在之前的例子中我们是通过listOfServers来维护一个服务列表的,但是这样的方式是有问题的,当我们的服务节点很多时这个listOfServers列表就会很长,还有另外一个如果服务节点发生上下线时,客户端是没办法感知的,这样会导致请求可能会发到失败的节点上,而且当节点IP要发生变化时,这个列表也要重新维护,竟然有个问题那就要有解决问题的方案,在分布式的架构中,解决这问题很简单,那就是引用第三方组件来管理这个服务列表就行了,这时Eureka应时而出;
spring-cloud-server.ribbon.listOfServers= localhost:8080,localhost:8081
一,Eureka基本介绍
Spring Cloud 封装了 Netflix 公司开发的 Eureka 模块来实现服务注册和发现(请对比Zookeeper)。
Eureka 采用了 C-S 的设计架构。Eureka Server 作为服务注册功能的服务器,它是服务注册中心。
而系统中的其他微服务,使用 Eureka 的客户端连接到 Eureka Server并维持心跳连接。这样系统的维护人员就可以通过 Eureka Server 来监控系统中各个微服务是否正常运行。SpringCloud 的一些其他模块(比如Zuul)就可以通过 Eureka Server 来发现系统中的其他微服务,并执行相关的逻辑。
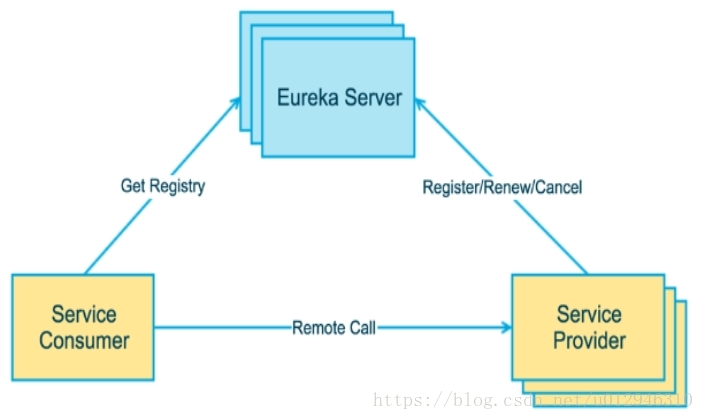
Eureka包含两个组件:Eureka Server和Eureka Client
Eureka Server提供服务注册服务
各个节点启动后,会在EurekaServer中进行注册,这样EurekaServer中的服务注册表中将会存储所有可用服务节点的信息,服务节点的信息可以在界面中直观的看到
EurekaClient是一个Java客户端,用于简化Eureka Server的交互,客户端同时也具备一个内置的、使用轮询(round-robin)负载算法的负载均衡器。在应用启动后,将会向Eureka Server发送心跳(默认周期为30秒)。如果Eureka Server在多个心跳周期内没有接收到某个节点的心跳,EurekaServer将会从服务注册表中把这个服务节点移除(默认90秒)
Eureka三大角色:
- Eureka Server 提供服务注册和发现
- Service Provider服务提供方将自身服务注册到Eureka,从而使服务消费方能够找到
- Service Consumer服务消费方从Eureka获取注册服务列表,从而能够消费服务
作为服务注册中心,Eureka 和 Zookeeper对比的优势:
著名的CAP理论指出,一个分布式系统不可能同时满足C(一致性)、A(可用性)和P(分区容错性)。由于分区容错性P在是分布式系统中必须要保证的,因此我们只能在A和C之间进行权衡。
因此
Zookeeper保证的是CP,
Eureka则是AP。
Zookeeper保证CP
当向注册中心查询服务列表时,我们可以容忍注册中心返回的是几分钟以前的注册信息,但不能接受服务直接down掉不可用。也就是说,服务注册功能对可用性的要求要高于一致性。但是zk会出现这样一种情况,当master节点因为网络故障与其他节点失去联系时,剩余节点会重新进行leader选举。问题在于,选举leader的时间太长,30 ~ 120s, 且选举期间整个zk集群都是不可用的,这就导致在选举期间注册服务瘫痪。在云部署的环境下,因网络问题使得zk集群失去master节点是较大概率会发生的事,虽然服务能够最终恢复,但是漫长的选举时间导致的注册长期不可用是不能容忍的。
Eureka保证AP
Eureka看明白了这一点,因此在设计时就优先保证可用性。Eureka各个节点都是平等的,几个节点挂掉不会影响正常节点的工作,剩余的节点依然可以提供注册和查询服务。而Eureka的客户端在向某个Eureka注册或时如果发现连接失败,则会自动切换至其它节点,只要有一台Eureka还在,就能保证注册服务可用(保证可用性),只不过查到的信息可能不是最新的(不保证强一致性)。除此之外,Eureka还有一种自我保护机制,如果在15分钟内超过85%的节点都没有正常的心跳,那么Eureka就认为客户端与注册中心出现了网络故障,此时会出现以下几种情况:
1. Eureka不再从注册列表中移除因为长时间没收到心跳而应该过期的服务
2. Eureka仍然能够接受新服务的注册和查询请求,但是不会被同步到其它节点上(即保证当前节点依然可用)
3. 当网络稳定时,当前实例新的注册信息会被同步到其它节点中
因此, Eureka可以很好的应对因网络故障导致部分节点失去联系的情况,而不会像zookeeper那样使整个注册服务瘫痪。
二,Eureka 具体实现分析
