入门拾遗
一、作用域
只要变量在内存中就能被调用!但是(函数的栈有点区别)
对于变量的作用域,执行声明并在内存中存在,如果变量在内存中存在就可以被调用。
1 if 1==1: 2 name = 'tianshuai' 3 print name
所以下面的说法是不对的:
外层变量,可以被内层变量使用
内层变量,无法被外层变量使用
二、三元运算
1 result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2
例子:
1 name = raw_input("please input your name: ") 2 if name = "tianshuai": 3 print "you are so shuai!!!" 4 else: 5 print "you are ok"
上面的例子可以用三元运算一句解决:
1 name = raw_input("please input your name: ") 2 shuai = "shuaige" if name == "tianshuai" else "is ok" 3 print shuai
注:循环可以包含循环,列表可以包含列表,元组当然也可以包含元组,字典可以包含字典!思想不要太局限!放开想!
三、python是一门什么语言
编程语言主要从以下几个角度进行分类:
编译型和解释型
静态语言和动态语言
强类型定义语言和弱类型语言
编译型和解释型:
编译型,其实他和汇编语言是一样的:也是有一个负责翻译的程序来对我们的源代码进行转换,生成相对应的可执行代码。
这个说的更专业一点,就是编辑(Complie),而负责编译的程序自然就称谓编译器(Compiler)。如果我们写的程序代码都包含在一个源
文 件中,那么通常编译之后就会生成一个可执行文件,我们就直接运行了,而对于一个比较复杂的项目,为了方便管理,我们通常把代码分散在各个原文件中,作为不 通的模块来组织。这是编译各个文件时就会生成目标文件(Objec file)而不是之前所说的可执行文件。一般一个源文件的编译都会对应一个目标文件。这些目标文件里的内容基本上已经是可执行代码了,但是由于只是整个项 目的一部分,所以我们还不能直接运行。待所有的源文件编译都大功告成,我们就可以最后把这些半成品的目标文件“打包”成一个可执行文件了,这个工作由另一 个程序负责完成,由于过程好像是把包含可执行代码的目标文件连接装配起来,所以这个操作又称为连接(Link),而负责连接的程序就叫。。。。。连接程序 (Linker)。连接程序除了连接文件之外,可能还有各种资源,图标文件啊、声音等。连接完成后,一般就可以得到我们降妖的可执行文件了。
上面我们大概介绍了编译型语言的特点,现在在看看解释性。从字面上来看“编译”和“解释”都有“翻译”的意思,他们的区别则在于翻译的时机不一样。
打个比方:如果你打算预读一本外文书,而你不知道这么外语,那么你可以找一名翻译,给他足够的时间让他从头到尾把整本书翻译好,
然后把书的母语版交给你阅读。这个过程就编译,或者你也立刻让这名翻译辅助你阅读,让他一句一句的给你翻译,如果你想往回看某个章节他也的重新给你翻译。
两 种方式:前者就相当于我们刚才说的编译型:一次把所有的代码转换成机器语言,然后写成可执行文件。
而后者就相当于我们要的节诶实行:在程序运行的前一刻, 还只有源程序而没有可执行程序;而程每执行到资源程序的某一条执行,则会有一个称之为解释程序的外壳程序,将源代码转换成二进制代码以供执行,总而言之就 是不断的解释、执行、解释、执行。。。所以解释型语言是离不开解释程序的。
由于程序总是以源代码的形式出现,因此只要有相应的解释器,一直几乎不成问题。编译型程序虽然源代码也可以执行,但前提必须针对不通的系统分别进行编译,对于复杂的工程来说,的确是一件不小的时间小号,而且何忧可能一些细节的地方还有修改源代码。
但是解释性程序省却了编译的步骤,修改调试也非常方便,编辑完毕之后即可运行,不必想编译型语言修改了小小的改动要等很长的Compiling...Linking...
不过凡是有利有弊,由于解释性程序试讲编译的过程放在执行过程中,这就决定了解释性程序注定要比编译型慢上一大截,就想几百倍的速度差距也不足为奇
但 既然编译型与解释性各有优缺点又相互对立,所以一批新星的语言都有把两者折中起来的趋势,例如Java语言虽然比较接近解释性语言的特性,但在执行之前预 先进行一次预编译,生成的代码是介于机器码和Java源代码之间的中介码,运行的时候而又JVM(Java的虚拟机平台,可视为解释器)解释执行。他即保 留了源代码的高抽象、可抑制的特点,又已完成了对源代码的大部分预编译工作,所以执行起来比“纯解释性”程序要快的多。宗旨,随着设计技术与硬件的不断发 展,编译型与解释性两种方式的界限正在不断的变模糊
静态语言和动态语言:
通常我们所说的动态语言、静态语言是指动态类型语言和静态类型语言。
1、 动态类型语言:动态类型语言是指在运行期间才去做数据类型检查的语言,也就是说,在动态类型的语言编程时,永远也不用给任何变量指定数据类型,该语言会在 第一次赋值给变量是,在内部将数据类型记录下来。Python和Ruby就是典型类型的动态类型语言,其他的各种脚本语言如VBScript也多少属于动 态类型语言。
2、静态类型语言:静态类型语言与动态类型语言刚好相反,他的数据类型是在编译期间检查的,也就是说在写程序的时候要声明所有变量的数据类型,C/C++是静态类型的典型代表,其他的静态类型语言还有C#、JAVA等
对于动态语言与静态语言的区分,套用一句比较流行的话是:Static typing when possible,dynamic typing when needed
强类型定义语言和弱类型语言
1、强类型定义语言:强制数据类型定义的语言。也就是说,一旦一个变量被指定了某个数据类型,如果不经过强制转换,那么他就永远是这个数据类型了。举个例子:如果你定义了一个整形变量a,那么程序根本不可能讲a当作字符串类型处理。强类型定义语言是类型安全的语言。
2、弱类型定义语言:数据类型可以被忽略的语言。他与强类型定义语言相反,一个变量可以赋予不同数据类型。
强类型定义语言在速度上可能略逊色与弱类型定义语言,但是他是强类型定义语言带来的严谨性能够有效便面许多错误,另外,“这么语言是不是动态语言”与“这么语言是否类型安全”之间是完全没有联系的。
例如:Python是动态语言,也是强类型定义语言(类型安全的语言);VBScript是动态语言是弱类型定义语言(类型不安全的语言);
JAVA是静态语言,是强类型定义语言(类型安全的语言)
Python基础
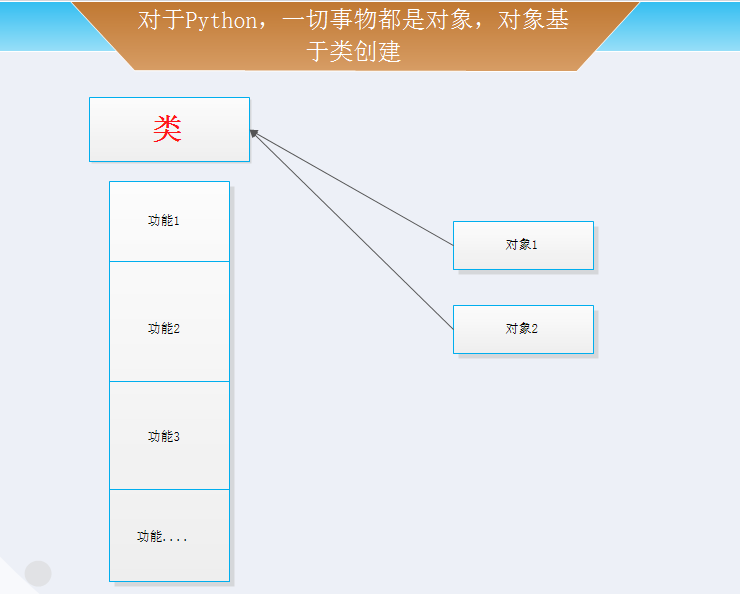
一、整数
如: 18、73、84
每一个整数都具备如下功能:

