在C++中,我们知道多态很大程度上依赖于虚函数,而虚函数的地址存放于虚函数表之中。运行期多态就是通过虚函数和虚函数表实现的。类的对象内部会有指向类内部的虚表地址的指针。通过这个指针调用虚函数。虚函数的调用会被编译器转换为对虚函数表的访问。虚函数表就像一个地图一样,指明了实际所应该调用的函数。如果一个类有虚函数,那么这个类的所有对象共享一个虚函数表。
虚函数表的相关实现和怎么用虚函数实现多态的原理可以参考这个博主的文章,写的很好理解
虚函数表大致像下面这样:
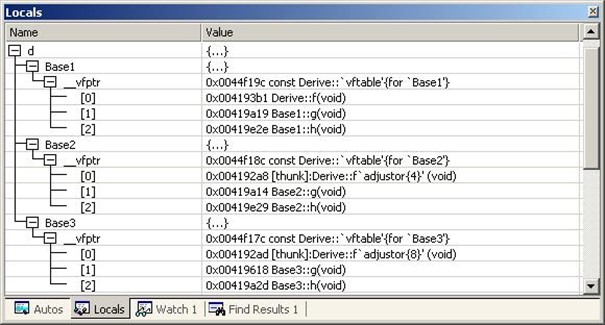
-
根据C++ 虚函数表原理,我们可以考虑用C来尝试,其实C++很大一部分是由C衍生过来的,所以我们下面 用一个例子来模拟一下。若用C语言来实现多态,可以利用"结构在内存中的布局与结构的声明具有一致的顺序"这一事实来实现继承,再通过一个函数指针结构体来实现虚函数来实现多态。
-
struct Point { int x, y; }; struct Shape // 基类 { struct Methods* methods; // 指向“虚函数表” }; struct Methods // 将C++对应类中所有虚函数封装到一个结构体里面 { float (*getPerimeter)(Shape * shape); float (*getArea)(Shape * shape); char* (*getShape)(Shape * shape); }; /*Rectangle*/ struct Rectangle { struct Methods * methods; //包含继承Shape后的成员函数结构体的指针 Point leftTop; //Shape之外派生的成员变量 Point rightBottom; //Shape之外派生的成员变量 }; float Rectangle_getPerimeter(Shape * shape) // 计算矩形周长 { Rectangle * r = (Rectangle *) shape; return (float)(r->rightBottom.x - r->leftTop.x + r->rightBottom.y - r->leftTop.y) * 2; } float Rectangle_getArea(Shape * shape) // 计算矩形面积 { Rectangle * r = (Rectangle *) shape; return (float)(r->rightBottom.x - r->leftTop.x) * (r->rightBottom.y - r->leftTop.y); } char* Rectangle_getShape(Shape * shape) { return "Rectangle"; } struct Methods rectangleMethods = // 绑定Rectangle“类”实现的“虚函数” { &Rectangle_getPerimeter, &Rectangle_getArea, &Rectangle_getShape }; struct Circle { struct Methods * methods; Point center; float radius; }; float Circle_getPerimeter(Shape * shape) // 计算圆周长 { Circle * c = (Circle *) shape; return (float)2 * 3.14 * c->radius; } float Circle_getArea(Shape * shape) // 计算圆面积 { Circle * c = (Circle *) shape; return (float)3.14*(c->radius)*(c->radius); } char* Circle_getShape(Shape * shape) { return "Circle"; } struct Methods circleMethods = // 绑定Circle“类”实现的“虚函数” { &Circle_getPerimeter, &Circle_getArea, &Circle_getShape }; /*main*/ Shape* shapes[2]; // 基类指针数组 Shape* new_rectangle(Point a, Point b) // 创建Rectangle对象 { struct Rectangle* r = (Rectangle* )malloc(sizeof(Rectangle)); r->methods = &rectangleMethods; r->leftTop = a; r->rightBottom = b; return (Shape*)r; } Shape* new_circle(Point a, float r) // 创建Circle对象 { struct Circle* c = (Circle*)malloc(sizeof(Circle)); c->methods = &circleMethods; c->center = a; c->radius = r; return (Shape*)c; } int main() { Point c ={0,0}; shapes[0] = new_circle(c,10); Point a ={2,3}; Point b = {9,8}; shapes[1] = new_rectangle(a, b); for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) printf("%s's perimeter is: %f ", (*shapes[i]->methods->getShape)(shapes[i]), (*shapes[i]->methods->getPerimeter)(shapes[i])); for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) printf("%s's area is: %f ", (*shapes[i]->methods->getShape)(shapes[i]), (*shapes[i]->methods->getArea)(shapes[i])); getchar(); return 0;
-