前面说到了服务间调用引发的问题,那么下面看对于消费者要调用服务提供者的地址Eureka是怎么解决的, Eureka会把所有服务提供者的地址以键值对的形式将服务提供者列表在Eureka中进行维护着,竟然服务提供者全部以键值对的形式维护在Eureka中了,那对于服务调用者来说,当他要调用某个服务时,他只用发送要调用的服务者名称就可以拿到服务集群的列表了,这时服务地址维护难的问题就解决了,下面来看下Eureka是怎么解决上下线的动态感知的,看下图,假如服务提供者有三个服务地址;这时服务调用者会从Eureka拿到所有的服务提供者地址并且存储到本地,他在调用时就可以通过Ribbon调用到本地的服务集群列表,然后通过IRule算法获取到一个具体的服务地址,然后发起一个远程的调用,那么现在有个问题就是,当三个服务提供者中某一个节点挂掉了,对于服务调用者他是如何感知的呢?或者换一种说法,如果服务提供者发生了扩容,对于服务调用者是如何感知的;因为现在所有服务的地址都是维护在Eureka中的,那么当服务失效的话Eureka要做的有两件事,第一件事是收到失效的地址然后更新本地列表,第二件事是通知服务调用者更新自己的本地列表;现在先来看第一件事,Eureka是如何感知到服务节点挂了,其实通过前面源码分析应该可以知道有一个很简单的方法那就是心跳检测,就是通过一个定时任务去PING下服务能否收到心跳的方式来判断服务提供者是否存活;第一件事完成了接下来看第二件事服务调用者是如何感知到Eureka的列表发生改变的,其实这个解决方案不外就两种方案,第一种方案是push,通过调用端和注册中心建立一个通信管道并且维持这个会话这种法式有个不好的地方就是要维护大量会话;另一种就是pull,这个方式就比较简单,通过一个定时任务,每隔一段时间就去注册中心拉取一下数据,但这玩意也有一个问题,就是数据更新有延时;其实还有一种方式就是用long-poll长轮询的方式去访问注册中心,这个方式有个好处就是能实时感知又不用维护大量会话;这就是服务注册中心的整体原理;

三、常用的注册中心解决方案
- 它是非持久化存储(内存 存储)
- ap(模型)
- 集群节点的角色是相等的
- raft
- 有一至性问题(redis-sentinel / nacos 选举 )
- long polling(长轮询)
- zab协议(paxos)
- push
- raft
- long polling
- raft
- long polling
四、Eureka应用
项目结构如下
父pom
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ghy</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<modules>
<module>spring-cloud-eureka</module>
</modules>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<spring-boot.version>2.3.0.RELEASE</spring-boot.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR4</spring-cloud.version>
<zipkin-version>2.11.8</zipkin-version>
<mybatis.version>2.1.3</mybatis.version>
<docker.image.prefix>yaohui</docker.image.prefix>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--@Data注解包;所有服务共用-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-server</artifactId>
<version>1.5.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>
spring-cloud-eureka的pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ghy</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-eureka</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>spring-cloud-eureka</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>com.ghy</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<start-class>com.ghy.eureka.EurekaApplication</start-class>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
spring-cloud-eureka的application.yml
server: port: 8761 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost client: register-with-eureka: true fetch-registry: false serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ spring: application: name: cloud-eureka-server
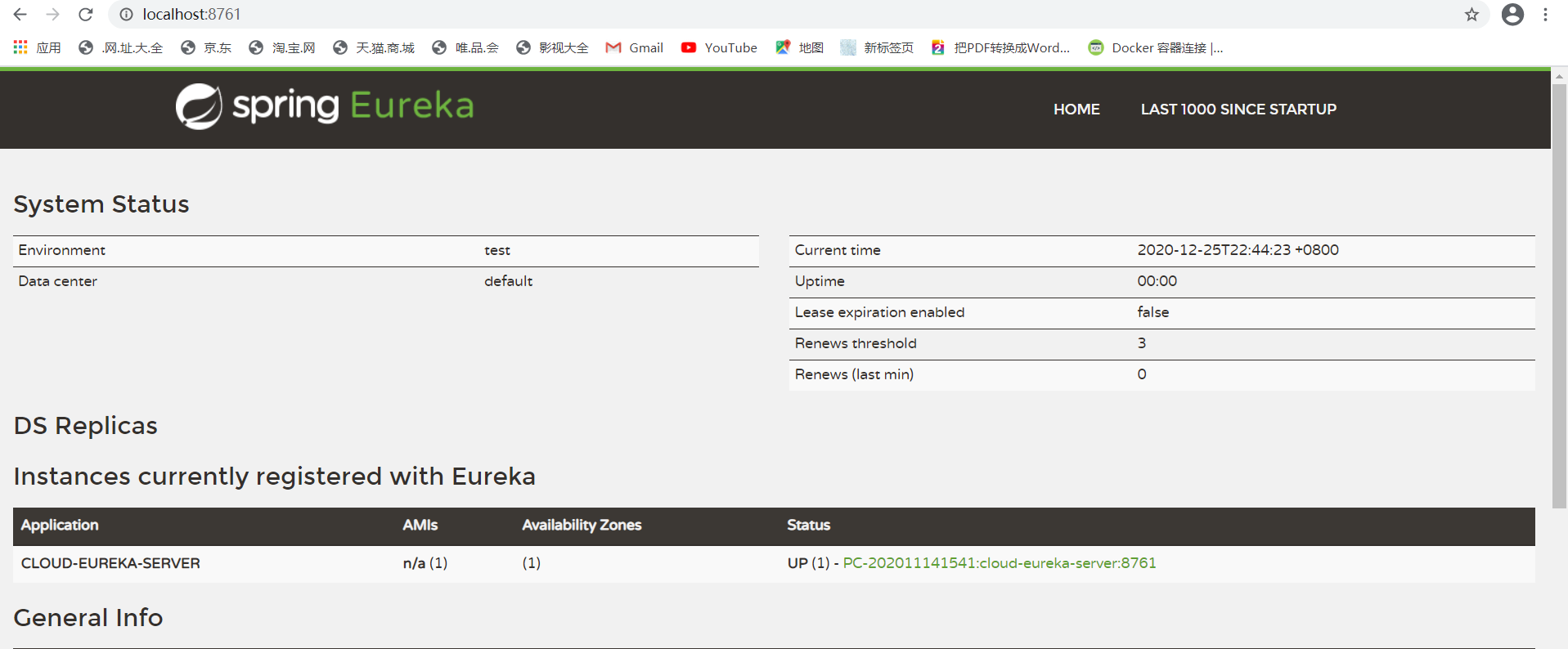
在启动类上加入@EnableEurekaServer注解然后启动项目,访问8761
下面来演示下其它服务注册到eureka中,项目列表如下

spring-cloud-service项目中的appliation.yml配置如下