class int(object): """ int(x=0) -> int or long int(x, base=10) -> int or long Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero. If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int('0b100', base=0) """ def bit_length(self): """ 返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数 """ """ int.bit_length() -> int Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. >>> bin(37) '0b100101' >>> (37).bit_length() """ return 0 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 返回该复数的共轭复数 """ """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """ pass def __abs__(self): """ 返回绝对值 """ """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ pass def __add__(self, y): """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ pass def __and__(self, y): """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """ pass def __cmp__(self, y): """ 比较两个数大小 """ """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ pass def __coerce__(self, y): """ 强制生成一个元组 """ """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """ pass def __divmod__(self, y): """ 相除,得到商和余数组成的元组 """ """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ pass def __div__(self, y): """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """ pass def __float__(self): """ 转换为浮点类型 """ """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """ pass def __floordiv__(self, y): """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """ pass def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __getattribute__(self, name): """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 内部调用 __new__方法或创建对象时传入参数使用 """ pass def __hash__(self): """如果对象object为哈希表类型,返回对象object的哈希值。哈希值为整数。在字典查找中,哈希值用于快速比较字典的键。两个数值如果相等,则哈希值也相等。""" """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ pass def __hex__(self): """ 返回当前数的 十六进制 表示 """ """ x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """ pass def __index__(self): """ 用于切片,数字无意义 """ """ x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """ pass def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__ """ 构造方法,执行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 时,自动调用,暂时忽略 """ """ int(x=0) -> int or long int(x, base=10) -> int or long Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero. If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int('0b100', base=0) # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __int__(self): """ 转换为整数 """ """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """ pass def __invert__(self): """ x.__invert__() <==> ~x """ pass def __long__(self): """ 转换为长整数 """ """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """ pass def __lshift__(self, y): """ x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """ pass def __mod__(self, y): """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ pass def __mul__(self, y): """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """ pass def __neg__(self): """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __nonzero__(self): """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """ pass def __oct__(self): """ 返回改值的 八进制 表示 """ """ x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """ pass def __or__(self, y): """ x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """ pass def __pos__(self): """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """ pass def __pow__(self, y, z=None): """ 幂,次方 """ """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ pass def __radd__(self, y): """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """ pass def __rand__(self, y): """ x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """ pass def __rdivmod__(self, y): """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """ pass def __rdiv__(self, y): """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """ pass def __repr__(self): """转化为解释器可读取的形式 """ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __str__(self): """转换为人阅读的形式,如果没有适于人阅读的解释形式的话,则返回解释器课阅读的形式""" """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ pass def __rfloordiv__(self, y): """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """ pass def __rlshift__(self, y): """ x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """ pass def __rmod__(self, y): """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ pass def __rmul__(self, y): """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """ pass def __ror__(self, y): """ x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """ pass def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ pass def __rrshift__(self, y): """ x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """ pass def __rshift__(self, y): """ x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """ pass def __rsub__(self, y): """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ pass def __rtruediv__(self, y): """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """ pass def __rxor__(self, y): """ x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """ pass def __sub__(self, y): """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ pass def __truediv__(self, y): """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """ pass def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): """ 返回数值被截取为整形的值,在整形中无意义 """ pass def __xor__(self, y): """ x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """ pass denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 分母 = 1 """ """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 虚数,无意义 """ """the imaginary part of a complex number""" numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 分子 = 数字大小 """ """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 实属,无意义 """ """the real part of a complex number""" int
二、长整型
可能如:2147483649、9223372036854775807
每个长整型都具备如下功能:

class long(object): """ long(x=0) -> long long(x, base=10) -> long Convert a number or string to a long integer, or return 0L if no arguments are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int('0b100', base=0) 4L """ def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ long.bit_length() -> int or long Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. >>> bin(37L) '0b100101' >>> (37L).bit_length() """ return 0 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any long. """ pass def __abs__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ pass def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ pass def __and__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """ pass def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ pass def __coerce__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """ pass def __divmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ pass def __div__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """ pass def __float__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """ pass def __floordiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """ pass def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __hash__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ pass def __hex__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """ pass def __index__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """ pass def __init__(self, x=0): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ pass def __int__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """ pass def __invert__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__invert__() <==> ~x """ pass def __long__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """ pass def __lshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """ pass def __mod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ pass def __mul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """ pass def __neg__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __nonzero__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """ pass def __oct__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """ pass def __or__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """ pass def __pos__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """ pass def __pow__(self, y, z=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ pass def __radd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """ pass def __rand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """ pass def __rdivmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """ pass def __rdiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __rfloordiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """ pass def __rlshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """ pass def __rmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ pass def __rmul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """ pass def __ror__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """ pass def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ pass def __rrshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """ pass def __rshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """ pass def __rsub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ pass def __rtruediv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """ pass def __rxor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """ pass def __sizeof__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Returns size in memory, in bytes """ pass def __str__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ pass def __sub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ pass def __truediv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """ pass def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Truncating an Integral returns itself. """ pass def __xor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """ pass denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the imaginary part of a complex number""" numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the real part of a complex number""" long
三、浮点型
如:3.14、2.88
每个浮点型都具备如下功能:

