01.深浅拷贝
浅copy与deepcopy(What)
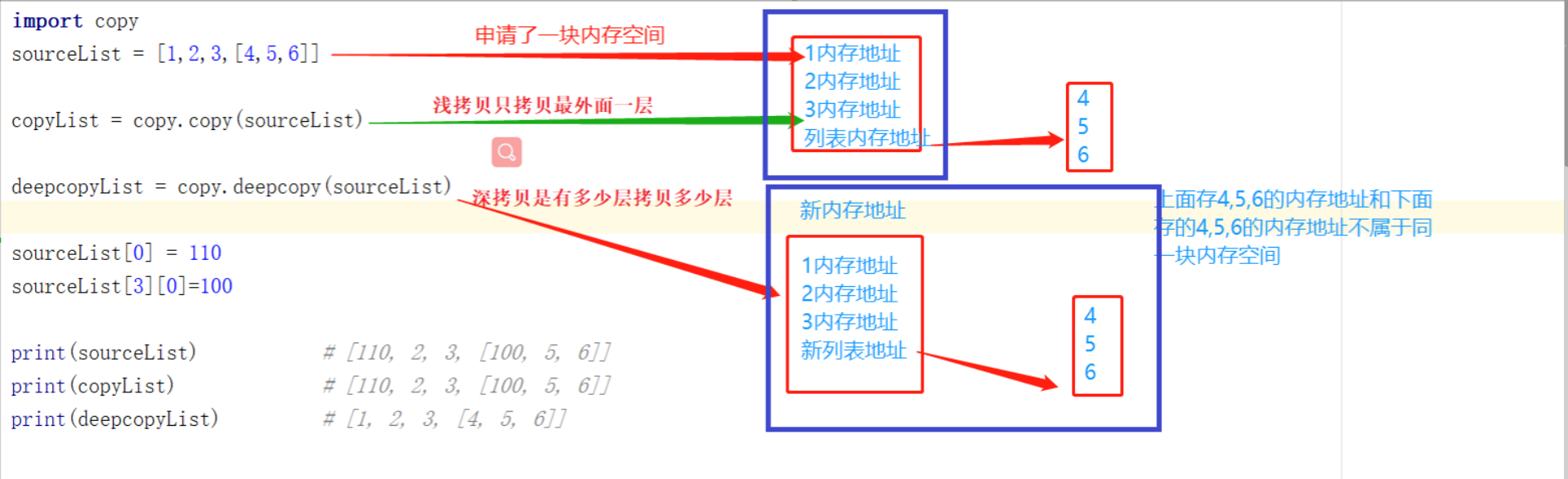
- 浅copy: 不管多么复杂的数据结构,浅拷贝都只会copy一层
- deepcopy : 深拷贝会完全复制原变量相关的所有数据,在内存中生成一套完全一样的内容,我们对这两个变量中任意一个修改都不会影响其他变量
import copy sourceList = [1,2,3,[4,5,6]] copyList = copy.copy(sourceList) deepcopyList = copy.deepcopy(sourceList) sourceList[3][0]=100 print(sourceList) # [1, 2, 3, [100, 5, 6]] print(copyList) # [1, 2, 3, [100, 5, 6]] print(deepcopyList) # [1, 2, 3, [4, 5, 6]]
02.变量及其存储
1、python的一切变量都是对象,变量的存储,采用了引用语义的方式,存储的只是一个变量的值所在的内存地址,而不是这个变量的只本身
2、不管多么复杂的数据结构,浅拷贝都只会copy一层。
理解:两个人公用一张桌子,只要桌子不变,桌子上的菜发生了变化两个人是共同感受的。
>>> str1 = 'hello' >>> str2 = str1 #1、让str1和str2变量都存储了‘hello’所在的内存地址 >>> id(str1) 22748280 >>> id(str1) 22748280 >>> #2、当str1的值变成‘new hello’后str1的值被重新赋值成'new hello'的内存地址,而str2的值依旧是‘hello’的内存地址 >>> str1 = 'new hello' >>> id(str1) 22748320 >>> id(str2) 22748280 #3、不管多么复杂的数据结构,浅拷贝都只会copy一层。 >>> sourceList = [1,2,[3,4]] >>> newList = sourceList >>> l[2][0]=100 >>> sourceList [1, 2, [100, 4]] >>> newList [1, 2, [100, 4]]
03.is和==区别
is不仅数据一样内存地址也一样
== 只判断数据和数据类型一样即可