前言:【模式总览】——————————by xingoo
模式意图
自定义某种语言后,给定一种文法标准,定义解释器,进行解析。
做过搜索的朋友们可能更了解一些,平时我们搜索所需要的词库,通常就需要用这种方式来实现。
应用场景
1 有复杂的语法分析场景
2 需要高效的解释,胜过快速的效率(即看中解释的结果,而放弃效率)
模式结构
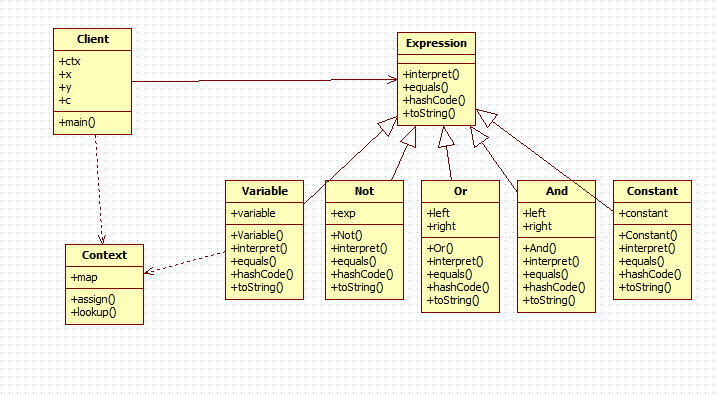
Expression 语法解释器的抽线模型
/** * 指定抽象表达式,具体表达式必须实现的方法 * @author xingoo * */ abstract class Expression{ /** * 以上下文环境为准,解释指定的表达式 * @param ctx * @return */ public abstract boolean interpret(Context ctx); /** * 检验两个表达式,是否相同 */ public abstract boolean equals(Object o); /** * 返回表达式代表的hashCode */ public abstract int hashCode(); /** * 转换成字符串 */ public abstract String toString(); }
以下是具体的解释器实现过程,这里主要模仿JAVA模式中的例子

/** * 常量表达式 * @author xingoo * */ class Constant extends Expression{ private boolean value; public Constant(boolean value){ this.value = value; } public boolean interpret(Context ctx){ return value; } public boolean equals(Object o){ if(o!=null && o instanceof Constant){ return this.value == ((Constant)o).value; } return false; } public int hashCode() { return (this.toString()).hashCode(); } public String toString() { return new Boolean(value).toString(); } } /** * 变量表达式 * @author xingoo * */ class Variable extends Expression{ private String name; public Variable(String name){ this.name = name; } public boolean interpret(Context ctx) { return ctx.lookup(this); } public boolean equals(Object o) { if(o!=null && o instanceof Variable){ return this.name.equals(((Variable)o).name); } return false; } public int hashCode() { return (this.toString()).hashCode(); } public String toString() { return name; } } /** * 与 表达式 * @author xingoo * */ class And extends Expression{ private Expression left,right; public And(Expression left,Expression right){ this.left = left; this.right = right; } public boolean interpret(Context ctx) { return left.interpret(ctx) && right.interpret(ctx); } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if(o!=null && o instanceof And){ return this.left.equals(((And)o).left) && this.right.equals(((And)o).right); } return false; } public int hashCode() { return (this.toString()).hashCode(); } public String toString() { return "("+left.toString()+" AND "+right.toString()+")"; } } /** * 或 表达式 * @author xingoo * */ class Or extends Expression{ private Expression left,right; public Or(Expression left,Expression right){ this.left = left; this.right = right; } public boolean interpret(Context ctx) { return left.interpret(ctx) || right.interpret(ctx); } public boolean equals(Object o) { if(o!=null && o instanceof Or){ return this.left.equals(((Or)o).left) && this.right.equals(((Or)o).right); } return false; } public int hashCode() { return (this.toString()).hashCode(); } public String toString() { return "("+left.toString()+" Or "+right.toString()+")"; } } /** * 非 表达式 * @author xingoo * */ class Not extends Expression{ private Expression exp; public Not(Expression exp){ this.exp = exp; } public boolean interpret(Context ctx) { return !exp.interpret(ctx); } public boolean equals(Object o) { if(o!=null && o instanceof Not){ return this.exp.equals(((Not)o).exp); } return false; } public int hashCode() { return (this.toString()).hashCode(); } public String toString() { return "(Not "+exp.toString()+")"; } }
Context 上下文环境,存储一些表达式的内容
/** * 上下文环境 * @author xingoo * */ class Context{ private HashMap map = new HashMap(); public void assign(Variable var,boolean value){ map.put(var, new Boolean(value)); } public boolean lookup(Variable var) throws IllegalArgumentException{ Boolean value = (Boolean)map.get(var); if(value == null){ throw new IllegalArgumentException(); } return value.booleanValue(); } }
全部代码

