目录
1. 数据结构中的概念
1、数据结构是什么
1、简单来说,数据结果就是设计数据以何种方式存储在计算机中
2、比如:列表,集合,与字典等都是一种数据结构
3、程序 = 数据结构 + 算法
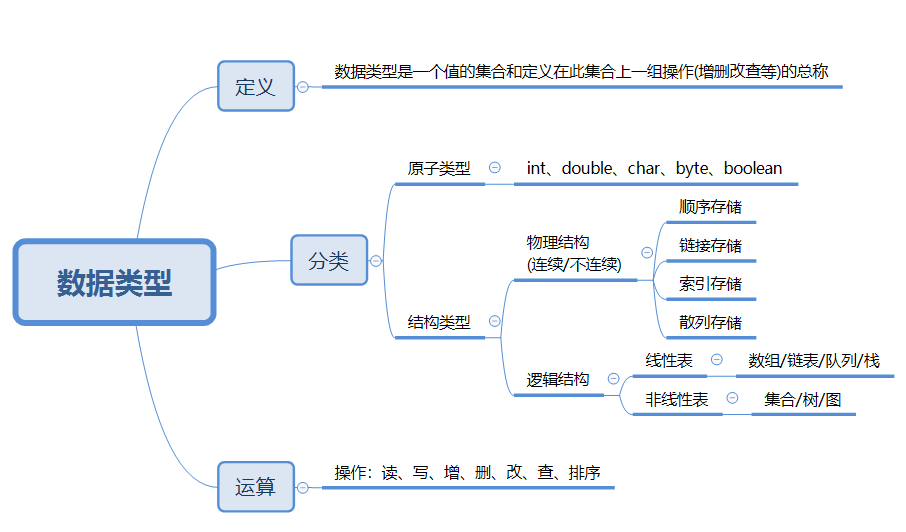
2、数据结构与数据类型
1)数据类型:
说明:数据类型是一个值的集合和定义在此集合上一组操作(通常是增删改查或者操作读写的方法)的总称
数据类型:int、str、boolean、byte
2)数据结构:
说明:数据以什么方式构成,如何进行存储(数据结构是数据类型中的一种:结构类型)
数据结构:数组、栈、队列、链表、树、图、堆、散列表等
python数据结构:列表、集合、字典、元祖
3、数据结构与数据类型比较
1. 数据类型的分类为:原子类型 和 结构类型;
2. 原子类型 = 一种值的集合 + 定义在值集合上的一组操作。(比如:python中的int,float,字符串)
3. 结构类型 = 一种数据结构 + 定义在这种数据结构上的一组操作。(比如:python中的列表,字典,元组)
原子类型 + 结构类型 = 数据类型
注:数据类型是一个值的集合和定义在此集合上一组操作(通常是增删改查或者操作读写的方法)的总称
2. 栈(stack)
1、栈的定义
栈是一种数据集合,可以理解为只能在一端进行插入或删除操作的列表
2、栈的特点
后进先出(last-in, first-out)
3、栈的概念
栈顶,栈底
4、栈的基本操作
进栈(压栈):push
出栈:pop
取栈顶:gettop

#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class Stack(object): def __init__(self): self.stack = [] # 初始化一个栈 def push(self,item): # 入栈 self.stack.append(item) def gettop(self): # 获取栈顶元素 return self.stack[-1] def pop(self): # 出栈 return self.stack.pop() if __name__ == '__main__': s = Stack() s.push(1) s.push(2) print(s.stack) python实现栈功能
5、栈的使用:匹配括号是否成对出现

def check_kuohao(s): stack = [] for char in s: if char in ['(','[','{']: stack.append(char) elif char == ')': if len(stack)>0 and stack[-1] == '(': stack.pop() else: return False elif char == ']': if len(stack) > 0 and stack[-1] == '[': stack.pop() else: return False elif char == '}': if len(stack) > 0 and stack[-1] == '{': stack.pop() else: return False if len(stack) == 0: return True else: return False print(check_kuohao('(){}{}[]')) #True 匹配括号是否成对出现
3. 队列
1、队列定义
1、队列是一个数据集合,仅允许在列表的一端进行插入,另一端进行删除
2、插入的一端称为队尾(rear),插入动作叫进队或入队
3、进行删除的一端称为对头(front),删除动作称为出队
4、队列性质:先进先出(First-in, First-out)
5、双向队列:队列的两端都允许进行进队和出队操作
2、对列使用方法
1、导入: from collectios import deque
2、创建队列:queue = deque(li)
3、进队: append
4、出队: popleft
5、双向队列队首进队:appendleft
6、双向队列队尾出队:pop