server: port: 8080 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ #指向服务注册中心的地址 spring: application: name: spring-cloud-service
启动spring-cloud-service然后再看注册中心
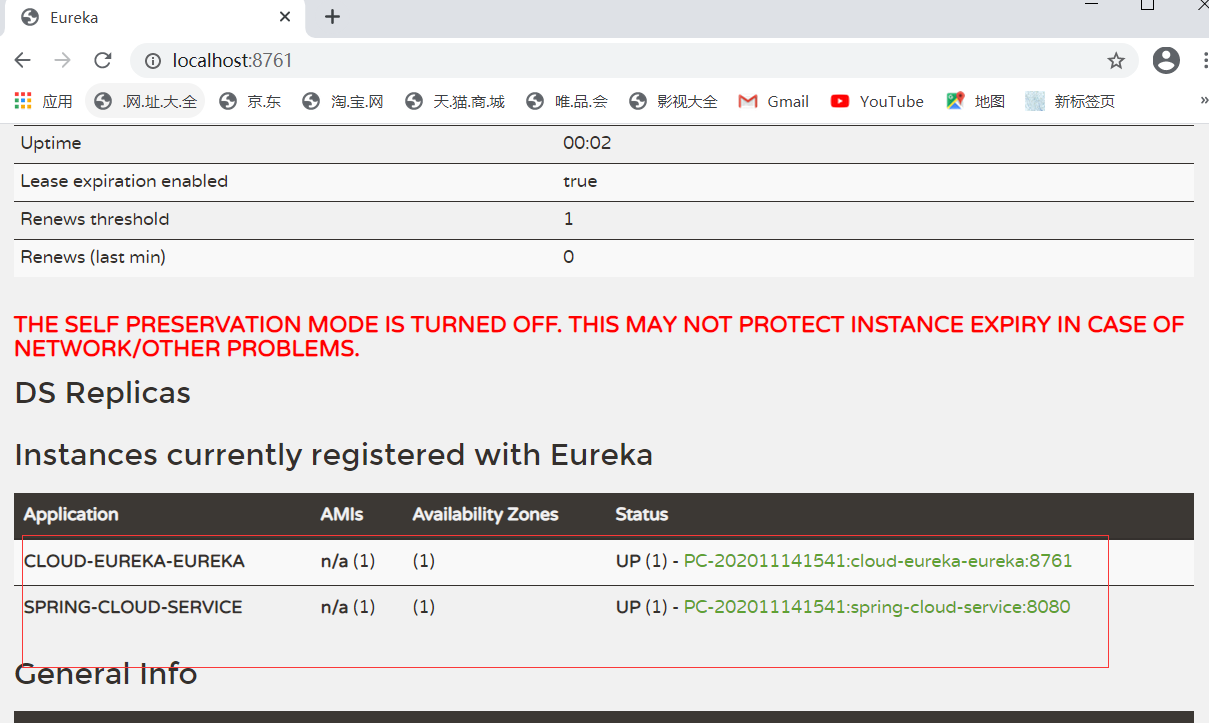
如果想注册多个服务提供者很简单,改变端口号启动就可以了

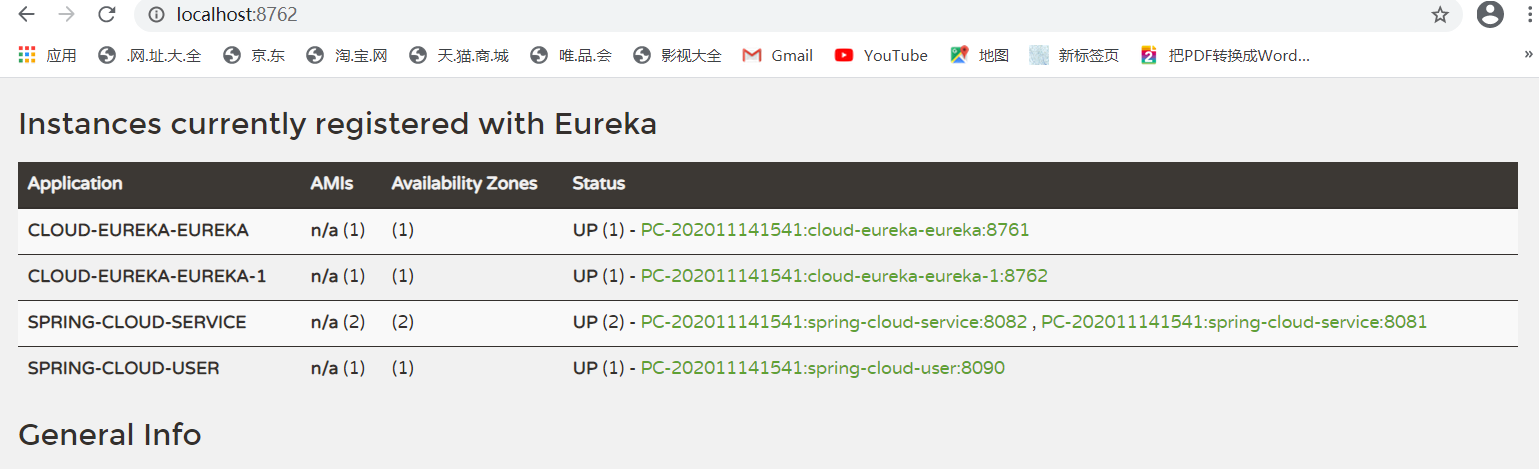
然后再看注册中心可以发现有多个节点了

服务提供者注册进去就是写业务代码了,我们新建一个maven工程项目spring-cloud-api,把业务接口写在spring-cloud-api工程中,并且在spring-cloud-service中引入maven包
代码如下:
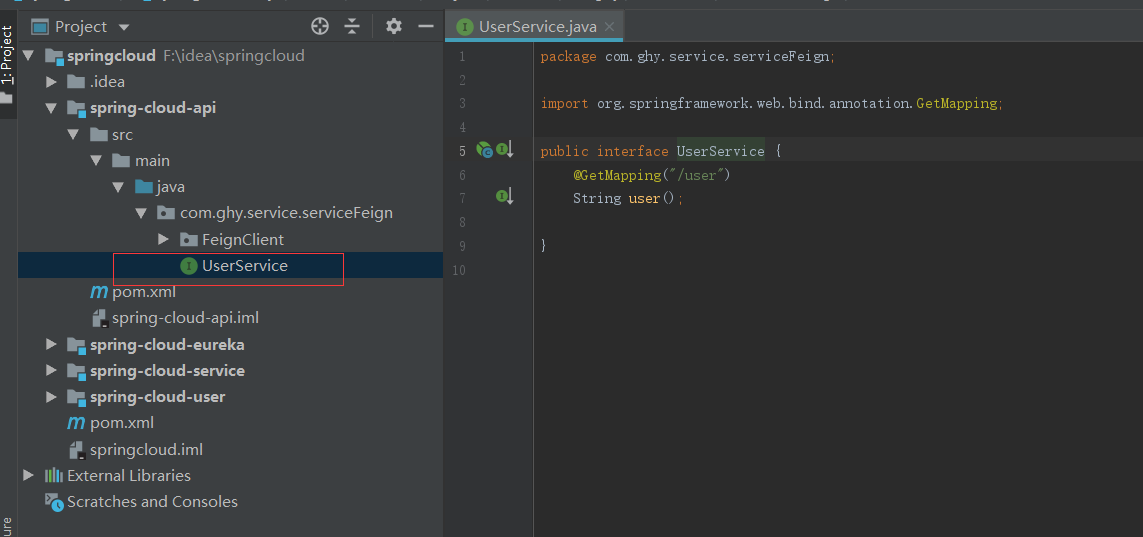
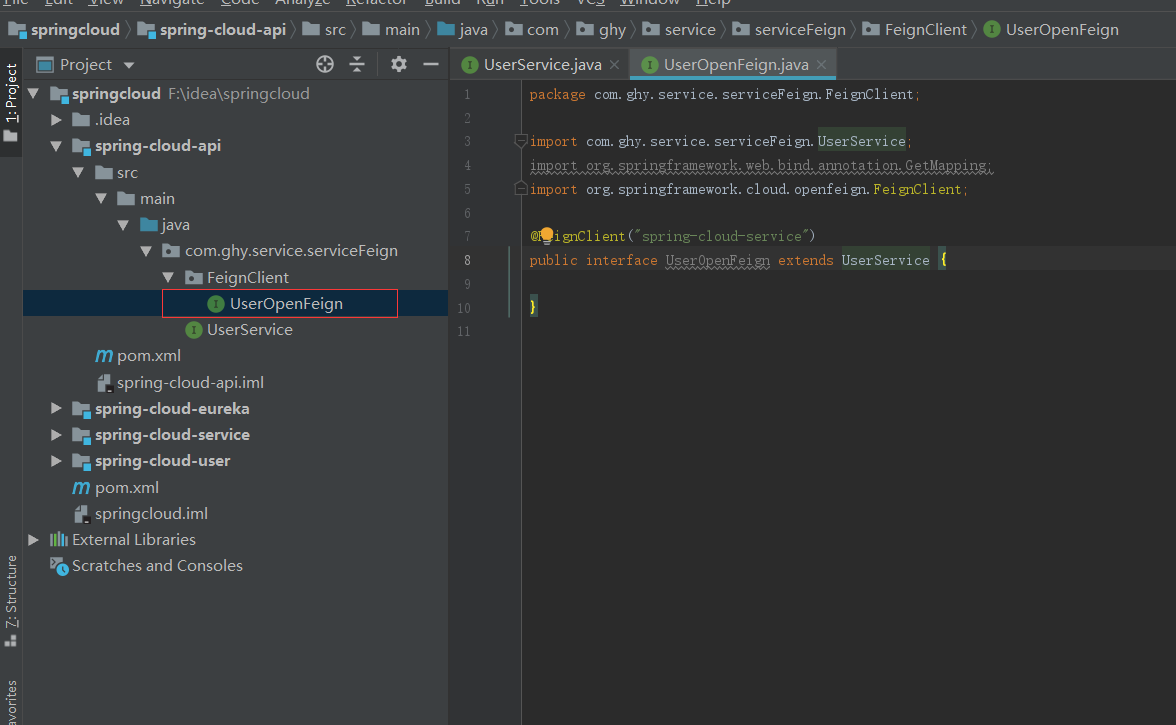
然后在spring-cloud-service中引入spring-cloud-api这个maven工程
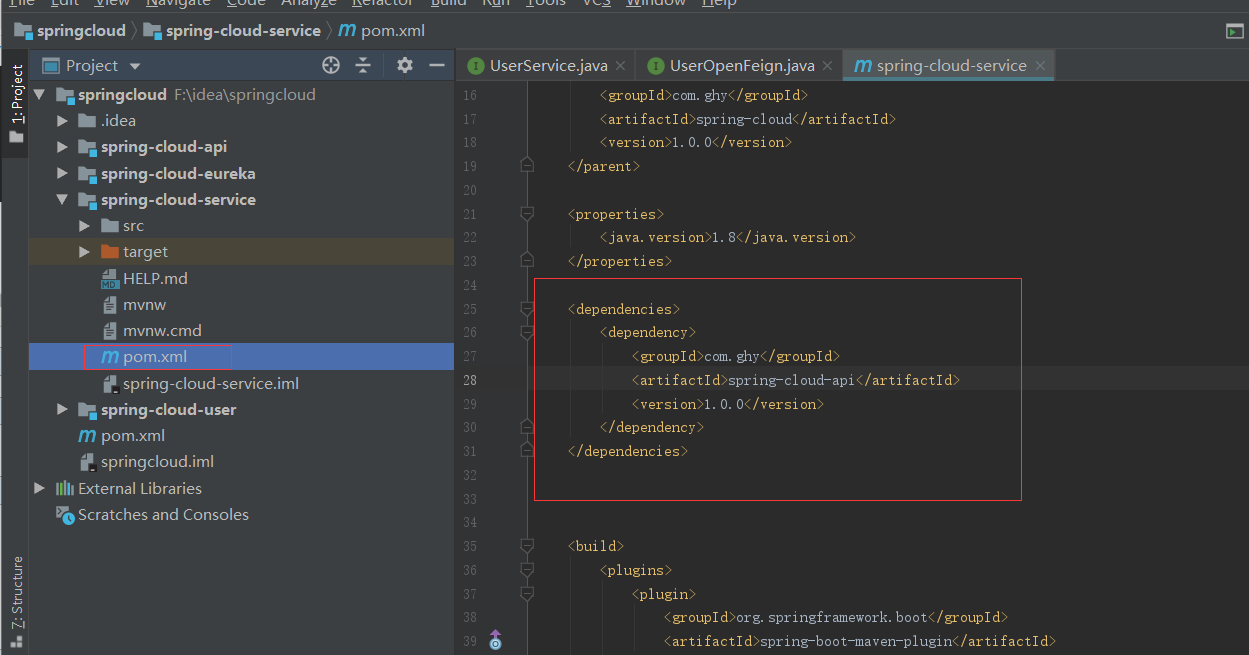
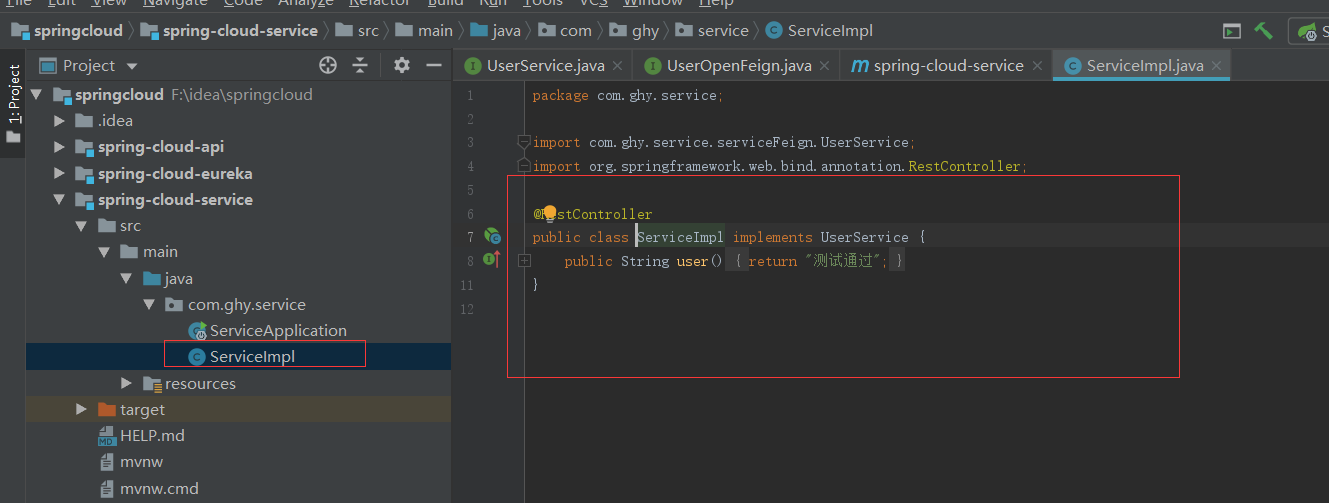
这样服务端的注册和业务代码就写完了,下面写调用者的代码
首先建立springboot工程spring-cloud-user
服务提供者的yml配置文件
server: port: 8090 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ #指向服务注册中心的地址 spring: application: name: spring-cloud-user
调用代码

在服务提供者中加上@EnableFeignClients指向Feign的包路径
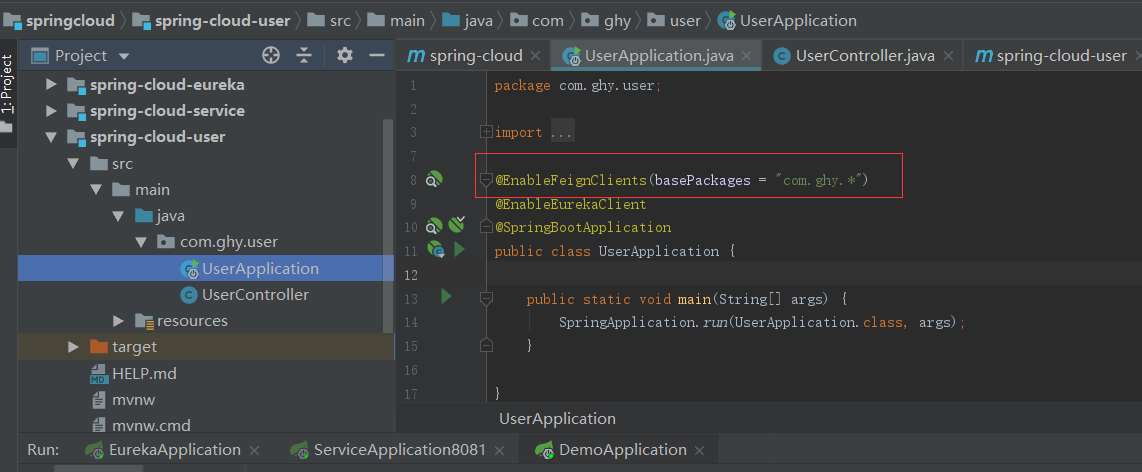
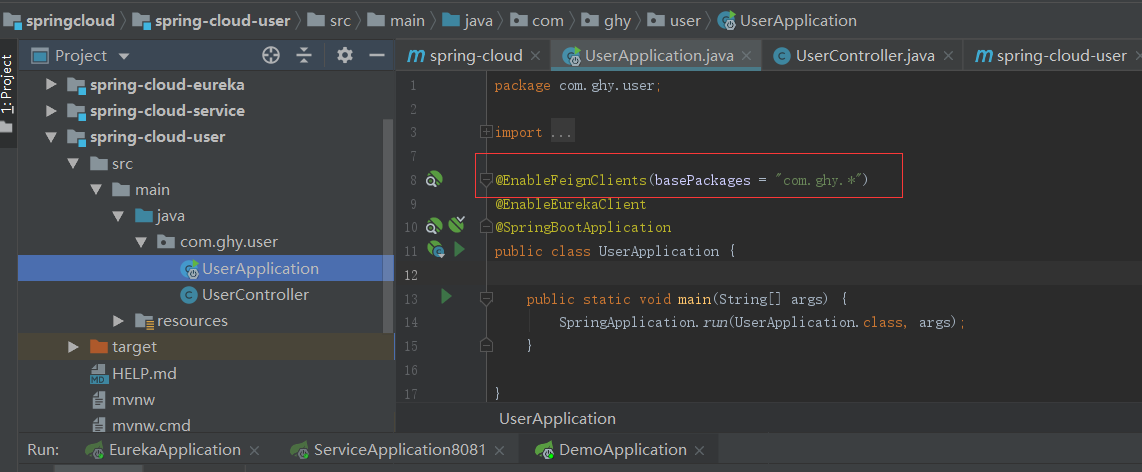
启动项目,会发现所有服务都注册上来了
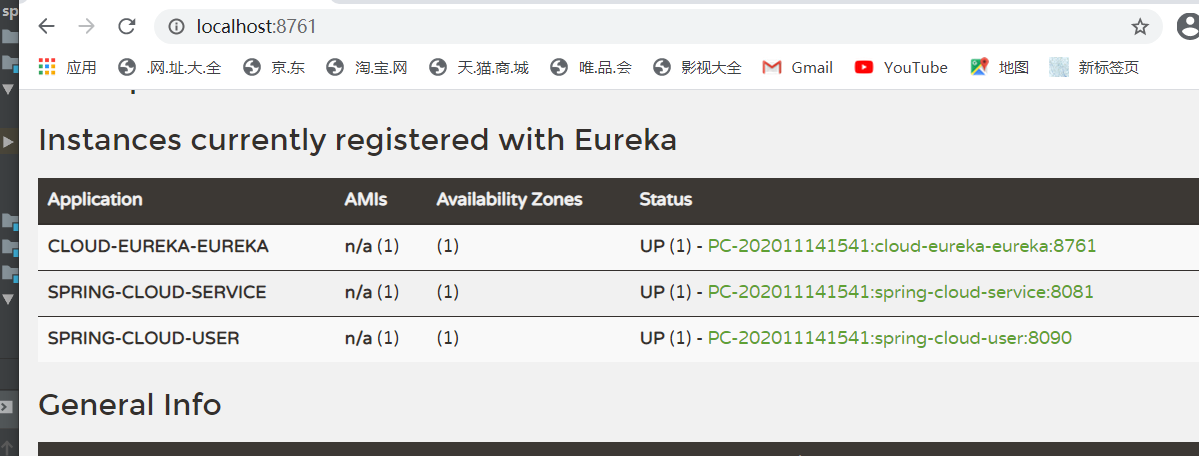
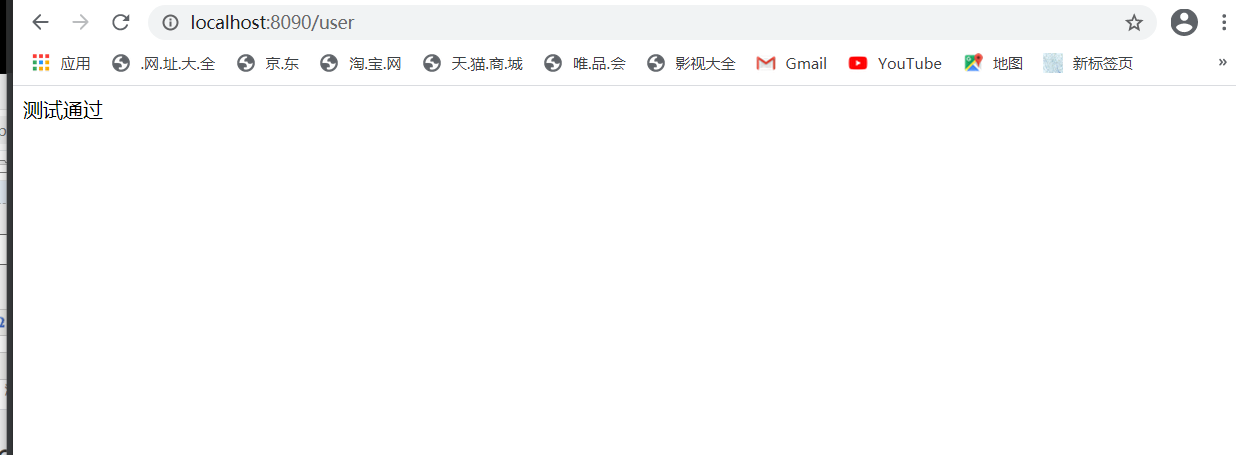
然后访问接口调用服务,可以发现服务调用者成功调用了服务提供者的服务
五、Eureka的高可用
当其中一台的服务发生故障时不影响整体服务状况,不能因为一台服务器的问题导致服务停止,高可用的方法有三种:主从方式、双机双工方式、集群工作方式。而Zookeeper采用的是主从方式、Eureka则采用的是集群方式,当多台服务器相互注册就形成了高可用,这样当其中的一台停止提供服务时,剩余的则会继续提供服务。
将spring-cloud-api的项目复制一份

spring-cloud-eureka-1中的配置如下
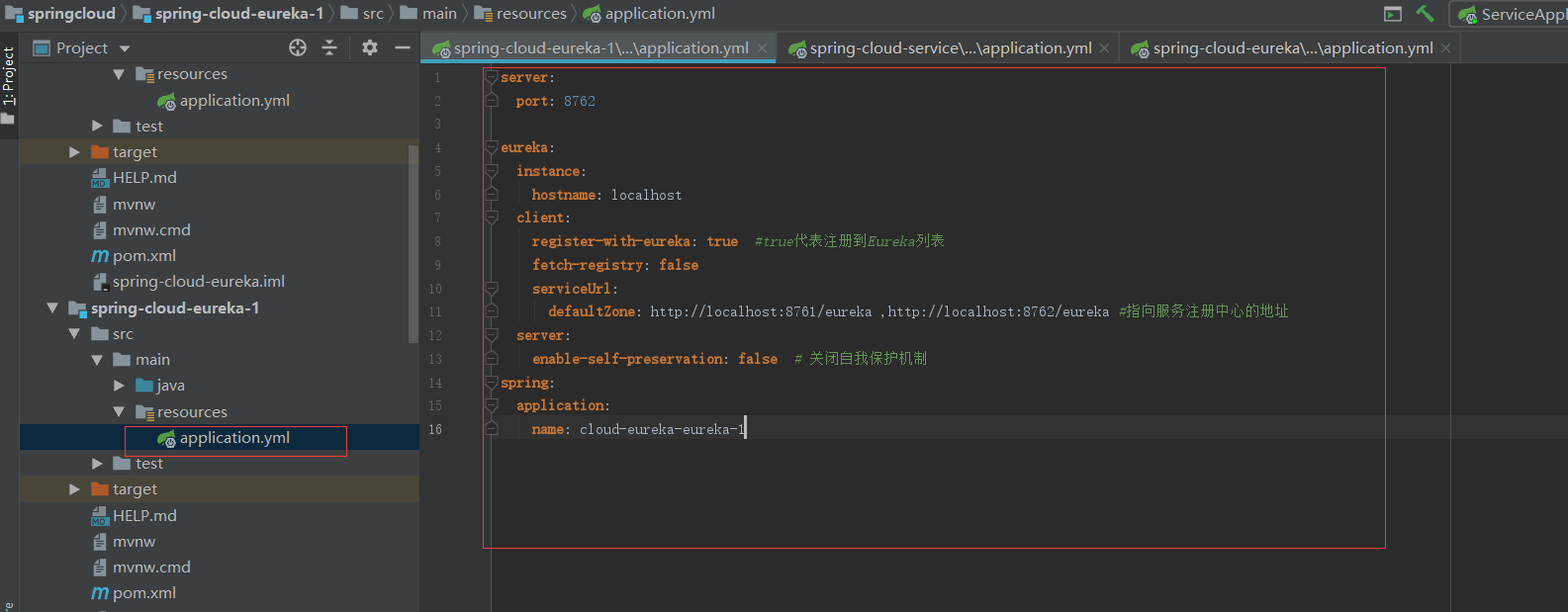
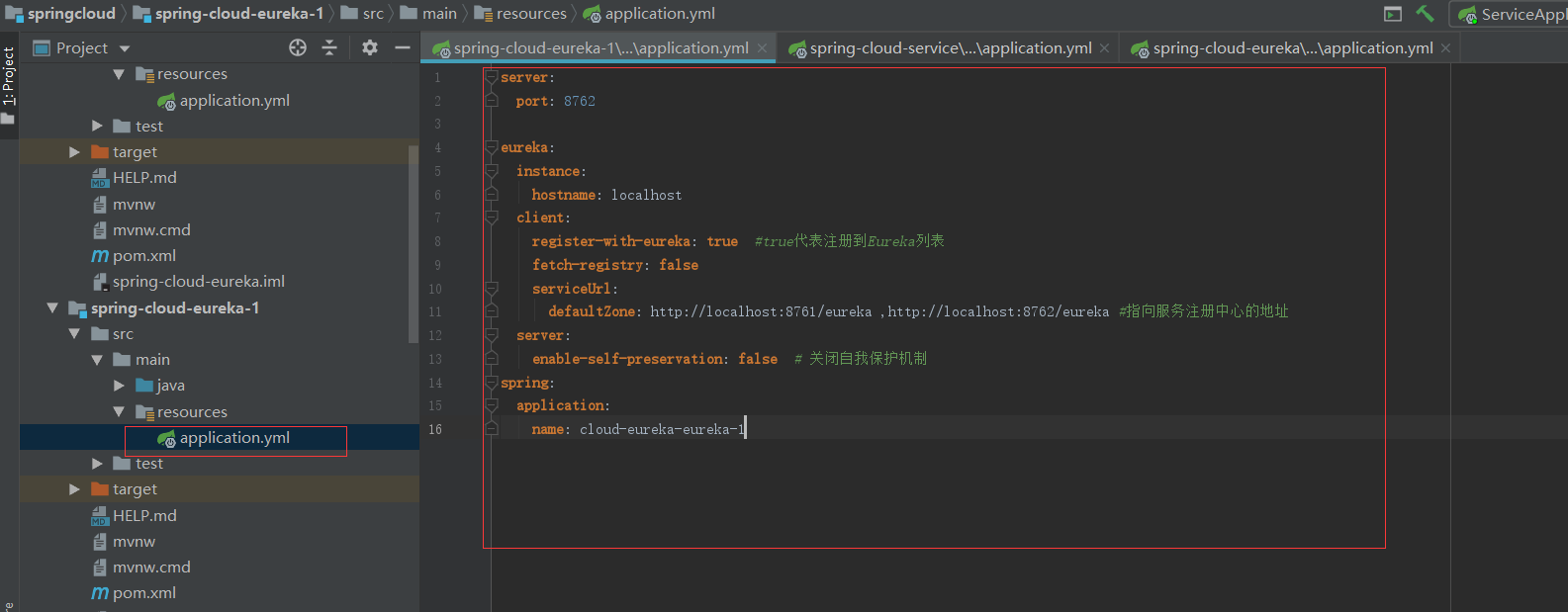
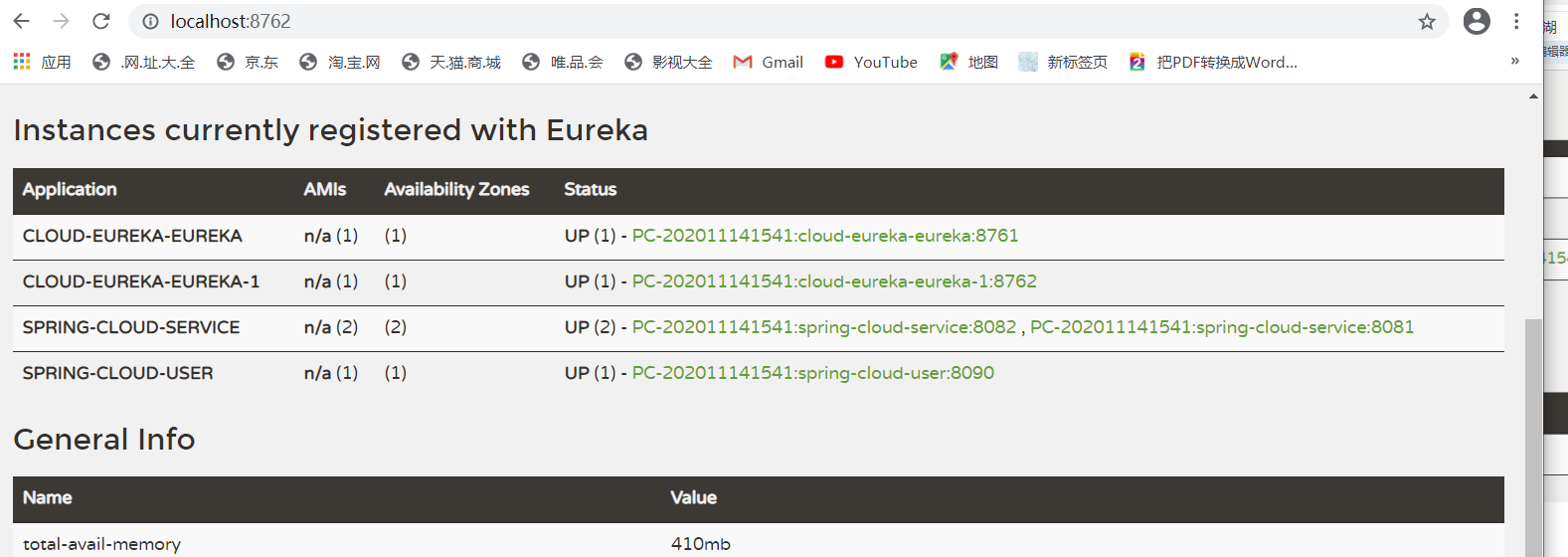
然后要做的事就是把其它所有服务的配置中心都改成
eureka: instance: hostname: localhost client: register-with-eureka: true #true代表注册到Eureka列表 fetch-registry: false serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka ,http://localhost:8762/eureka #指向服务注册中心的地址

六、Eureka的自我保护机制的原理
Eureka Server在运行期间会去统计心跳失败的比例在15分钟之内是否低于85% , 如果低于85%,Eureka Server会认为当前实例的客户端与自己的心跳连接出现了网络故障,那么Eureka Server会把这些实例保护起来,让这些实例不会过期导致实例剔除。这样做的目的是为了减少网络不稳定或者网络分区的情况下,Eureka Server将健康服务剔除下线的问题。 使用自我保护机制可以使得Eureka 集群更加健壮和稳定的运行。进入自我保护状态后,会出现以下几种情况Eureka Server不再从注册列表中移除因为长时间没有收到心跳而应该剔除的过期服务Eureka Server仍然能够接受新服务的注册和查询请求,但是不会被同步到其他节点上,保证当前节点依然可用。
6.1、自我保护机制的开启
#设置 eureka server同步失败的等待时间默认5分
#在这期间,它不向客户端提供服务注册信息
eureka.server.wait-time-in-ms-when-sync-empty=10000
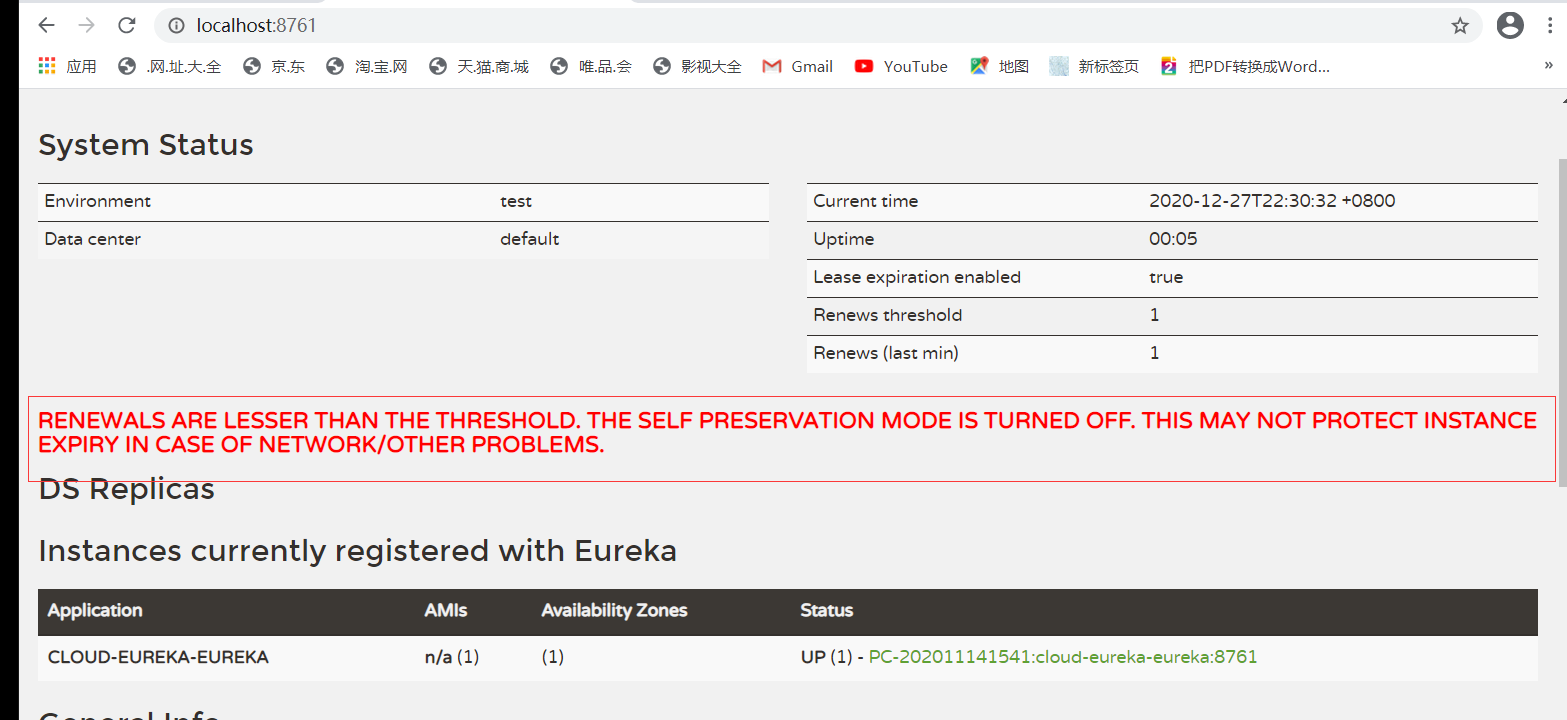
看下图可以发现进入了保护阶段,进入保护阶段有问题的节点就不会被剔除
在Eureka的自我保护机制中,有两个很重要的变量,Eureka的自我保护机制,都是围绕这两个变量来实现的,在AbstractInstanceRegistry这个类中定义的
protected volatile int numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold; //每分钟最小续约数量