class float(object): """ float(x) -> floating point number Convert a string or number to a floating point number, if possible. """ def as_integer_ratio(self): """ 获取改值的最简比 """ """ float.as_integer_ratio() -> (int, int) Return a pair of integers, whose ratio is exactly equal to the original float and with a positive denominator. Raise OverflowError on infinities and a ValueError on NaNs. >>> (10.0).as_integer_ratio() (10, 1) >>> (0.0).as_integer_ratio() (0, 1) >>> (-.25).as_integer_ratio() (-1, 4) """ pass def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self, the complex conjugate of any float. """ pass def fromhex(self, string): """ 将十六进制字符串转换成浮点型 """ """ float.fromhex(string) -> float Create a floating-point number from a hexadecimal string. >>> float.fromhex('0x1.ffffp10') 2047.984375 >>> float.fromhex('-0x1p-1074') -4.9406564584124654e-324 """ return 0.0 def hex(self): """ 返回当前值的 16 进制表示 """ """ float.hex() -> string Return a hexadecimal representation of a floating-point number. >>> (-0.1).hex() '-0x1.999999999999ap-4' >>> 3.14159.hex() '0x1.921f9f01b866ep+1' """ return "" def is_integer(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return True if the float is an integer. """ pass def __abs__(self): """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ pass def __add__(self, y): """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ pass def __coerce__(self, y): """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """ pass def __divmod__(self, y): """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ pass def __div__(self, y): """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """ pass def __eq__(self, y): """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __float__(self): """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """ pass def __floordiv__(self, y): """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """ pass def __format__(self, format_spec): """ float.__format__(format_spec) -> string Formats the float according to format_spec. """ return "" def __getattribute__(self, name): """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getformat__(self, typestr): """ float.__getformat__(typestr) -> string You probably don't want to use this function. It exists mainly to be used in Python's test suite. typestr must be 'double' or 'float'. This function returns whichever of 'unknown', 'IEEE, big-endian' or 'IEEE, little-endian' best describes the format of floating point numbers used by the C type named by typestr. """ return "" def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __ge__(self, y): """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __hash__(self): """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ pass def __init__(self, x): pass def __int__(self): """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __long__(self): """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """ pass def __lt__(self, y): """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass def __mod__(self, y): """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ pass def __mul__(self, y): """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """ pass def __neg__(self): """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __nonzero__(self): """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """ pass def __pos__(self): """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """ pass def __pow__(self, y, z=None): """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ pass def __radd__(self, y): """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """ pass def __rdivmod__(self, y): """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """ pass def __rdiv__(self, y): """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """ pass def __repr__(self): """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __rfloordiv__(self, y): """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """ pass def __rmod__(self, y): """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ pass def __rmul__(self, y): """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """ pass def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ pass def __rsub__(self, y): """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ pass def __rtruediv__(self, y): """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """ pass def __setformat__(self, typestr, fmt): """ float.__setformat__(typestr, fmt) -> None You probably don't want to use this function. It exists mainly to be used in Python's test suite. typestr must be 'double' or 'float'. fmt must be one of 'unknown', 'IEEE, big-endian' or 'IEEE, little-endian', and in addition can only be one of the latter two if it appears to match the underlying C reality. Override the automatic determination of C-level floating point type. This affects how floats are converted to and from binary strings. """ pass def __str__(self): """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ pass def __sub__(self, y): """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ pass def __truediv__(self, y): """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """ pass def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the Integral closest to x between 0 and x. """ pass imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the imaginary part of a complex number""" real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """the real part of a complex number""" float
四、字符串
如:'luotianshuai'、'wupeiqi'
每个字符串都具备如下功能:
class str(basestring): """ str(object='') -> string Return a nice string representation of the object. If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object. """ def capitalize(self): """ 首字母变大写 """ """ S.capitalize() -> string Return a copy of the string S with only its first character capitalized. """ return "" def center(self, width, fillchar=None): """ 内容居中,width:总长度;fillchar:空白处填充内容,默认无 """ """ S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> string Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space) """ return "" def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None): """ 子序列个数 """ """ S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. """ return 0 def decode(self, encoding=None, errors=None): """ 解码 """ """ S.decode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object Decodes S using the codec registered for encoding. encoding defaults to the default encoding. errors may be given to set a different error handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise a UnicodeDecodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore' and 'replace' as well as any other name registered with codecs.register_error that is able to handle UnicodeDecodeErrors. """ return object() def encode(self, encoding=None, errors=None): """ 编码,针对unicode """ """ S.encode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object Encodes S using the codec registered for encoding. encoding defaults to the default encoding. errors may be given to set a different error handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and 'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with codecs.register_error that is able to handle UnicodeEncodeErrors. """ return object() def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None): """ 是否以 xxx 结束 """ """ S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise. With optional start, test S beginning at that position. With optional end, stop comparing S at that position. suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try. """ return False def expandtabs(self, tabsize=None): """ 将tab转换成空格,默认一个tab转换成8个空格 """ """ S.expandtabs([tabsize]) -> string Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces. If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed. """ return "" def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None): """ 子序列位置,如果没找到,则返回-1 """ """ S.find(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found, such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. Return -1 on failure. """ return 0 def format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format """ 字符串格式化,动态参数,将函数式编程时细说 """ """ S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> string Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs. The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}'). """ pass def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None): """ 寻找子序列位置,如果没找到,则异常 """ S.index(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int Like S.find() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found. """ return 0 def isalnum(self): """ 是否是字母和数字 """ """ S.isalnum() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. """ return False def isalpha(self): """ 是否是字母 """ """ S.isalpha() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. """ return False def isdigit(self): """ 是否是数字 """ """ S.isdigit() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are digits and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. """ return False def islower(self): """ 是否小写 """ """ S.islower() -> bool Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is at least one cased character in S, False otherwise. """ return False def isspace(self): """ S.isspace() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are whitespace and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. """ return False def istitle(self): """ S.istitle() -> bool Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one character in S, i.e. uppercase characters may only follow uncased characters and lowercase characters only cased ones. Return False otherwise. """ return False def isupper(self): """ S.isupper() -> bool Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is at least one cased character in S, False otherwise. """ return False def join(self, iterable): """ 连接 """ """ S.join(iterable) -> string Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable. The separator between elements is S. """ return "" def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None): """ 内容左对齐,右侧填充 """ """ S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> string Return S left-justified in a string of length width. Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space). """ return "" def lower(self): """ 变小写 """ """ S.lower() -> string Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase. """ return "" def lstrip(self, chars=None): """ 移除左侧空白 """ """ S.lstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed. If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping """ return "" def partition(self, sep): """ 分割,前,中,后三部分 """ """ S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not found, return S and two empty strings. """ pass def replace(self, old, new, count=None): """ 替换 """ """ S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> string Return a copy of string S with all occurrences of substring old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is given, only the first count occurrences are replaced. """ return "" def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None): """ S.rfind(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found, such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. Return -1 on failure. """ return 0 def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None): """ S.rindex(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int Like S.rfind() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found. """ return 0 def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None): """ S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> string Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space) """ return "" def rpartition(self, sep): """ S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not found, return two empty strings and S. """ pass def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None): """ S.rsplit([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and working to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any whitespace string is a separator. """ return [] def rstrip(self, chars=None): """ S.rstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed. If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping """ return "" def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None): """ 分割, maxsplit最多分割几次 """ """ S.split([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are removed from the result. """ return [] def splitlines(self, keepends=False): """ 根据换行分割 """ """ S.splitlines(keepends=False) -> list of strings Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries. Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends is given and true. """ return [] def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None): """ 是否起始 """ """ S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise. With optional start, test S beginning at that position. With optional end, stop comparing S at that position. prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try. """ return False def strip(self, chars=None): """ 移除两段空白 """ """ S.strip([chars]) -> string or unicode Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing whitespace removed. If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping """ return "" def swapcase(self): """ 大写变小写,小写变大写 """ """ S.swapcase() -> string Return a copy of the string S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase and vice versa. """ return "" def title(self): """ S.title() -> string Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with uppercase characters, all remaining cased characters have lowercase. """ return "" def translate(self, table, deletechars=None): """ 转换,需要先做一个对应表,最后一个表示删除字符集合 intab = "aeiou" outtab = "12345" trantab = maketrans(intab, outtab) str = "this is string example....wow!!!" print str.translate(trantab, 'xm') """ """ S.translate(table [,deletechars]) -> string Return a copy of the string S, where all characters occurring in the optional argument deletechars are removed, and the remaining characters have been mapped through the given translation table, which must be a string of length 256 or None. If the table argument is None, no translation is applied and the operation simply removes the characters in deletechars. """ return "" def upper(self): """ S.upper() -> string Return a copy of the string S converted to uppercase. """ return "" def zfill(self, width): """方法返回指定长度的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。""" """ S.zfill(width) -> string Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field of the specified width. The string S is never truncated. """ return "" def _formatter_field_name_split(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def _formatter_parser(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __add__(self, y): """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ pass def __contains__(self, y): """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """ pass def __eq__(self, y): """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __format__(self, format_spec): """ S.__format__(format_spec) -> string Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec. """ return "" def __getattribute__(self, name): """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getitem__(self, y): """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __getslice__(self, i, j): """ x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] Use of negative indices is not supported. """ pass def __ge__(self, y): """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __hash__(self): """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ pass def __init__(self, string=''): # known special case of str.__init__ """ str(object='') -> string Return a nice string representation of the object. If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object. # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __len__(self): """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __lt__(self, y): """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass def __mod__(self, y): """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ pass def __mul__(self, n): """ x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __repr__(self): """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __rmod__(self, y): """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ pass def __rmul__(self, n): """ x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """ pass def __sizeof__(self): """ S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """ pass def __str__(self): """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ pass
五、列表
如:['shuaige','tianshuai']、['wupeiqi', 'alex']
每个列表都具备如下功能:

