单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是 Java 中最简单的设计模式之一。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
这种模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类负责创建自己的对象,同时确保只有单个对象被创建。这个类提供了一种访问其唯一的对象的方式,可以直接访问,不需要实例化该类的对象。
注意:
- 1、单例类只能有一个实例。
- 2、单例类必须自己创建自己的唯一实例。
- 3、单例类必须给所有其他对象提供这一实例。
上面这几句引自https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/singleton-pattern.html
众所周知,单例模式分为懒汉式和饿汉式。下面我逐一介绍。
饿汉式:
public class HungryMan {
private HungryMan(){}
private static final HungryMan HUNGRY_MAN = new HungryMan();
public static HungryMan getInstance(){
return HUNGRY_MAN;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HungryMan hungryMan1 = HungryMan.getInstance();
HungryMan hungryMan2 = HungryMan.getInstance();
System.out.println(hungryMan1.hashCode());
System.out.println(hungryMan2.hashCode());
}
}
说明创建的是同一个对象
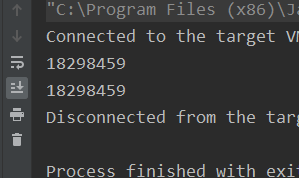
但是饿汉式会造成资源的浪费
懒汉式:
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan(){}
public static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance(){
if(lazyMan == null){
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
return lazyMan;
}
return lazyMan;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LazyMan lazyMan1 = LazyMan.getInstance();
LazyMan lazyMan2 = LazyMan.getInstance();
System.out.println(lazyMan1.hashCode());
System.out.println(lazyMan2.hashCode());
}
}
看到两个对象是一样的

但是多线程的情况下懒汉式是不安全的
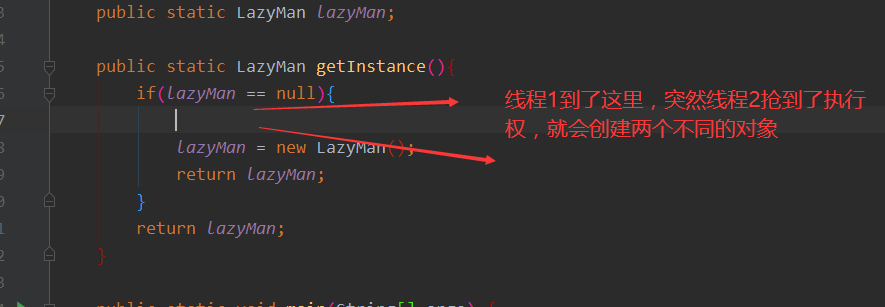
检验不安全:
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan(){}
public static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance(){
if(lazyMan == null){
//睡一会
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
return lazyMan;
}
return lazyMan;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
System.out.println(instance.hashCode());
}).start();
}
}
}
哈希值是不一样的,所以懒汉式在并发的情况下是不安全的

加了锁的懒汉式
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan(){}
public static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance(){
if(lazyMan == null){
synchronized(LazyMan.class){
if(lazyMan == null){
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
return lazyMan;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
System.out.println(instance.hashCode());
}).start();
}
}
}
延迟一秒的结果(代码中没有体现)