protected volatile int expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews; //预期每分钟收到续约的 客户端数量,取决于注册到eureka server上的服务数量
protected void updateRenewsPerMinThreshold() { this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold = (int) (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews * (60.0 / serverConfig.getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds()) * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold()); }
1.在Eureka初始化时在EurekaBootstrap这个类中,有一个 initEurekaServerContext 方法
protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception { EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig = new DefaultEurekaServerConfig(); // For backward compatibility JsonXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(), XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH); XmlXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(), XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH); logger.info("Initializing the eureka client..."); logger.info(eurekaServerConfig.getJsonCodecName()); ServerCodecs serverCodecs = new DefaultServerCodecs(eurekaServerConfig); ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager = null; if (eurekaClient == null) { EurekaInstanceConfig instanceConfig = isCloud(ConfigurationManager.getDeploymentContext()) ? new CloudInstanceConfig() : new MyDataCenterInstanceConfig(); applicationInfoManager = new ApplicationInfoManager( instanceConfig, new EurekaConfigBasedInstanceInfoProvider(instanceConfig).get()); EurekaClientConfig eurekaClientConfig = new DefaultEurekaClientConfig(); eurekaClient = new DiscoveryClient(applicationInfoManager, eurekaClientConfig); } else { applicationInfoManager = eurekaClient.getApplicationInfoManager(); } PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry; if (isAws(applicationInfoManager.getInfo())) { registry = new AwsInstanceRegistry( eurekaServerConfig, eurekaClient.getEurekaClientConfig(), serverCodecs, eurekaClient ); awsBinder = new AwsBinderDelegate(eurekaServerConfig, eurekaClient.getEurekaClientConfig(), registry, applicationInfoManager); awsBinder.start(); } else { registry = new PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl( eurekaServerConfig, eurekaClient.getEurekaClientConfig(), serverCodecs, eurekaClient ); } PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes = getPeerEurekaNodes( registry, eurekaServerConfig, eurekaClient.getEurekaClientConfig(), serverCodecs, applicationInfoManager ); serverContext = new DefaultEurekaServerContext( eurekaServerConfig, serverCodecs, registry, peerEurekaNodes, applicationInfoManager ); EurekaServerContextHolder.initialize(serverContext); serverContext.initialize(); logger.info("Initialized server context"); // Copy registry from neighboring eureka node int registryCount = registry.syncUp(); registry.openForTraffic(applicationInfoManager, registryCount); // Register all monitoring statistics. EurekaMonitors.registerAllStats(); }
@Override public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) { // Renewals happen every 30 seconds and for a minute it should be a factor of 2. this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count;//初始化expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();//更新numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold logger.info("Got {} instances from neighboring DS node", count); logger.info("Renew threshold is: {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold); this.startupTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (count > 0) { this.peerInstancesTransferEmptyOnStartup = false; } DataCenterInfo.Name selfName = applicationInfoManager.getInfo().getDataCenterInfo().getName(); boolean isAws = Name.Amazon == selfName; if (isAws && serverConfig.shouldPrimeAwsReplicaConnections()) { logger.info("Priming AWS connections for all replicas.."); primeAwsReplicas(applicationInfoManager); } logger.info("Changing status to UP"); applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.UP); super.postInit(); }
2.PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.cancel
protected boolean internalCancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) { try { read.lock(); CANCEL.increment(isReplication); Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName); Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToCancel = null; if (gMap != null) { leaseToCancel = gMap.remove(id); } recentCanceledQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(), appName + "(" + id + ")")); InstanceStatus instanceStatus = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.remove(id); if (instanceStatus != null) { logger.debug("Removed instance id {} from the overridden map which has value {}", id, instanceStatus.name()); } if (leaseToCancel == null) { CANCEL_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication); logger.warn("DS: Registry: cancel failed because Lease is not registered for: {}/{}", appName, id); return false; } else { leaseToCancel.cancel(); InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToCancel.getHolder(); String vip = null; String svip = null; if (instanceInfo != null) { instanceInfo.setActionType(ActionType.DELETED); recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(leaseToCancel)); instanceInfo.setLastUpdatedTimestamp(); vip = instanceInfo.getVIPAddress(); svip = instanceInfo.getSecureVipAddress(); } invalidateCache(appName, vip, svip); logger.info("Cancelled instance {}/{} (replication={})", appName, id, isReplication); } } finally { read.unlock(); } synchronized (lock) { if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) { // Since the client wants to cancel it, reduce the number of clients to send renews. this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews - 1; updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); } } return true; }
3.PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.register
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) { try { read.lock(); Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName()); REGISTER.increment(isReplication); if (gMap == null) { final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>(); gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap); if (gMap == null) { gMap = gNewMap; } } Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId()); // Retain the last dirty timestamp without overwriting it, if there is already a lease if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) { Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp(); Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp(); logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp); // this is a > instead of a >= because if the timestamps are equal, we still take the remote transmitted // InstanceInfo instead of the server local copy. if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) { logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" + " than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp); logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant"); registrant = existingLease.getHolder(); } } else { // The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration synchronized (lock) { if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) { // Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renews this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1; updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); } } logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration"); } Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration); if (existingLease != null) { lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp()); } gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease); recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>( System.currentTimeMillis(), registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")")); // This is where the initial state transfer of overridden status happens if (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) { logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the " + "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId()); if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) { logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId()); overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus()); } } InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId()); if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) { logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap); registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap); } // Set the status based on the overridden status rules InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication); registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus); // If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestamp if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) { lease.serviceUp(); } registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED); recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease)); registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp(); invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress()); logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})", registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication); } finally { read.unlock(); } }
4.PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.scheduleRenewalThresholdUpdateTask
private void scheduleRenewalThresholdUpdateTask() { timer.schedule(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { updateRenewalThreshold(); } }, serverConfig.getRenewalThresholdUpdateIntervalMs(), serverConfig.getRenewalThresholdUpdateIntervalMs()); }
private void updateRenewalThreshold() { try { Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications(); int count = 0; for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) { for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) { if (this.isRegisterable(instance)) { ++count; } } } synchronized (lock) { // Update threshold only if the threshold is greater than the // current expected threshold or if self preservation is disabled. if ((count) > (serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold() * expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews) || (!this.isSelfPreservationModeEnabled())) { this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count; updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); } } logger.info("Current renewal threshold is : {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Cannot update renewal threshold", e); } }
七、自我保护机制触发任务
protected void postInit() { renewsLastMin.start(); if (evictionTaskRef.get() != null) { evictionTaskRef.get().cancel(); } evictionTaskRef.set(new EvictionTask()); evictionTimer.schedule(evictionTaskRef.get(), serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs(), serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs()); }
private final AtomicLong lastExecutionNanosRef = new AtomicLong(0l); @Override public void run() { try { long compensationTimeMs = getCompensationTimeMs(); logger.info("Running the evict task with compensationTime {}ms", compensationTimeMs); evict(compensationTimeMs); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Could not run the evict task", e); } }
public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) { logger.debug("Running the evict task");
if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) { logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled."); return; }
- 是否开启了自我保护机制,如果没有,则跳过,默认是开启
- 计算是否需要开启自我保护,判断最后一分钟收到的续约数量是否大于numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold
public boolean isLeaseExpirationEnabled() { if (!isSelfPreservationModeEnabled()) { // The self preservation mode is disabled, hence allowing the instances to expire. return true; } return numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold > 0 && getNumOfRenewsInLastMin() > numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold; }