面向对象
语言的分类








Python的类
定义
class ClassName: pass

class MyCalss: """A example class"""#文档字符串 x = 'abc'#类属性 def foo(self):#类属性foo,也是方法 return 'myclass'
类对象及类属性

实例化
a = MyClass() #实例化

__init__方法

class MyCalss: def __init__(self):#初始化 print('init') a = MyCalss()
![]()
实例对象


self
class Person: def __init__(self): print(id(self)) c = Person() #会调用__init__ print('p={}'.format(id(c))) #输出结果: 43079160 c=43079160

实例变量和类变量


class Person: age = 7 height = 175 def __init__(self,name,age=23): self.name = name self.age = age tom = Person('tom') jerry = Person('jerry',20) Person.age = 30 print(Person.age,tom.age,jerry.age) print(Person.__dict__,tom.__dict__,jerry.__dict__,sep=' ') Person.height += 5 print(Person.__dict__,tom.__dict__,jerry.__dict__,sep=' ') tom.height = 176 print(Person.__dict__,tom.__dict__,jerry.__dict__,sep=' ') Person.weight = 65 print(Person.__dict__['weight']) print(tom.__dict__['weight'])#KeyError
![]()


装饰一个类

#增加类变量 def add_name(name,cls): cls.NAME = name #动态增加类属性 #改进成装饰器(带参) def add_name1(name): def wrapper(cls): cls.NAME = name return cls return wrapper @add_name1('tom') class Person: AGE = 1 print(Person.NAME)

类方法和静态方法

普通函数


类方法



静态方法


方法的调用
class Person: def normal_method(): print('nomal') def method(self): print("{}'s method ".format(self)) @classmethod def class_method(cls): print('class = {0.__name__} {0}'.format(cls)) cls.HEIGHT =175 @staticmethod def static_method(): print(Person.HEIGHT) #~~~类访问~~~ print(1,Person.normal_method()) # print(2,Person.method())#报错 print(3,Person.class_method()) print(4,Person.static_method()) #~~~实例访问~~~ tom = Person() # print(5,tom.normal_method())#报错 print(6,tom.method()) print(7,tom.class_method()) print(8,tom.static_method())

访问控制
私有属性Private





一般来说,可以在内部自定义一个方法来访问私有变量。
私有变量的本质

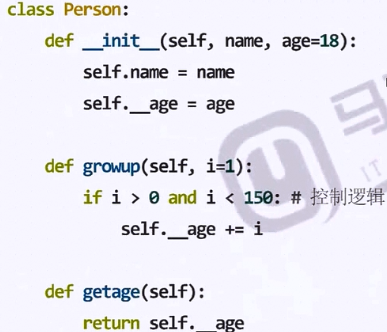




![]()
保护变量
![]()



私有方法
![]()


私有方法的本质

私有成员的总结


补丁

#test1.py from test2 import Person from test3 import get_score def monkeypatch4Person(): Person.get_score = get_score print(Person().get_score()) monkeypatch4Person() print(Person().get_score()) #输出如下: {'English': 78, 'Chinese': 86, 'History': 82} #打补丁前 {'name': 'Person', 'English': 88, 'Chinese': 90, 'History': 85} #打补丁后
#test2.py class Person: def get_score(self): ret = {'English':78,'Chinese':86,'History':82} return ret
#test3.py def get_score(self): return dict(name=self.__class__.__name__,English=88,Chinese=90,History=85)

属性装饰器

class Person: def __init__(self,chinese,english,history): self._chinese = chinese self._eng = english self.__his = history def gethis(self): return self.__his def sethis(self,value): self.__his = value def seteng(self,value): self._eng = value @property def chinese(self): return self._chinese @chinese.setter def chinese(self,value): self._chinese = value @chinese.deleter def chinese(self): # del self._chinese print('del self._chinese') #x = property(getx, setx, delx, "I'm the 'x' property.") eng = property(lambda self:self._eng,seteng) student = Person(80,90,88) print(student.chinese)#80 student.chinese = 100 print(student.chinese)#100 del student.chinese print(student.eng)#90 student.eng =110 print(student.eng)#110

对象的销毁


方法重载(overload)

重写也就是覆盖的意思,即override。
封装

练习


#1.其结构值得参考! from random import randint class RandomGenerator: def __init__(self,count=10,start=1,stop=100): self.count = count self.start = start self.stop = stop self.gen = self._generatr() def _generatr(self): while True: yield [randint(self.start,self.stop) for _ in range(self.count)] def gengerate(self,count): self.count = count return next(self.gen) rg = RandomGenerator() lst = rg.gengerate(10) print(lst)
#2 class Point: def __init__(self,x,y): self.x = x self.y = y def __repr__(self): return '{}:{}'.format(self.x,self.y) lst1 = [Point(*v) for v in zip(rg.gengerate(10),rg.gengerate(10))] print(lst1) #输出如下: [36:14, 84:20, 31:84, 68:82, 36:48, 87:67, 64:49, 8:15, 55:73, 90:75]
#3 class Car: def __init__(self,mark=None,color=None,price=None,speed=None): self._mark = mark self._color = color self._price = price self._speed = speed class CarInfo: def __init__(self): self.lst = [] def addcar(self,car:Car): self.lst.append(car) def showcarinfo(self): return self.lst
#4 class Temperature: def __init__(self,t,unit='c'): self._c = None self._f = None self._k = None if unit == 'k': self._c = self.k2c(t) self._k = t elif unit == 'f': self._c = self.f2c(t) self._f = t else: self._c = t @property def k(self): if self._k is None: self._k = self.c2k(self._c) return self._k @property def f(self): if self._f is None: self._f = self.c2f(self._c) return self._f @property def c(self): return self._c @classmethod def c2f(cls,c): return c*9/5+32 @classmethod def f2c(cls,f): return (f-32)*5/9 @classmethod def c2k(cls,c): return c+273.15 @classmethod def k2c(cls,k): return k-273.15 @classmethod def f2k(cls,f): return cls.c2k(cls.f2c(f)) @classmethod def k2f(cls,k): return cls.c2f(cls.k2c(k)) print(Temperature.c2f(40)) print(Temperature.c2k(40)) print(Temperature.f2c(104.0)) print(Temperature.f2k(104.0)) print(Temperature.k2c(313.5)) print(Temperature.k2f(313.5)) t = Temperature(40) print(t.c,t.f,t.k) t = Temperature(313.5,'k') print(t.c,t.f,t.k)
#简单购物车 class Color: RED = 0 BLUE = 1 GREEN = 2 BLACK = 3 GOLDEN = 4 OTHER = 100 class Item: def __init__(self,**kwargs): self.__info = kwargs def __repr__(self): return str(sorted(self.__info.items())) class Cart: def __init__(self): self.items = [] def additem(self,item:Item): self.items.append(item) def gatallitems(self): return self.items mycart = Cart() myphone = Item(mark='Iponhe',color=Color.GOLDEN,memory='64G') mycart.additem(myphone) mycar = Item(mark='BMW',color=Color.BLACK,memory='220/s') mycart.additem(mycar) print(mycart.gatallitems())