1 package com.xingoo.interpreter; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 /** 5 * 指定抽象表达式,具体表达式必须实现的方法 6 * @author xingoo 7 * 8 */ 9 abstract class Expression{ 10 /** 11 * 以上下文环境为准,解释指定的表达式 12 * @param ctx 13 * @return 14 */ 15 public abstract boolean interpret(Context ctx); 16 /** 17 * 检验两个表达式,是否相同 18 */ 19 public abstract boolean equals(Object o); 20 /** 21 * 返回表达式代表的hashCode 22 */ 23 public abstract int hashCode(); 24 /** 25 * 转换成字符串 26 */ 27 public abstract String toString(); 28 } 29 /** 30 * 常量表达式 31 * @author xingoo 32 * 33 */ 34 class Constant extends Expression{ 35 private boolean value; 36 public Constant(boolean value){ 37 this.value = value; 38 } 39 public boolean interpret(Context ctx){ 40 return value; 41 } 42 public boolean equals(Object o){ 43 if(o!=null && o instanceof Constant){ 44 return this.value == ((Constant)o).value; 45 } 46 return false; 47 } 48 public int hashCode() { 49 return (this.toString()).hashCode(); 50 } 51 public String toString() { 52 return new Boolean(value).toString(); 53 } 54 } 55 /** 56 * 变量表达式 57 * @author xingoo 58 * 59 */ 60 class Variable extends Expression{ 61 private String name; 62 63 public Variable(String name){ 64 this.name = name; 65 } 66 67 public boolean interpret(Context ctx) { 68 return ctx.lookup(this); 69 } 70 71 public boolean equals(Object o) { 72 if(o!=null && o instanceof Variable){ 73 return this.name.equals(((Variable)o).name); 74 } 75 return false; 76 } 77 78 public int hashCode() { 79 return (this.toString()).hashCode(); 80 } 81 public String toString() { 82 return name; 83 } 84 85 } 86 /** 87 * 与 表达式 88 * @author xingoo 89 * 90 */ 91 class And extends Expression{ 92 private Expression left,right; 93 94 public And(Expression left,Expression right){ 95 this.left = left; 96 this.right = right; 97 } 98 99 public boolean interpret(Context ctx) { 100 return left.interpret(ctx) && right.interpret(ctx); 101 } 102 103 @Override 104 public boolean equals(Object o) { 105 if(o!=null && o instanceof And){ 106 return this.left.equals(((And)o).left) && this.right.equals(((And)o).right); 107 } 108 return false; 109 } 110 111 public int hashCode() { 112 return (this.toString()).hashCode(); 113 } 114 115 public String toString() { 116 return "("+left.toString()+" AND "+right.toString()+")"; 117 } 118 } 119 /** 120 * 或 表达式 121 * @author xingoo 122 * 123 */ 124 class Or extends Expression{ 125 private Expression left,right; 126 127 public Or(Expression left,Expression right){ 128 this.left = left; 129 this.right = right; 130 } 131 132 public boolean interpret(Context ctx) { 133 return left.interpret(ctx) || right.interpret(ctx); 134 } 135 136 public boolean equals(Object o) { 137 if(o!=null && o instanceof Or){ 138 return this.left.equals(((Or)o).left) && this.right.equals(((Or)o).right); 139 } 140 return false; 141 } 142 143 public int hashCode() { 144 return (this.toString()).hashCode(); 145 } 146 147 public String toString() { 148 return "("+left.toString()+" Or "+right.toString()+")"; 149 } 150 } 151 /** 152 * 非 表达式 153 * @author xingoo 154 * 155 */ 156 class Not extends Expression{ 157 private Expression exp; 158 159 public Not(Expression exp){ 160 this.exp = exp; 161 } 162 163 public boolean interpret(Context ctx) { 164 return !exp.interpret(ctx); 165 } 166 167 public boolean equals(Object o) { 168 if(o!=null && o instanceof Not){ 169 return this.exp.equals(((Not)o).exp); 170 } 171 return false; 172 } 173 174 public int hashCode() { 175 return (this.toString()).hashCode(); 176 } 177 178 public String toString() { 179 return "(Not "+exp.toString()+")"; 180 } 181 182 } 183 /** 184 * 上下文环境 185 * @author xingoo 186 * 187 */ 188 class Context{ 189 190 private HashMap map = new HashMap(); 191 192 public void assign(Variable var,boolean value){ 193 map.put(var, new Boolean(value)); 194 } 195 196 public boolean lookup(Variable var) throws IllegalArgumentException{ 197 Boolean value = (Boolean)map.get(var); 198 if(value == null){ 199 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 200 } 201 return value.booleanValue(); 202 } 203 } 204 public class Client { 205 private static Context ctx; 206 private static Expression exp; 207 public static void main(String[] args) { 208 ctx = new Context(); 209 Variable x = new Variable("x"); 210 Variable y = new Variable("y"); 211 212 Constant c = new Constant(true); 213 214 //放入上下文中 215 ctx.assign(x, false); 216 ctx.assign(y, true); 217 218 exp = new Or(new And(c,x),new And(y,new Not(x))); 219 System.out.println("x = "+x.interpret(ctx)); 220 System.out.println("y = "+y.interpret(ctx)); 221 System.out.println(exp.toString() +" = "+exp.interpret(ctx)); 222 } 223 }
运行结果
x = false y = true ((true AND x) Or (y AND (Not x))) = true
