以前写过一篇WCF自定义用户名密码认证,用户必须输入正确的用户名和密码才能调用WCF服务提供的操作契约(OperationContract),但没有限制某个用户可调用契约的范围,即默认每个用户都可调用该服务下的所有契约,WCF自定义授权用来为用户授权特定的操作契约,并在用户调用的时候对用户的授权进行验证,只有通过验证的用户才可调用该契约,这中将权限控制在OperationContract层次对企业级应用来说是必要的。
要实现WCF自定义授权必须先实现自定义用户名密码认证,要不然WCF怎么知道调用者是谁?因上次写的那个自定义用户名密码认证示例实在年代久远了,这次用VS2010重新写了个,并将WCF自定义授权加了进去,示例代码在评论一楼下载,先看下运行效果:
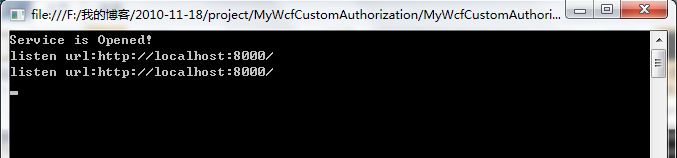
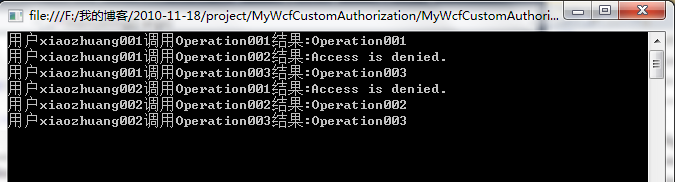
该服务共有三个操作契约(Operation001、Operation002、Operation003),用两个不用的用户(xiaozhuang001、xiaozhuang002)调用,xiaozhuang001具有调用Operation001和Operation003的权限,xiaozhuang002具有调用Operation002和Operation003的权限。
解决方案结构如图
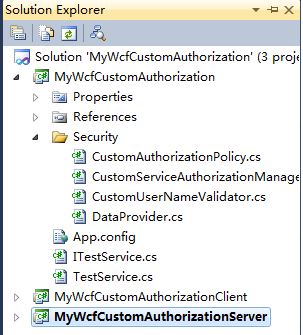
由三个项目组成,MyWcfCustomAuthorization是WCF Service Library,MyWcfCustomAuthorizationServer控制台项目用来为MyWcfCustomAuthorization项目提供宿主,MyWcfCustomAuthorizationClient用来调用WCF服务契约。
MyWcfCustomAuthorization下面的的Security目录下分为四个文件:
1、DataProvider.cs顾名思义数据供应器
2、CustomUserNameValidator.cs实现自定义用户名密码认证功能
3、CustomAuthorizationPolicy.cs为用户授权操作契约
4、CustomServiceAuthorizationManager.cs对用户要调用的操作契约进行权限验证。
CustomAuthorizationPolicy.cs主要代码如下:
 CustomAuthorizationPolicy代码
CustomAuthorizationPolicy代码
{
string id;
public CustomAuthorizationPolicy()
{
id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
}
public bool Evaluate(EvaluationContext evaluationContext, ref object state)
{
bool bRet = false;
CustomAuthState customstate = null;
// If the state is null, then this has not been called before so
// set up a custom state.
if (state == null)
{
customstate = new CustomAuthState();
state = customstate;
}
else
customstate = (CustomAuthState)state;
// If claims have not been added yet...
if (!customstate.ClaimsAdded)
{
// Create an empty list of claims.
IList<Claim> claims = new List<Claim>();
// Iterate through each of the claim sets in the evaluation context.
foreach (ClaimSet cs in evaluationContext.ClaimSets)
// Look for Name claims in the current claimset.
foreach (Claim c in cs.FindClaims(ClaimTypes.Name, Rights.PossessProperty))
{
// Get the list of operations the given username is allowed to call.
foreach (Right right in DataProvider.GetUserRightList(c.Resource.ToString()))
{
Console.WriteLine("正在给用户(" + c.Resource + ")赋权限:" + right.OperationName);
claims.Add(new Claim(DataProvider.ClaimType,right.OperationName, Rights.PossessProperty));
//Console.WriteLine("Claim added {0}", s);
}
}
// Add claims to the evaluation context.
evaluationContext.AddClaimSet(this, new DefaultClaimSet(this.Issuer, claims));
// Record that claims were added.
customstate.ClaimsAdded = true;
// Return true, indicating that this method does not need to be called again.
bRet = true;
}
else
{
// Should never get here, but just in case, return true.
bRet = true;
}
return bRet;
}
public ClaimSet Issuer
{
get { return ClaimSet.System; }
}
public string Id
{
get { return id; }
}
// Internal class for keeping track of state.
class CustomAuthState
{
bool bClaimsAdded;
public CustomAuthState()
{
bClaimsAdded = false;
}
public bool ClaimsAdded
{
get { return bClaimsAdded; }
set { bClaimsAdded = value; }
}
}
}
从求值上下(EvaluationContext)文中找到用户名,根据用户名从DataProvider中取得该用户的操作契约集合,转换为权限集合,并将该用户的权限集合加入到求值上下文中,上面的代码大部分都是MSDN上的,但我调试发现:虽然代码中判断了如果已经增加过权限则再不增加的逻辑,但这个似乎没有作用,因为CustomAuthorizationPolicy这个对象的生存期只是在调用操作契约的过程中,所以每次调用契约都要创建实例,所以导致 if (state == null)这句的state永远都是空的,也就是每次调用都要增加一遍权限,这是个大问题,要是在这个类里面读数据库来获取用户权限的话会形成巨大的性能瓶颈,所以大家千万不要这么做。
CustomServiceAuthorizationManager.cs的主要代码如下:
 CustomServiceAuthorizationManager 代码
CustomServiceAuthorizationManager 代码
{
protected override bool CheckAccessCore(OperationContext operationContext)
{
// Extract the action URI from the OperationContext. Match this against the claims
// in the AuthorizationContext.