class list(object): """ list() -> new empty list list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items """ def append(self, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.append(object) -- append object to end """ pass def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """ return 0 def extend(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.extend(iterable) -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable """ pass def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. Raises ValueError if the value is not present. """ return 0 def insert(self, index, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index """ pass def pop(self, index=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last). Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range. """ pass def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.remove(value) -- remove first occurrence of value. Raises ValueError if the value is not present. """ pass def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* """ pass def sort(self, cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) -- stable sort *IN PLACE*; cmp(x, y) -> -1, 0, 1 """ pass def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ pass def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """ pass def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """ pass def __delslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__delslice__(i, j) <==> del x[i:j] Use of negative indices is not supported. """ pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ pass def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] Use of negative indices is not supported. """ pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __iadd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iadd__(y) <==> x+=y """ pass def __imul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__imul__(y) <==> x*=y """ pass def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of list.__init__ """ list() -> new empty list list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __reversed__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the list """ pass def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """ pass def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """ pass def __setslice__(self, i, j, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__setslice__(i, j, y) <==> x[i:j]=y Use of negative indices is not supported. """ pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ L.__sizeof__() -- size of L in memory, in bytes """ pass __hash__ = None list
六、元组
如:('shuai','ge','tianshuai')、('wupeiqi', 'alex')
每个元组都具备如下功能:

class tuple(object): """ tuple() -> empty tuple tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object. """ def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """ return 0 def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. Raises ValueError if the value is not present. """ return 0 def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ pass def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """ pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] Use of negative indices is not supported. """ pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __hash__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ pass def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of tuple.__init__ """ tuple() -> empty tuple tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object. # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """ pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__sizeof__() -- size of T in memory, in bytes """ pass tuple
七、字典
如:{'name': 'luotianshuai', 'age': 18} 、{'host': '2.2.2.2', 'port': 80]}
ps:循环时,默认循环key
每个字典都具备如下功能:

class dict(object): """ dict() -> new empty dictionary dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's (key, value) pairs dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via: d = {} for k, v in iterable: d[k] = v dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2) """ def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 清除内容 """ """ D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D. """ pass def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 浅拷贝 """ """ D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D """ pass @staticmethod # known case def fromkeys(S, v=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ dict.fromkeys(S[,v]) -> New dict with keys from S and values equal to v. v defaults to None. """ pass def get(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 根据key获取值,d是默认值 """ """ D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None. """ pass def has_key(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 是否有key """ """ D.has_key(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """ return False def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 所有项的列表形式 """ """ D.items() -> list of D's (key, value) pairs, as 2-tuples """ return [] def iteritems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 项可迭代 """ """ D.iteritems() -> an iterator over the (key, value) items of D """ pass def iterkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ key可迭代 """ """ D.iterkeys() -> an iterator over the keys of D """ pass def itervalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ value可迭代 """ """ D.itervalues() -> an iterator over the values of D """ pass def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 所有的key列表 """ """ D.keys() -> list of D's keys """ return [] def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 获取并在字典中移除 """ """ D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value. If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised """ pass def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 获取并在字典中移除 """ """ D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a 2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty. """ pass def setdefault(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 如果key不存在,则创建,如果存在,则返回已存在的值且不修改 """ """ D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D """ pass def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update """ 更新 {'name':'alex', 'age': 18000} [('name','sbsbsb'),] """ """ D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F. If E present and has a .keys() method, does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k] If E present and lacks .keys() method, does: for (k, v) in E: D[k] = v In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k] """ pass def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 所有的值 """ """ D.values() -> list of D's values """ return [] def viewitems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 所有项,只是将内容保存至view对象中 """ """ D.viewitems() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items """ pass def viewkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.viewkeys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys """ pass def viewvalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.viewvalues() -> an object providing a view on D's values """ pass def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ pass def __contains__(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.__contains__(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """ return False def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """ pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __init__(self, seq=None, **kwargs): # known special case of dict.__init__ """ dict() -> new empty dictionary dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's (key, value) pairs dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via: d = {} for k, v in iterable: d[k] = v dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2) # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """ pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes """ pass __hash__ = None dict
练习:
1 练习:元素分类 2 有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。 3 即: {'k1': 大于66 , 'k2': 小于66}
回答:
a=[11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] dict1={'k1':[],'k2':[]} for i in a: if i >66: dict1['k1'].append(i) else: dict1['k2'].append(i) print dict1 最好的是用下面的方法来动态的扩展字典: a=[11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] dict1={} #动态的增加字典 for i in a: if i >66: if 'k1' in dict1.keys(): dict1['k1'].append(i) else: dict1['k1'] = [i,] else: if 'k2' in dict1.keys(): dict1['k2'].append(i) else: dict1['k2'] = [i,] print dict1
八、set集合
set是一个无序且不重复的元素集合

class set(object): """ set() -> new empty set object set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements. """ def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 添加 """ """ Add an element to a set. This has no effect if the element is already present. """ pass def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements from this set. """ pass def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a shallow copy of a set. """ pass def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.) """ pass def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 删除当前set中的所有包含在 new set 里的元素 """ """ Remove all elements of another set from this set. """ pass def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 移除元素 """ """ Remove an element from a set if it is a member. If the element is not a member, do nothing. """ pass def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 取交集,新创建一个set """ """ Return the intersection of two or more sets as a new set. (i.e. elements that are common to all of the sets.) """ pass def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 取交集,修改原来set """ """ Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. """ pass def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 如果没有交集,返回true """ """ Return True if two sets have a null intersection. """ pass def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 是否是子集 """ """ Report whether another set contains this set. """ pass def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 是否是父集 """ """ Report whether this set contains another set. """ pass def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 移除 """ """ Remove and return an arbitrary set element. Raises KeyError if the set is empty. """ pass def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 移除 """ """ Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. """ pass def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 差集,创建新对象""" """ Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.) """ pass def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 差集,改变原来 """ """ Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. """ pass def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 并集 """ """ Return the union of sets as a new set. (i.e. all elements that are in either set.) """ pass def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 更新 """ """ Update a set with the union of itself and others. """ pass def __and__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """ pass def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ pass def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x. """ pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __iand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iand__(y) <==> x&=y """ pass def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of set.__init__ """ set() -> new empty set object set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements. # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __ior__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ior__(y) <==> x|=y """ pass def __isub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__isub__(y) <==> x-=y """ pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ pass def __ixor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ixor__(y) <==> x^=y """ pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __or__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """ pass def __rand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """ pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return state information for pickling. """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __ror__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """ pass def __rsub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ pass def __rxor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """ pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """ pass def __sub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ pass def __xor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """ pass __hash__ = None set
练习:
1 练习:寻找差异 2 # 数据库中原有 3 old_dict = { 4 "#1":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 }, 5 "#2":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 } 6 "#3":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 } 7 } 8 9 # cmdb 新汇报的数据 10 new_dict = { 11 "#1":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 800 }, 12 "#3":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 } 13 "#4":{ 'hostname':c2, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 } 14 } 15 16 需要删除:? 17 需要新建:? 18 需要更新:? 注意:无需考虑内部元素是否改变,只要原来存在,新汇报也存在,就是需要更新
回答:
#!/usr/bin/env python #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- old_dict = { "#1":{ 'hostname':'c1', 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 }, "#2":{ 'hostname':'c1', 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 }, "#3":{ 'hostname':'c1', 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 } } # cmdb 新汇报的数据 new_dict = { "#1":{ 'hostname':'c1', 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 800 }, "#3":{ 'hostname':'c1', 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 }, "#4":{ 'hostname':'c2', 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 } } for k in new_dict: old_dict[k] = new_dict[k] print old_dict #也可以用update old_dict.update(new_dict)
九、collection系列
1、计数器(counter)
Counter是对字典类型的补充,用于追踪值的出现次数。
ps:具备字典的所有功能 + 自己的功能
1 c = Counter('abcdeabcdabcaba') 2 print c 3 输出:Counter({'a': 5, 'b': 4, 'c': 3, 'd': 2, 'e': 1})