from queue import Queue #1. 基本FIFO队列 先进先出 FIFO即First in First Out,先进先出 #2. maxsize设置队列中,数据上限,小于或等于0则不限制,容器中大于这个数则阻塞,直到队列中的数据被消掉 q = Queue(maxsize=0) #3. 写入队列数据 q.put(0) q.put(1) q.put(2) #4. 输出当前队列所有数据 print(q.queue) #5. 删除队列数据,并返回该数据 q.get() #6. 输也所有队列数据 print(q.queue) python操作队列queue
3、队列应用场景
1. 队列主要的功能是在多个进程间共享数据,实现业务解耦,提高效率
2. 生产者线程只需要把任务放入队列中,消费者线程只需要到队列中取数据进行处理
4、队列与列表区别
1. 列表中数据虽然是排列的,但数据被取走后还会保留,而队列中这个容器的数据被取后将不会保留
4. 链表
1、单链表
注:链表中每个元素都是一个对象,每个对象称为一个节点,包含有数据域key和指向下一节点的指针next,通过各个节点间的相互连接,最终串联成一个链表
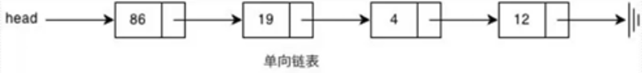

class Node(object): def __init__(self, item,next=None): self.item = item self.next = next l = Node(1,Node(2,Node(3,Node(4)))) print(l.item) print(l.next.item) python模拟链表数据类型

#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class Node(object): def __init__(self, item): self.item = item self.next = None class DLinkList(object): def __init__(self): self._head = None def is_empty(self): return self._head == None def append(self, item): '''尾部追加元素''' node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node else: cur = self._head while cur.next != None: cur = cur.next cur.next = node def add(self, item): """头部插入元素""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node # 如果是空链表,将_head指向node else: node.next = self._head # 将node的next指向_head的头节点 self._head = node # 将_head 指向node def travel(self): cur = self._head while cur != None: print cur.item, cur = cur.next print "" def remove(self, item): """删除元素""" if self.is_empty(): return else: cur = self._head if cur.item == item: # 如果首节点的元素即是要删除的元素 if cur.next == None: # 如果链表只有这一个节点 self._head = None else: # 将_head指向第二个节点 self._head = cur.next return while cur != None: if cur.next.item == item: cur.next = cur.next.next break cur = cur.next def insert(self, pos, item): """在指定位置添加节点""" if pos <= 0: self.add(item) elif pos > (self.length() - 1): self.append(item) else: node = Node(item) cur = self._head count = 0 # 移动到指定位置的前一个位置 while count < (pos - 1): count += 1 cur_next = cur.next # 将node的next指向cur的下一个节点 cur.next = node node.next = cur_next def length(self): """返回链表的长度""" cur = self._head count = 0 while cur != None: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count if __name__ == '__main__': ll = DLinkList() # 1、将链表后面追加三个元素:1,2,3 ll.append(1) ll.append(2) ll.append(3) ll.travel() # 1 2 3 # 2、将链表头部插入一个元素:0 ll.add(0) ll.travel() # 1 2 3 ==> 0 1 2 3 # 3、删除链表中的元素:3 ll.remove(3) ll.travel() # 0 1 2 3 ==> 0 1 2 # 4、在链表的第2号位置插入元素:8 ll.insert(2,8) ll.travel() # 0 1 2 ==> 0 8 1 2 单链表增删改查