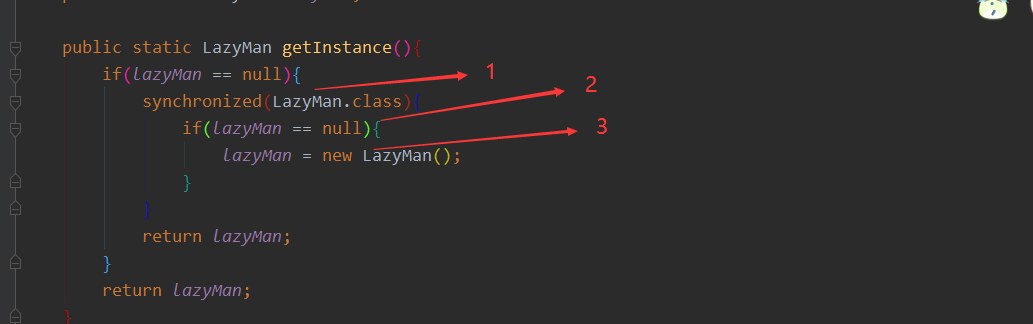
线程A执行到3的位置,线程B抢到执行权,停留在1的位置,因为有锁不能继续执行,线程A创建对象,线程B即使能执行到2的位置,但是因为对象不是null,还是不能执行到3的位置,不能创建新的对象。
但是,另一个问题来了
public static LazyMan getInstance(){
if(lazyMan == null){
synchronized(LazyMan.class){
if(lazyMan == null){
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
/**
* lazyMan = new LazyMan();
* 但是这句话并不是一个原子性的,它有三个步骤
* 1、开辟一段内存地址
* 2、执行构造函数,初始化对象
* 3、将对象指向这段内存地址
* 完美的情况下是 1 2 3 ,但是可能 万一是 1 3 2
* 开辟完内存地址,指向这段内存地址,初始化对象
* 此时的初始化对象已经无济于事,因为已经指向内存地址了
* 这就导致,不是原子性的问题带来的影响
*/
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
return lazyMan;
}
所以我们需要加上volatile
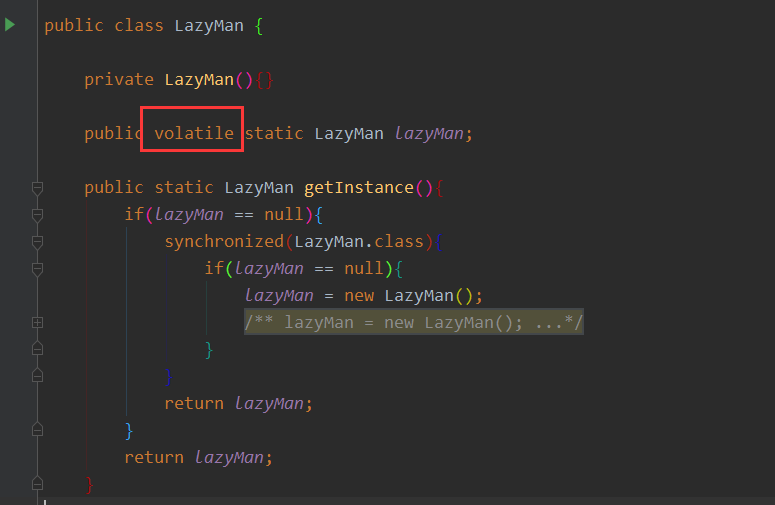
但是我们依旧可以通过反射来破坏
package com.xiaofei.single;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author xiaofei
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020/9/12 18:47
*/
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan(){}
public volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance(){
if(lazyMan == null){
synchronized(LazyMan.class){
if(lazyMan == null){
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
return lazyMan;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LazyMan lazyMan1 = LazyMan.getInstance();
Constructor<LazyMan> constructor = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
LazyMan lazyMan2 = constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(lazyMan1.hashCode());
System.out.println(lazyMan2.hashCode());
}
}
可以发现,反射依旧可以破坏
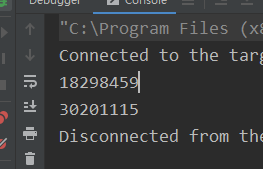
下面我们用到终极办法:枚举
public enum SingleEnum {
SINGLENUM;
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleEnum singlenum1 = SingleEnum.SINGLENUM;
SingleEnum singlenum2 = SingleEnum.SINGLENUM;
System.out.println(singlenum1.hashCode());
System.out.println(singlenum2.hashCode());
}
}
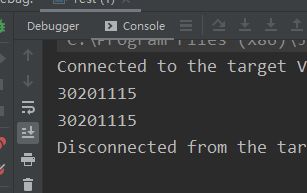
枚举写法简单,而且不会被反射破坏