1 ######################################################################## 2 ### Counter 3 ######################################################################## 4 5 class Counter(dict): 6 '''Dict subclass for counting hashable items. Sometimes called a bag 7 or multiset. Elements are stored as dictionary keys and their counts 8 are stored as dictionary values. 9 10 >>> c = Counter('abcdeabcdabcaba') # count elements from a string 11 12 >>> c.most_common(3) # three most common elements 13 [('a', 5), ('b', 4), ('c', 3)] 14 >>> sorted(c) # list all unique elements 15 ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] 16 >>> ''.join(sorted(c.elements())) # list elements with repetitions 17 'aaaaabbbbcccdde' 18 >>> sum(c.values()) # total of all counts 19 20 >>> c['a'] # count of letter 'a' 21 >>> for elem in 'shazam': # update counts from an iterable 22 ... c[elem] += 1 # by adding 1 to each element's count 23 >>> c['a'] # now there are seven 'a' 24 >>> del c['b'] # remove all 'b' 25 >>> c['b'] # now there are zero 'b' 26 27 >>> d = Counter('simsalabim') # make another counter 28 >>> c.update(d) # add in the second counter 29 >>> c['a'] # now there are nine 'a' 30 31 >>> c.clear() # empty the counter 32 >>> c 33 Counter() 34 35 Note: If a count is set to zero or reduced to zero, it will remain 36 in the counter until the entry is deleted or the counter is cleared: 37 38 >>> c = Counter('aaabbc') 39 >>> c['b'] -= 2 # reduce the count of 'b' by two 40 >>> c.most_common() # 'b' is still in, but its count is zero 41 [('a', 3), ('c', 1), ('b', 0)] 42 43 ''' 44 # References: 45 # http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiset 46 # http://www.gnu.org/software/smalltalk/manual-base/html_node/Bag.html 47 # http://www.demo2s.com/Tutorial/Cpp/0380__set-multiset/Catalog0380__set-multiset.htm 48 # http://code.activestate.com/recipes/259174/ 49 # Knuth, TAOCP Vol. II section 4.6.3 50 51 def __init__(self, iterable=None, **kwds): 52 '''Create a new, empty Counter object. And if given, count elements 53 from an input iterable. Or, initialize the count from another mapping 54 of elements to their counts. 55 56 >>> c = Counter() # a new, empty counter 57 >>> c = Counter('gallahad') # a new counter from an iterable 58 >>> c = Counter({'a': 4, 'b': 2}) # a new counter from a mapping 59 >>> c = Counter(a=4, b=2) # a new counter from keyword args 60 61 ''' 62 super(Counter, self).__init__() 63 self.update(iterable, **kwds) 64 65 def __missing__(self, key): 66 """ 对于不存在的元素,返回计数器为0 """ 67 'The count of elements not in the Counter is zero.' 68 # Needed so that self[missing_item] does not raise KeyError 69 return 0 70 71 def most_common(self, n=None): 72 """ 数量大于等n的所有元素和计数器 """ 73 '''List the n most common elements and their counts from the most 74 common to the least. If n is None, then list all element counts. 75 76 >>> Counter('abcdeabcdabcaba').most_common(3) 77 [('a', 5), ('b', 4), ('c', 3)] 78 79 ''' 80 # Emulate Bag.sortedByCount from Smalltalk 81 if n is None: 82 return sorted(self.iteritems(), key=_itemgetter(1), reverse=True) 83 return _heapq.nlargest(n, self.iteritems(), key=_itemgetter(1)) 84 85 def elements(self): 86 """ 计数器中的所有元素,注:此处非所有元素集合,而是包含所有元素集合的迭代器 """ 87 '''Iterator over elements repeating each as many times as its count. 88 89 >>> c = Counter('ABCABC') 90 >>> sorted(c.elements()) 91 ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C'] 92 93 # Knuth's example for prime factors of 1836: 2**2 * 3**3 * 17**1 94 >>> prime_factors = Counter({2: 2, 3: 3, 17: 1}) 95 >>> product = 1 96 >>> for factor in prime_factors.elements(): # loop over factors 97 ... product *= factor # and multiply them 98 >>> product 99 100 Note, if an element's count has been set to zero or is a negative 101 number, elements() will ignore it. 102 103 ''' 104 # Emulate Bag.do from Smalltalk and Multiset.begin from C++. 105 return _chain.from_iterable(_starmap(_repeat, self.iteritems())) 106 107 # Override dict methods where necessary 108 109 @classmethod 110 def fromkeys(cls, iterable, v=None): 111 # There is no equivalent method for counters because setting v=1 112 # means that no element can have a count greater than one. 113 raise NotImplementedError( 114 'Counter.fromkeys() is undefined. Use Counter(iterable) instead.') 115 116 def update(self, iterable=None, **kwds): 117 """ 更新计数器,其实就是增加;如果原来没有,则新建,如果有则加一 """ 118 '''Like dict.update() but add counts instead of replacing them. 119 120 Source can be an iterable, a dictionary, or another Counter instance. 121 122 >>> c = Counter('which') 123 >>> c.update('witch') # add elements from another iterable 124 >>> d = Counter('watch') 125 >>> c.update(d) # add elements from another counter 126 >>> c['h'] # four 'h' in which, witch, and watch 127 128 ''' 129 # The regular dict.update() operation makes no sense here because the 130 # replace behavior results in the some of original untouched counts 131 # being mixed-in with all of the other counts for a mismash that 132 # doesn't have a straight-forward interpretation in most counting 133 # contexts. Instead, we implement straight-addition. Both the inputs 134 # and outputs are allowed to contain zero and negative counts. 135 136 if iterable is not None: 137 if isinstance(iterable, Mapping): 138 if self: 139 self_get = self.get 140 for elem, count in iterable.iteritems(): 141 self[elem] = self_get(elem, 0) + count 142 else: 143 super(Counter, self).update(iterable) # fast path when counter is empty 144 else: 145 self_get = self.get 146 for elem in iterable: 147 self[elem] = self_get(elem, 0) + 1 148 if kwds: 149 self.update(kwds) 150 151 def subtract(self, iterable=None, **kwds): 152 """ 相减,原来的计数器中的每一个元素的数量减去后添加的元素的数量 """ 153 '''Like dict.update() but subtracts counts instead of replacing them. 154 Counts can be reduced below zero. Both the inputs and outputs are 155 allowed to contain zero and negative counts. 156 157 Source can be an iterable, a dictionary, or another Counter instance. 158 159 >>> c = Counter('which') 160 >>> c.subtract('witch') # subtract elements from another iterable 161 >>> c.subtract(Counter('watch')) # subtract elements from another counter 162 >>> c['h'] # 2 in which, minus 1 in witch, minus 1 in watch 163 >>> c['w'] # 1 in which, minus 1 in witch, minus 1 in watch 164 -1 165 166 ''' 167 if iterable is not None: 168 self_get = self.get 169 if isinstance(iterable, Mapping): 170 for elem, count in iterable.items(): 171 self[elem] = self_get(elem, 0) - count 172 else: 173 for elem in iterable: 174 self[elem] = self_get(elem, 0) - 1 175 if kwds: 176 self.subtract(kwds) 177 178 def copy(self): 179 """ 拷贝 """ 180 'Return a shallow copy.' 181 return self.__class__(self) 182 183 def __reduce__(self): 184 """ 返回一个元组(类型,元组) """ 185 return self.__class__, (dict(self),) 186 187 def __delitem__(self, elem): 188 """ 删除元素 """ 189 'Like dict.__delitem__() but does not raise KeyError for missing values.' 190 if elem in self: 191 super(Counter, self).__delitem__(elem) 192 193 def __repr__(self): 194 if not self: 195 return '%s()' % self.__class__.__name__ 196 items = ', '.join(map('%r: %r'.__mod__, self.most_common())) 197 return '%s({%s})' % (self.__class__.__name__, items) 198 199 # Multiset-style mathematical operations discussed in: 200 # Knuth TAOCP Volume II section 4.6.3 exercise 19 201 # and at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiset 202 # 203 # Outputs guaranteed to only include positive counts. 204 # 205 # To strip negative and zero counts, add-in an empty counter: 206 # c += Counter() 207 208 def __add__(self, other): 209 '''Add counts from two counters. 210 211 >>> Counter('abbb') + Counter('bcc') 212 Counter({'b': 4, 'c': 2, 'a': 1}) 213 214 ''' 215 if not isinstance(other, Counter): 216 return NotImplemented 217 result = Counter() 218 for elem, count in self.items(): 219 newcount = count + other[elem] 220 if newcount > 0: 221 result[elem] = newcount 222 for elem, count in other.items(): 223 if elem not in self and count > 0: 224 result[elem] = count 225 return result 226 227 def __sub__(self, other): 228 ''' Subtract count, but keep only results with positive counts. 229 230 >>> Counter('abbbc') - Counter('bccd') 231 Counter({'b': 2, 'a': 1}) 232 233 ''' 234 if not isinstance(other, Counter): 235 return NotImplemented 236 result = Counter() 237 for elem, count in self.items(): 238 newcount = count - other[elem] 239 if newcount > 0: 240 result[elem] = newcount 241 for elem, count in other.items(): 242 if elem not in self and count < 0: 243 result[elem] = 0 - count 244 return result 245 246 def __or__(self, other): 247 '''Union is the maximum of value in either of the input counters. 248 249 >>> Counter('abbb') | Counter('bcc') 250 Counter({'b': 3, 'c': 2, 'a': 1}) 251 252 ''' 253 if not isinstance(other, Counter): 254 return NotImplemented 255 result = Counter() 256 for elem, count in self.items(): 257 other_count = other[elem] 258 newcount = other_count if count < other_count else count 259 if newcount > 0: 260 result[elem] = newcount 261 for elem, count in other.items(): 262 if elem not in self and count > 0: 263 result[elem] = count 264 return result 265 266 def __and__(self, other): 267 ''' Intersection is the minimum of corresponding counts. 268 269 >>> Counter('abbb') & Counter('bcc') 270 Counter({'b': 1}) 271 272 ''' 273 if not isinstance(other, Counter): 274 return NotImplemented 275 result = Counter() 276 for elem, count in self.items(): 277 other_count = other[elem] 278 newcount = count if count < other_count else other_count 279 if newcount > 0: 280 result[elem] = newcount 281 return result 282 283 Counter 284 285 Counter
2、有序字典(orderedDict )
orderdDict是对字典类型的补充,他记住了字典元素添加的顺序