#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class Node(object): def __init__(self, item): self.item = item self.next = None class DLinkList(object): def __init__(self): self._head = None def is_empty(self): return self._head == None def append(self, item): '''尾部追加元素''' node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node else: cur = self._head while cur.next != None: cur = cur.next cur.next = node def add(self, item): """头部插入元素""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node # 如果是空链表,将_head指向node else: node.next = self._head # 将node的next指向_head的头节点 self._head = node # 将_head 指向node def travel(self): cur = self._head while cur != None: print cur.item, cur = cur.next print "" def remove(self, item): """删除元素""" if self.is_empty(): return else: cur = self._head if cur.item == item: # 如果首节点的元素即是要删除的元素 if cur.next == None: # 如果链表只有这一个节点 self._head = None else: # 将_head指向第二个节点 self._head = cur.next return while cur != None: if cur.next.item == item: cur.next = cur.next.next break cur = cur.next def insert(self, pos, item): """在指定位置添加节点""" if pos <= 0: self.add(item) elif pos > (self.length() - 1): self.append(item) else: node = Node(item) cur = self._head count = 0 # 移动到指定位置的前一个位置 while count < (pos - 1): count += 1 cur_next = cur.next # 将node的next指向cur的下一个节点 cur.next = node node.next = cur_next def length(self): """返回链表的长度""" cur = self._head count = 0 while cur != None: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count if __name__ == '__main__': ll = DLinkList() # 1、将链表后面追加三个元素:1,2,3 ll.append(1) ll.append(2) ll.append(3) ll.travel() # 1 2 3 # 2、将链表头部插入一个元素:0 ll.add(0) ll.travel() # 1 2 3 ==> 0 1 2 3 # 3、删除链表中的元素:3 ll.remove(3) ll.travel() # 0 1 2 3 ==> 0 1 2 # 4、在链表的第2号位置插入元素:8 ll.insert(2,8) ll.travel() # 0 1 2 ==> 0 8 1 2 单链表增删改查

#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class ListNode(object): def __init__(self, val, next=None): self.val = val self.next = next # 归并法: 对链表排序 class Solution: def sortList(self, head): if head is None or head.next is None: return head pre = head slow = head # 使用快慢指针来确定中点 fast = head while fast and fast.next: pre = slow slow = slow.next fast = fast.next.next left = head right = pre.next pre.next = None # 从中间打断链表 left = self.sortList(left) right = self.sortList(right) return self.merge(left, right) def merge(self, left, right): pre = ListNode(-1) first = pre while left and right: if left.val < right.val: pre.next = left pre = left left = left.next else: pre.next = right pre = right right = right.next if left: pre.next = left else: pre.next = right return first.next node1 = ListNode(4) node2 = ListNode(3) node3 = ListNode(2) node4 = ListNode(1) node1.next = node2 node2.next = node3 node3.next = node4 s = Solution() result = s.sortList(node1) while (result != None): print result.val, # 1 2 3 4 result = result.next 链表排序:归并排序算法实现

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- def mergesort(seq): if len(seq) <= 1: return seq mid = int(len(seq) / 2) left = mergesort(seq[:mid]) right = mergesort(seq[mid:]) return merge(left, right) def merge(left, right): result = [] i, j = 0, 0 while i < len(left) and j < len(right): if left[i] <= right[j]: result.append(left[i]) i += 1 else: result.append(right[j]) j += 1 result += left[i:] result += right[j:] return result if __name__ == '__main__': seq = [10,4,6,3,8,2,5,7] print mergesort(seq) # [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10] 对python列表排序:归并排序 对比
2、双链表
注:双链表中每个节点有两个指针:一个指针指向后面节点、一个指向前面节点


