allowed_packet=16M。同时注意:修改了my.ini文件之后,需要重新启动mysql服务。
4.2 向数据表中插入大数据类型
@Test
public void testInsert() throws Exception {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth,photo)values(?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, "xiaoran");
ps.setObject(2, "xiaoran@qq.com");
ps.setObject(3, "2000-10-9");
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("mao.jpg"));
ps.setBlob(4, is);
ps.execute();
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, null);
}
4.3 修改数据表中的Blob类型字段
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "update customers set photo = ? where id = ?";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 填充占位符
// 操作Blob类型的变量
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("coffee.png");
ps.setBlob(1, fis);
ps.setInt(2, 25);
ps.execute();
fis.close();
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
4.4 从数据表中读取大数据类型
@Test
public void testQuery() throws Exception {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth,photo from customers where name = ?";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, "xiaoran");
InputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
//方式一:
// int id = rs.getInt(1);
// String name = rs.getString(2);
// String email = rs.getString(4);
// Date birth = rs.getDate(4);
//方式二:
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String email = rs.getString("email");
Date birth = rs.getDate("birth");
Customer customer = new Customer(id, name, email, birth);
System.out.println(customer);
Blob photo = rs.getBlob("photo");
is = photo.getBinaryStream();
fos = new FileOutputStream("maomao.jpg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
}
is.close();
fos.close();
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs);
}