class OrderedDict(dict): 'Dictionary that remembers insertion order' # An inherited dict maps keys to values. # The inherited dict provides __getitem__, __len__, __contains__, and get. # The remaining methods are order-aware. # Big-O running times for all methods are the same as regular dictionaries. # The internal self.__map dict maps keys to links in a doubly linked list. # The circular doubly linked list starts and ends with a sentinel element. # The sentinel element never gets deleted (this simplifies the algorithm). # Each link is stored as a list of length three: [PREV, NEXT, KEY]. def __init__(self, *args, **kwds): '''Initialize an ordered dictionary. The signature is the same as regular dictionaries, but keyword arguments are not recommended because their insertion order is arbitrary. ''' if len(args) > 1: raise TypeError('expected at most 1 arguments, got %d' % len(args)) try: self.__root except AttributeError: self.__root = root = [] # sentinel node root[:] = [root, root, None] self.__map = {} self.__update(*args, **kwds) def __setitem__(self, key, value, dict_setitem=dict.__setitem__): 'od.__setitem__(i, y) <==> od[i]=y' # Setting a new item creates a new link at the end of the linked list, # and the inherited dictionary is updated with the new key/value pair. if key not in self: root = self.__root last = root[0] last[1] = root[0] = self.__map[key] = [last, root, key] return dict_setitem(self, key, value) def __delitem__(self, key, dict_delitem=dict.__delitem__): 'od.__delitem__(y) <==> del od[y]' # Deleting an existing item uses self.__map to find the link which gets # removed by updating the links in the predecessor and successor nodes. dict_delitem(self, key) link_prev, link_next, _ = self.__map.pop(key) link_prev[1] = link_next # update link_prev[NEXT] link_next[0] = link_prev # update link_next[PREV] def __iter__(self): 'od.__iter__() <==> iter(od)' # Traverse the linked list in order. root = self.__root curr = root[1] # start at the first node while curr is not root: yield curr[2] # yield the curr[KEY] curr = curr[1] # move to next node def __reversed__(self): 'od.__reversed__() <==> reversed(od)' # Traverse the linked list in reverse order. root = self.__root curr = root[0] # start at the last node while curr is not root: yield curr[2] # yield the curr[KEY] curr = curr[0] # move to previous node def clear(self): 'od.clear() -> None. Remove all items from od.' root = self.__root root[:] = [root, root, None] self.__map.clear() dict.clear(self) # -- the following methods do not depend on the internal structure -- def keys(self): 'od.keys() -> list of keys in od' return list(self) def values(self): 'od.values() -> list of values in od' return [self[key] for key in self] def items(self): 'od.items() -> list of (key, value) pairs in od' return [(key, self[key]) for key in self] def iterkeys(self): 'od.iterkeys() -> an iterator over the keys in od' return iter(self) def itervalues(self): 'od.itervalues -> an iterator over the values in od' for k in self: yield self[k] def iteritems(self): 'od.iteritems -> an iterator over the (key, value) pairs in od' for k in self: yield (k, self[k]) update = MutableMapping.update __update = update # let subclasses override update without breaking __init__ __marker = object() def pop(self, key, default=__marker): '''od.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value. If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised. ''' if key in self: result = self[key] del self[key] return result if default is self.__marker: raise KeyError(key) return default def setdefault(self, key, default=None): 'od.setdefault(k[,d]) -> od.get(k,d), also set od[k]=d if k not in od' if key in self: return self[key] self[key] = default return default def popitem(self, last=True): '''od.popitem() -> (k, v), return and remove a (key, value) pair. Pairs are returned in LIFO order if last is true or FIFO order if false. ''' if not self: raise KeyError('dictionary is empty') key = next(reversed(self) if last else iter(self)) value = self.pop(key) return key, value def __repr__(self, _repr_running={}): 'od.__repr__() <==> repr(od)' call_key = id(self), _get_ident() if call_key in _repr_running: return '...' _repr_running[call_key] = 1 try: if not self: return '%s()' % (self.__class__.__name__,) return '%s(%r)' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.items()) finally: del _repr_running[call_key] def __reduce__(self): 'Return state information for pickling' items = [[k, self[k]] for k in self] inst_dict = vars(self).copy() for k in vars(OrderedDict()): inst_dict.pop(k, None) if inst_dict: return (self.__class__, (items,), inst_dict) return self.__class__, (items,) def copy(self): 'od.copy() -> a shallow copy of od' return self.__class__(self) @classmethod def fromkeys(cls, iterable, value=None): '''OD.fromkeys(S[, v]) -> New ordered dictionary with keys from S. If not specified, the value defaults to None. ''' self = cls() for key in iterable: self[key] = value return self def __eq__(self, other): '''od.__eq__(y) <==> od==y. Comparison to another OD is order-sensitive while comparison to a regular mapping is order-insensitive. ''' if isinstance(other, OrderedDict): return dict.__eq__(self, other) and all(_imap(_eq, self, other)) return dict.__eq__(self, other) def __ne__(self, other): 'od.__ne__(y) <==> od!=y' return not self == other # -- the following methods support python 3.x style dictionary views -- def viewkeys(self): "od.viewkeys() -> a set-like object providing a view on od's keys" return KeysView(self) def viewvalues(self): "od.viewvalues() -> an object providing a view on od's values" return ValuesView(self) def viewitems(self): "od.viewitems() -> a set-like object providing a view on od's items" return ItemsView(self) OrderedDict
3、默认字典(defaultdict)
学前需求:
1 有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。 2 即: {'k1': 大于66 , 'k2': 小于66}