#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class Node(object): """双向链表节点""" def __init__(self, item): self.item = item self.next = None self.prev = None class DLinkList(object): """双向链表""" def __init__(self): self._head = None def is_empty(self): """判断链表是否为空""" return self._head == None def length(self): """返回链表的长度""" cur = self._head count = 0 while cur != None: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def travel(self): """遍历链表""" cur = self._head while cur != None: print cur.item, cur = cur.next print "" def add(self, item): """头部插入元素""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): # 如果是空链表,将_head指向node self._head = node else: # 将node的next指向_head的头节点 node.next = self._head # 将_head的头节点的prev指向node self._head.prev = node # 将_head 指向node self._head = node def append(self, item): """尾部插入元素""" node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): # 如果是空链表,将_head指向node self._head = node else: # 移动到链表尾部 cur = self._head while cur.next != None: cur = cur.next # 将尾节点cur的next指向node cur.next = node # 将node的prev指向cur node.prev = cur def search(self, item): """查找元素是否存在""" cur = self._head while cur != None: if cur.item == item: return True cur = cur.next return False def insert(self, pos, item): """在指定位置添加节点""" if pos <= 0: self.add(item) elif pos > (self.length() - 1): self.append(item) else: node = Node(item) cur = self._head count = 0 # 移动到指定位置的前一个位置 while count < (pos - 1): count += 1 cur = cur.next # 将node的prev指向cur node.prev = cur # 将node的next指向cur的下一个节点 node.next = cur.next # 将cur的下一个节点的prev指向node cur.next.prev = node # 将cur的next指向node cur.next = node def remove(self, item): """删除元素""" if self.is_empty(): return else: cur = self._head if cur.item == item: # 如果首节点的元素即是要删除的元素 if cur.next == None: # 如果链表只有这一个节点 self._head = None else: # 将第二个节点的prev设置为None cur.next.prev = None # 将_head指向第二个节点 self._head = cur.next return while cur != None: if cur.item == item: # 将cur的前一个节点的next指向cur的后一个节点 cur.prev.next = cur.next # 将cur的后一个节点的prev指向cur的前一个节点 cur.next.prev = cur.prev break cur = cur.next if __name__ == "__main__": ll = DLinkList() ll.add(1) ll.add(2) # ll.append(3) # ll.insert(2, 4) # ll.insert(4, 5) # ll.insert(0, 6) # print "length:",ll.length() # ll.travel() # print ll.search(3) # print ll.search(4) # ll.remove(1) print "length:",ll.length() ll.travel() 双链表增删改查

#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class Node(object): def __init__(self, item): self.item = item self.next = None self.prev = None class DLinkList(object): def __init__(self): self._head = None def is_empty(self): return self._head == None def append(self, item): node = Node(item) if self.is_empty(): self._head = node else: cur = self._head while cur.next != None: cur = cur.next cur.next = node node.prev = cur def travel(self): cur = self._head while cur != None: print cur.item, cur = cur.next if __name__ == '__main__': ll = DLinkList() ll.append(1) ll.append(2) ll.append(3) # print ll._head.item # 打印第一个元素:1 # print ll._head.next.item # 打印第二个元素:2 # print ll._head.next.next.item # 打印第三个元素:3 ll.travel() # 1 2 3 双链表追加和遍历
5. 数组
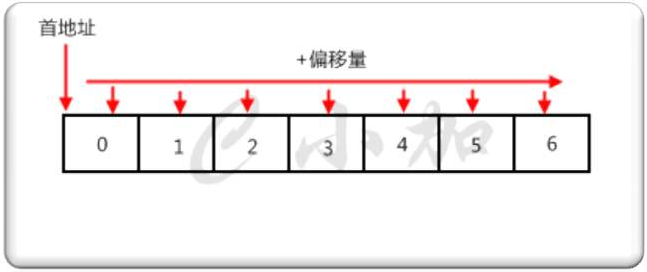
1、数组定义
1. 所谓数组,就是相同数据类型的元素按一定顺序排列的集合
2. 在Java等其他语言中并不是所有的数据都能存储到数组中,只有相同类型的数据才可以一起存储到数组中。
3. 因为数组在存储数据时是按顺序存储的,存储数据的内存也是连续的,所以他的特点就是寻址读取数据比较容易,插入和删除比较困难。
2、python中list与数组比较
1. python中的list是python的内置数据类型,list中的数据类不必相同的,而array的中的类型必须全部相同。
2. 在list中的数据类型保存的是数据的存放的地址,简单的说就是指针,并非数据
3. 否则这样保存一个list就太麻烦了,例如list1=[1,2,3,'a']需要4个指针和四个数据,增加了存储和消耗cpu。