在本章中,总结了PostgreSQL中的流程体系结构和内存体系结构,以帮助阅读后续章节。如果您已经熟悉它们,可以跳过本章
1.进程结构
Postgresql 是一个C/S架构的关系型数据库,由多个后台进程管理数据库,下面分别介绍一些这些进程
postgres server process 是所有进程的父进程
backend process 每一个客户端的连接都有一个后端进程存在
backgroud processes 为管理数据库而产生的一些进程
backgroud work processes 9.3以后版本开始有这个进程,这里不做详细介绍
进程架构图2.1:
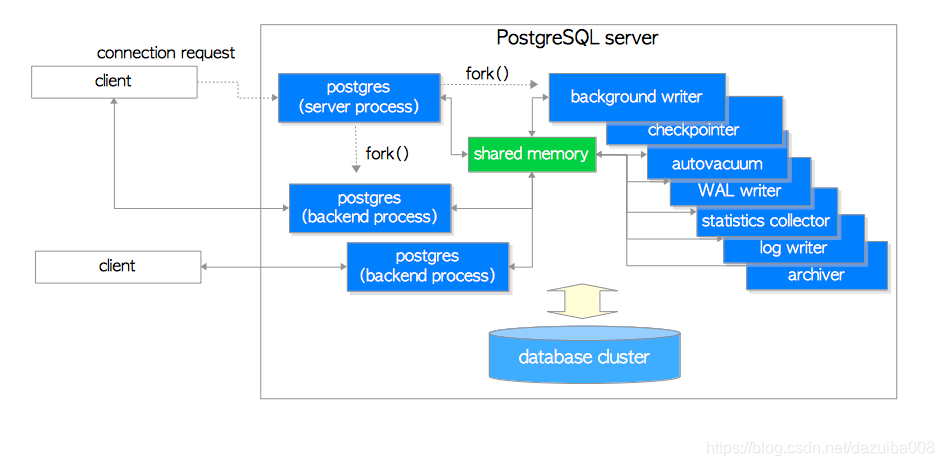
下面简短的介绍一些这几个进程的作用
1.1 postgres server process
正如上所说,是所有进程的父进程,早期的版本叫postmaster.
pg_ctl start执行后,这个进程就会启动,然后,从物理内存中分配内给给shared memory,然后产生很多其他的backgroup processes ,等待客户端来连接,每产生一个连接就会生成一个backend process,一个postgres server process只能监听一个端口,默认端口是5432。尽管一台机器可以运行多个server,但是端口必须不同。
1.2 backend processes
通过TCP协议和客户端建立通讯,当客户端断开时,连接消失。允许多个客户端同时连接,连接数由max_connections参数控制,默认是100,如果客户端频繁的和服务端建立连接然后断开,会增加数据库的开销,导致服务器负载不正常,因为数据库本身不提供连接池的功能,如果有需要,可以使用pgbouncer或者pgpool-II。
1.3 backgroud processes
下面列出了相关的服务端进程,这里只做简单的介绍
| process | description | reference |
|---|---|---|
| background writer | 进程将shared buffer pool中的脏数据写到磁盘,检查点总能触发这个进程 | Section 8.6 |
| checkpointer | 在9.2版本以后,检查点会触发产生这个进程 | Section 8.6, Section 9.7 |
| autovacuum launcher | 为vacuum process周期性的调用autovacuum work processes | Section 6.5 |
| WAL writer | 周期性的从wal buffer刷新数据到磁盘 | Section 9.9 |
| statistics collector | 收集统计信息进程,比如pg_stat_activity 和pg_stat_database的数据 | |
| logging collector (logger) | 将错误信息写入到日志 | |
| archiver | 将日志归档的进程. | Section 9.10 |
这里显示了PostgreSQL数据库的进程信息。在以下示例中,一个postgres服务器进程(pid为9687),两个后端进程(pids为9697和9717)以及表2.1中列出的几个后台进程正在运行。
-
postgres> pstree -p 9687
-
-+= 00001 root /sbin/launchd
-
-+- 09687 postgres /usr/local/pgsql/bin/postgres -D /usr/local/pgsql/data
-
|--= 09688 postgres postgres: logger process
-
|--= 09690 postgres postgres: checkpointer process
-
|--= 09691 postgres postgres: writer process
-
|--= 09692 postgres postgres: wal writer process
-
|--= 09693 postgres postgres: autovacuum launcher process
-
|--= 09694 postgres postgres: archiver process
-
|--= 09695 postgres postgres: stats collector process
-
|--= 09697 postgres postgres: postgres sampledb 192.168.1.100(54924) idle
-
--= 09717 postgres postgres: postgres sampledb 192.168.1.100(54964) idle in transaction
2.内存架构
在Postgresql中,内存大概被分为两块
Local memory area – 为每一个backend process 分配的内存
Shared memory area – PostgreSQL server 所有的backgroud process使用的内存
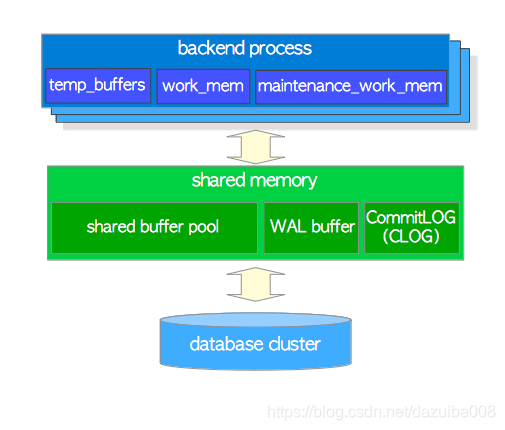
2.1 Local memory area
每一个backend process 都会分配一块local memory area, 每一块区域又分为三个子区域 ,见下表
| sub-area | description | reference |
|---|---|---|
| work_mem | 用户在sort,distinct,merge join,hash join的时候会用到这块区域 | Chapter 3 |
| maintenance_work_mem | vacuum,reindex会用到这块区域 | Section 6.1 |
| temp_buffers | 存储临时表会用到这块区域 |
2.2 Shared memory area
这块区域在服务器启动的时候分配,这块区域也是分为好几个子区域,见下面介绍
| sub-area | description | reference |
|---|---|---|
| shared buffer pool | 将表或者索引的page从磁盘加载到shared buffer,然后在shared buffer操作 | Chapter 8 |
| WAL buffer | 在服务端出现问题的时候,确保数据不会丢失,在写到磁盘之前,wal buffer是wal log的缓存区域 | Chapter 9 |
| commit log | 为了并发控制所有事物的状态的保持而分配的区域 |
另外,Postgresql还分配一些其他的内存区域:
- 为访问控制分配的子区域,比如轻量级锁,共享或者专有锁.
- 为其他backgroud process提供的子区域,比如检查点,vacuum.
- 为事物处理提供的子区域,比如事物中的保存点,和二阶段事物提交.
转载自:
https://blog.csdn.net/dazuiba008/article/details/80389220