values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] my_dict = {} for value in values: if value>66: if my_dict.has_key('k1'): my_dict['k1'].append(value) else: my_dict['k1'] = [value] else: if my_dict.has_key('k2'): my_dict['k2'].append(value) else: my_dict['k2'] = [value] 原生字典解决方法

from collections import defaultdict values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] my_dict = defaultdict(list) for value in values: if value>66: my_dict['k1'].append(value) else: my_dict['k2'].append(value) defaultdict字典解决方法
defaultdict是对字典的类型的补充,他默认给字典的值设置了一个类型。

class defaultdict(dict): """ defaultdict(default_factory[, ...]) --> dict with default factory The default factory is called without arguments to produce a new value when a key is not present, in __getitem__ only. A defaultdict compares equal to a dict with the same items. All remaining arguments are treated the same as if they were passed to the dict constructor, including keyword arguments. """ def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D. """ pass def __copy__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D. """ pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __init__(self, default_factory=None, **kwargs): # known case of _collections.defaultdict.__init__ """ defaultdict(default_factory[, ...]) --> dict with default factory The default factory is called without arguments to produce a new value when a key is not present, in __getitem__ only. A defaultdict compares equal to a dict with the same items. All remaining arguments are treated the same as if they were passed to the dict constructor, including keyword arguments. # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __missing__(self, key): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ __missing__(key) # Called by __getitem__ for missing key; pseudo-code: if self.default_factory is None: raise KeyError((key,)) self[key] = value = self.default_factory() return value """ pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return state information for pickling. """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass default_factory = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """Factory for default value called by __missing__().""" defaultdict
4、可命名元组(namedtuple)
根据nametuple可以创建一个包含tuple所有功能以及其他功能的类型。
1 import collections 2 3 Mytuple = collections.namedtuple('Mytuple',['x', 'y', 'z'])

class Mytuple(__builtin__.tuple) | Mytuple(x, y) | | Method resolution order: | Mytuple | __builtin__.tuple | __builtin__.object | | Methods defined here: | | __getnewargs__(self) | Return self as a plain tuple. Used by copy and pickle. | | __getstate__(self) | Exclude the OrderedDict from pickling | | __repr__(self) | Return a nicely formatted representation string | | _asdict(self) | Return a new OrderedDict which maps field names to their values | | _replace(_self, **kwds) | Return a new Mytuple object replacing specified fields with new values | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Class methods defined here: | | _make(cls, iterable, new=<built-in method __new__ of type object>, len=<built-in function len>) from __builtin__.type | Make a new Mytuple object from a sequence or iterable | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Static methods defined here: | | __new__(_cls, x, y) | Create new instance of Mytuple(x, y) | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data descriptors defined here: | | __dict__ | Return a new OrderedDict which maps field names to their values | | x | Alias for field number 0 | | y | Alias for field number 1 | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Data and other attributes defined here: | | _fields = ('x', 'y') | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | Methods inherited from __builtin__.tuple: | | __add__(...) | x.__add__(y) <==> x+y | | __contains__(...) | x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x | | __eq__(...) | x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y | | __ge__(...) | x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y | | __getattribute__(...) | x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name | | __getitem__(...) | x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] | | __getslice__(...) | x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j] | | Use of negative indices is not supported. | | __gt__(...) | x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y | | __hash__(...) | x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) | | __iter__(...) | x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) | | __le__(...) | x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y | | __len__(...) | x.__len__() <==> len(x) | | __lt__(...) | x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y | | __mul__(...) | x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n | | __ne__(...) | x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y | | __rmul__(...) | x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x | | __sizeof__(...) | T.__sizeof__() -- size of T in memory, in bytes | | count(...) | T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value | | index(...) | T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. | Raises ValueError if the value is not present. Mytuple Mytuple
5、双向队列(deque)
一个线程安全的双向队列

class deque(object): """ deque([iterable[, maxlen]]) --> deque object Build an ordered collection with optimized access from its endpoints. """ def append(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Add an element to the right side of the deque. """ pass def appendleft(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Add an element to the left side of the deque. """ pass def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements from the deque. """ pass def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """ return 0 def extend(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Extend the right side of the deque with elements from the iterable """ pass def extendleft(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Extend the left side of the deque with elements from the iterable """ pass def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove and return the rightmost element. """ pass def popleft(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove and return the leftmost element. """ pass def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.remove(value) -- remove first occurrence of value. """ pass def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* """ pass def rotate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Rotate the deque n steps to the right (default n=1). If n is negative, rotates left. """ pass def __copy__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a shallow copy of a deque. """ pass def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """ pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ pass def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """ pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ pass def __iadd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iadd__(y) <==> x+=y """ pass def __init__(self, iterable=(), maxlen=None): # known case of _collections.deque.__init__ """ deque([iterable[, maxlen]]) --> deque object Build an ordered collection with optimized access from its endpoints. # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """ pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """ pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return state information for pickling. """ pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ pass def __reversed__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the deque """ pass def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """ pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ D.__sizeof__() -- size of D in memory, in bytes """ pass maxlen = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """maximum size of a deque or None if unbounded""" __hash__ = None deque
注:既然有双向队列,也有单项队列(先进先出 FIFO )