string action = operationContext.RequestContext.RequestMessage.Headers.Action;
// Iterate through the various claim sets in the AuthorizationContext.
foreach (ClaimSet cs in operationContext.ServiceSecurityContext.AuthorizationContext.ClaimSets)
{
// Examine only those claim sets issued by System.
if (cs.Issuer == ClaimSet.System)
{
// Iterate through claims of type.
foreach (Claim c in cs.FindClaims(DataProvider.ClaimType, Rights.PossessProperty))
{
// If the Claim resource matches the action URI then return true to allow access.
Console.WriteLine("正在比较权限:" + action + "和" + c.Resource.ToString());
if (action == c.Resource.ToString())
return true;
}
}
}
// If this point is reached, return false to deny access.
return false;
}
}
从当前请求上下文中取得用户的操作契约,并和当前用户的权限集合中的操作契约对比,如果有相同的则说明该用户有调用该契约的权限。
配置文件部分
 serviceModel代码
serviceModel代码
<behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior>
<!-- To avoid disclosing metadata information, set the value below to false and remove the metadata endpoint above before deployment -->
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/>
<!-- To receive exception details in faults for debugging purposes, set the value below to true. Set to false before deployment to avoid disclosing exception information -->
<serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="true"/>
<serviceCredentials>
<serviceCertificate findValue="xiaozhuang-PC" x509FindType="FindBySubjectName" storeLocation="LocalMachine" storeName="My"/>
<userNameAuthentication userNamePasswordValidationMode="Custom" customUserNamePasswordValidatorType="MyWcfCustomAuthorization.Security.CustomUserNameValidator,MyWcfCustomAuthorization"/>
</serviceCredentials>
<serviceAuthorization serviceAuthorizationManagerType="MyWcfCustomAuthorization.Security.CustomServiceAuthorizationManager,MyWcfCustomAuthorization" >
<authorizationPolicies>
<add policyType="MyWcfCustomAuthorization.Security.CustomAuthorizationPolicy,MyWcfCustomAuthorization"/>
</authorizationPolicies>
</serviceAuthorization>
</behavior>
</serviceBehaviors>
</behaviors>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding>
<security mode="Message">
<message clientCredentialType="UserName"/>
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<services>
<service name="MyWcfCustomAuthorization.TestService">
<endpoint address="" binding="wsHttpBinding" contract="MyWcfCustomAuthorization.ITestService">
<identity>
<dns value="xiaozhuang-PC" />
</identity>
</endpoint>
<endpoint address="mex" binding="mexHttpBinding" contract="IMetadataExchange" />
<host>
<baseAddresses>
<add baseAddress="http://localhost:8000/MyWcfCustomAuthorization/TestService/" />
</baseAddresses>
</host>
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
采用了WCF4.0中简化的配置方式,在behavior节中增加服务认证部分和授权部分并,指定自定义用户名密码实现的类,自定义授权管理器实现的类和授权策略实现的类,在binding节中指定认证类型为userName。
服务端宿主的代码比较简单,客户端调用部分代码如下:
 Main代码
Main代码
{
TestServiceClient client = new TestServiceClient();
client.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = "xiaozhuang001";
client.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = "xiaozhuang001";
string returnStr = "";
try
{
returnStr = client.Operation001();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
returnStr = ex.Message;
}
Console.WriteLine("用户xiaozhuang001调用Operation001结果:" + returnStr);
try
{
returnStr = client.Operation002();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
returnStr = ex.Message;
}
Console.WriteLine("用户xiaozhuang001调用Operation002结果:" + returnStr);
try
{
returnStr = client.Operation003();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
returnStr = ex.Message;
}
Console.WriteLine("用户xiaozhuang001调用Operation003结果:" + returnStr);
//Console.WriteLine("xiaozhuang002:");
TestServiceClient client1 = new TestServiceClient();
client1.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = "xiaozhuang002";
client1.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = "xiaozhuang002";
try
{
returnStr = client1.Operation001();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
returnStr = ex.Message;
}
Console.WriteLine("用户xiaozhuang002调用Operation001结果:" + returnStr);
try
{
returnStr = client1.Operation002();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
returnStr = ex.Message;
}
Console.WriteLine("用户xiaozhuang002调用Operation002结果:" + returnStr);
try
{
returnStr = client1.Operation003();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
returnStr = ex.Message;
}
Console.WriteLine("用户xiaozhuang002调用Operation003结果:" + returnStr);
Console.ReadKey();
}
代码很简单,无需说明。
补充:在WCF的用户名密码认证那篇中我用了makecert.exe这个生成测试证书的命令,所以还要对应在客户端写绕过测试证书的代码,这次的不用了,在网上找了个工具SelfSSL (SelfSSL.exe) 可以帮助您生成和安装自签名 SSL 证书。有了这个工具,生成的证书就不会再报是未签名的了;并将这个工具封装成了一个Winform程序,大家运行代码时先要运行该程序安装好证书,并修改对应的配置文件部分才可以,主要是查找证书部分和DNS部分,要是你的电脑也叫xiaozhuang-PC就不用改了。
遗留问题:我用控制台宿主WCF类库,但为啥我在类库中写的Console.Write()啥的都在宿主程序中看不见呢?害得我用附加进程的方式调试,真麻烦,还望知道的朋友指点一下。