class Queue: """Create a queue object with a given maximum size. If maxsize is <= 0, the queue size is infinite. """ def __init__(self, maxsize=0): self.maxsize = maxsize self._init(maxsize) # mutex must be held whenever the queue is mutating. All methods # that acquire mutex must release it before returning. mutex # is shared between the three conditions, so acquiring and # releasing the conditions also acquires and releases mutex. self.mutex = _threading.Lock() # Notify not_empty whenever an item is added to the queue; a # thread waiting to get is notified then. self.not_empty = _threading.Condition(self.mutex) # Notify not_full whenever an item is removed from the queue; # a thread waiting to put is notified then. self.not_full = _threading.Condition(self.mutex) # Notify all_tasks_done whenever the number of unfinished tasks # drops to zero; thread waiting to join() is notified to resume self.all_tasks_done = _threading.Condition(self.mutex) self.unfinished_tasks = 0 def task_done(self): """Indicate that a formerly enqueued task is complete. Used by Queue consumer threads. For each get() used to fetch a task, a subsequent call to task_done() tells the queue that the processing on the task is complete. If a join() is currently blocking, it will resume when all items have been processed (meaning that a task_done() call was received for every item that had been put() into the queue). Raises a ValueError if called more times than there were items placed in the queue. """ self.all_tasks_done.acquire() try: unfinished = self.unfinished_tasks - 1 if unfinished <= 0: if unfinished < 0: raise ValueError('task_done() called too many times') self.all_tasks_done.notify_all() self.unfinished_tasks = unfinished finally: self.all_tasks_done.release() def join(self): """Blocks until all items in the Queue have been gotten and processed. The count of unfinished tasks goes up whenever an item is added to the queue. The count goes down whenever a consumer thread calls task_done() to indicate the item was retrieved and all work on it is complete. When the count of unfinished tasks drops to zero, join() unblocks. """ self.all_tasks_done.acquire() try: while self.unfinished_tasks: self.all_tasks_done.wait() finally: self.all_tasks_done.release() def qsize(self): """Return the approximate size of the queue (not reliable!).""" self.mutex.acquire() n = self._qsize() self.mutex.release() return n def empty(self): """Return True if the queue is empty, False otherwise (not reliable!).""" self.mutex.acquire() n = not self._qsize() self.mutex.release() return n def full(self): """Return True if the queue is full, False otherwise (not reliable!).""" self.mutex.acquire() n = 0 < self.maxsize == self._qsize() self.mutex.release() return n def put(self, item, block=True, timeout=None): """Put an item into the queue. If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default), block if necessary until a free slot is available. If 'timeout' is a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises the Full exception if no free slot was available within that time. Otherwise ('block' is false), put an item on the queue if a free slot is immediately available, else raise the Full exception ('timeout' is ignored in that case). """ self.not_full.acquire() try: if self.maxsize > 0: if not block: if self._qsize() == self.maxsize: raise Full elif timeout is None: while self._qsize() == self.maxsize: self.not_full.wait() elif timeout < 0: raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number") else: endtime = _time() + timeout while self._qsize() == self.maxsize: remaining = endtime - _time() if remaining <= 0.0: raise Full self.not_full.wait(remaining) self._put(item) self.unfinished_tasks += 1 self.not_empty.notify() finally: self.not_full.release() def put_nowait(self, item): """Put an item into the queue without blocking. Only enqueue the item if a free slot is immediately available. Otherwise raise the Full exception. """ return self.put(item, False) def get(self, block=True, timeout=None): """Remove and return an item from the queue. If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the default), block if necessary until an item is available. If 'timeout' is a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout' seconds and raises the Empty exception if no item was available within that time. Otherwise ('block' is false), return an item if one is immediately available, else raise the Empty exception ('timeout' is ignored in that case). """ self.not_empty.acquire() try: if not block: if not self._qsize(): raise Empty elif timeout is None: while not self._qsize(): self.not_empty.wait() elif timeout < 0: raise ValueError("'timeout' must be a non-negative number") else: endtime = _time() + timeout while not self._qsize(): remaining = endtime - _time() if remaining <= 0.0: raise Empty self.not_empty.wait(remaining) item = self._get() self.not_full.notify() return item finally: self.not_empty.release() def get_nowait(self): """Remove and return an item from the queue without blocking. Only get an item if one is immediately available. Otherwise raise the Empty exception. """ return self.get(False) # Override these methods to implement other queue organizations # (e.g. stack or priority queue). # These will only be called with appropriate locks held # Initialize the queue representation def _init(self, maxsize): self.queue = deque() def _qsize(self, len=len): return len(self.queue) # Put a new item in the queue def _put(self, item): self.queue.append(item) # Get an item from the queue def _get(self): return self.queue.popleft() Queue.Queue
迭代器和生成器
一、迭代器
对于Python 列表的 for 循环,他的内部原理:查看下一个元素是否存在,如果存在,则取出,如果不存在,则报异常 StopIteration。(python内部对异常已处理)

class listiterator(object) | Methods defined here: | | __getattribute__(...) | x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name | | __iter__(...) | x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) | | __length_hint__(...) | Private method returning an estimate of len(list(it)). | | next(...) | x.next() -> the next value, or raise StopIteration listiterator
二、生成器
range不是生成器 和 xrange 是生成器
readlines不是生成器 和 xreadlines 是生成器
1 >>> print range(10) 2 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 3 >>> print xrange(10) 4 xrange(10)
生成器内部基于yield创建,即:对于生成器只有使用时才创建,从而不避免内存浪费
1 练习:<br>有如下列表: 2 [13, 22, 6, 99, 11] 3 4 请按照一下规则计算: 5 13 和 22 比较,将大的值放在右侧,即:[13, 22, 6, 99, 11] 6 22 和 6 比较,将大的值放在右侧,即:[13, 6, 22, 99, 11] 7 22 和 99 比较,将大的值放在右侧,即:[13, 6, 22, 99, 11] 8 99 和 42 比较,将大的值放在右侧,即:[13, 6, 22, 11, 99,] 9 10 13 和 6 比较,将大的值放在右侧,即:[6, 13, 22, 11, 99,] 11 ...
深浅copy
为什么要拷贝?
|
1
|
当进行修改时,想要保留原来的数据和修改后的数据 |
数字字符串 和 集合 在修改时的差异?(深浅拷贝不同的终极原因)
|
1
2
3
|
在修改数据时: 数字字符串:在内存中新建一份数据 集合:修改内存中的同一份数据 |
对于集合,如何保留其修改前和修改后的数据?
|
1
|
在内存中拷贝一份 |
对于集合,如何拷贝其n层元素同时拷贝?
|
1
|
深拷贝 |
1 浅copy 2 >>> dict = {"a":("apple",),"bo":{"b":"banna","o":"orange"},"g":["grape","grapefruit"]} 3 >>> dict = {"a":("apple",),"bo":{"b":"banna","o":"orange"},"g":["grape","grapefruit"]} 4 >>> dict2 = dict.copy() 5 6 7 >>> dict["g"][0] = "shuaige" #第一次我修改的是第二层的数据 8 >>> print dict 9 {'a': ('apple',), 'bo': {'b': 'banna', 'o': 'orange'}, 'g': ['shuaige', 'grapefruit']} 10 >>> print dict2 11 {'a': ('apple',), 'bo': {'b': 'banna', 'o': 'orange'}, 'g': ['shuaige', 'grapefruit']} 12 >>> id(dict["g"][0]),id(dict2["g"][0]) 13 (140422980581296, 140422980581296) #从这里可以看出第二层他们是用的内存地址 14 >>> 15 16 17 >>> dict["a"] = "dashuaige" #注意第二次这里修改的是第一层 18 >>> print dict 19 {'a': 'dashuaige', 'bo': {'b': 'banna', 'o': 'orange'}, 'g': ['shuaige', 'grapefruit']} 20 >>> print dict2 21 {'a': ('apple',), 'bo': {'b': 'banna', 'o': 'orange'}, 'g': ['shuaige', 'grapefruit']} 22 >>> 23 >>> id(dict["a"]),id(dict2["a"]) 24 (140422980580816, 140422980552272) #从这里看到第一层他们修改后就不会是相同的内存地址了! 25 >>> 26 27 28 #这里看下,第一次我修改了dict的第二层的数据,dict2也跟着改变了,但是我第二次我修改了dict第一层的数据dict2没有修改。 29 说明:浅copy只是第一层是独立的,其他层面是公用的!作用节省内存 30 31 深copy 32 33 >>> import copy #深copy需要导入模块 34 >>> dict = {"a":("apple",),"bo":{"b":"banna","o":"orange"},"g":["grape","grapefruit"]} 35 >>> dict2 = copy.deepcopy(dict) 36 >>> print dict 37 {'a': ('apple',), 'bo': {'b': 'banna', 'o': 'orange'}, 'g': ['grape', 'grapefruit']} 38 >>> print dict2 39 {'a': ('apple',), 'bo': {'b': 'banna', 'o': 'orange'}, 'g': ['grape', 'grapefruit']} 40 >>> dict["g"][0] = "shuaige" #修改第二层数据 41 >>> print dict 42 {'a': ('apple',), 'bo': {'b': 'banna', 'o': 'orange'}, 'g': ['shuaige', 'grapefruit']} 43 >>> print dict2 44 {'a': ('apple',), 'bo': {'b': 'banna', 'o': 'orange'}, 'g': ['grape', 'grapefruit']} 45 >>> id(dict["g"][0]),id(dict2["g"][0]) 46 (140422980580816, 140422980580288) #从这里看到第二个数据现在也不是公用了 47 48 # 通过这里可以看出他们现在是一个完全独立的,当你修改dict时dict2是不会改变的因为是两个独立的字典!

