一、什么是Django ContentTypes?
Django ContentTypes是由Django框架提供的一个核心功能,它对当前项目中所有基于Django驱动的model提供了更高层次的抽象接口。主要用来创建模型间的通用关系(generic relation)。
进一步了解ContentTypes可以直接查阅以下这两个链接:
- Django official documentation:The contenttypes framework
- stackoverflow: How exactly do Django content types work?
二、Django ContentTypes做了什么?
当创建一个django项目时,可以看到在默认的INSTALL_APPS已经包含了django.contrib.contenttypes。
# Application definition
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'app01.apps.App01Config',
]
注意:django.contrib.contenttypes是在django.contrib.auth之后,这是因为auth中的permission系统是根据contenttypes来实现的。
导入contenttypes组件:
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
查看django.contrib.contenttypes.models.ContentType类的内容:
class ContentType(models.Model):
app_label = models.CharField(max_length=100)
model = models.CharField(_('python model class name'), max_length=100)
objects = ContentTypeManager()
class Meta:
verbose_name = _('content type')
verbose_name_plural = _('content types')
db_table = 'django_content_type'
unique_together = (('app_label', 'model'),)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
可以看到ContentType就是一个简单的django model,而且它在数据库中的表的名字为django_content_type。
在第一次对Django的model进行migrate之后,就可以发现在数据库中出现了一张默认生成的名为django_content_type的表。
如果没有建立任何的model,默认django_content_type是前六项:
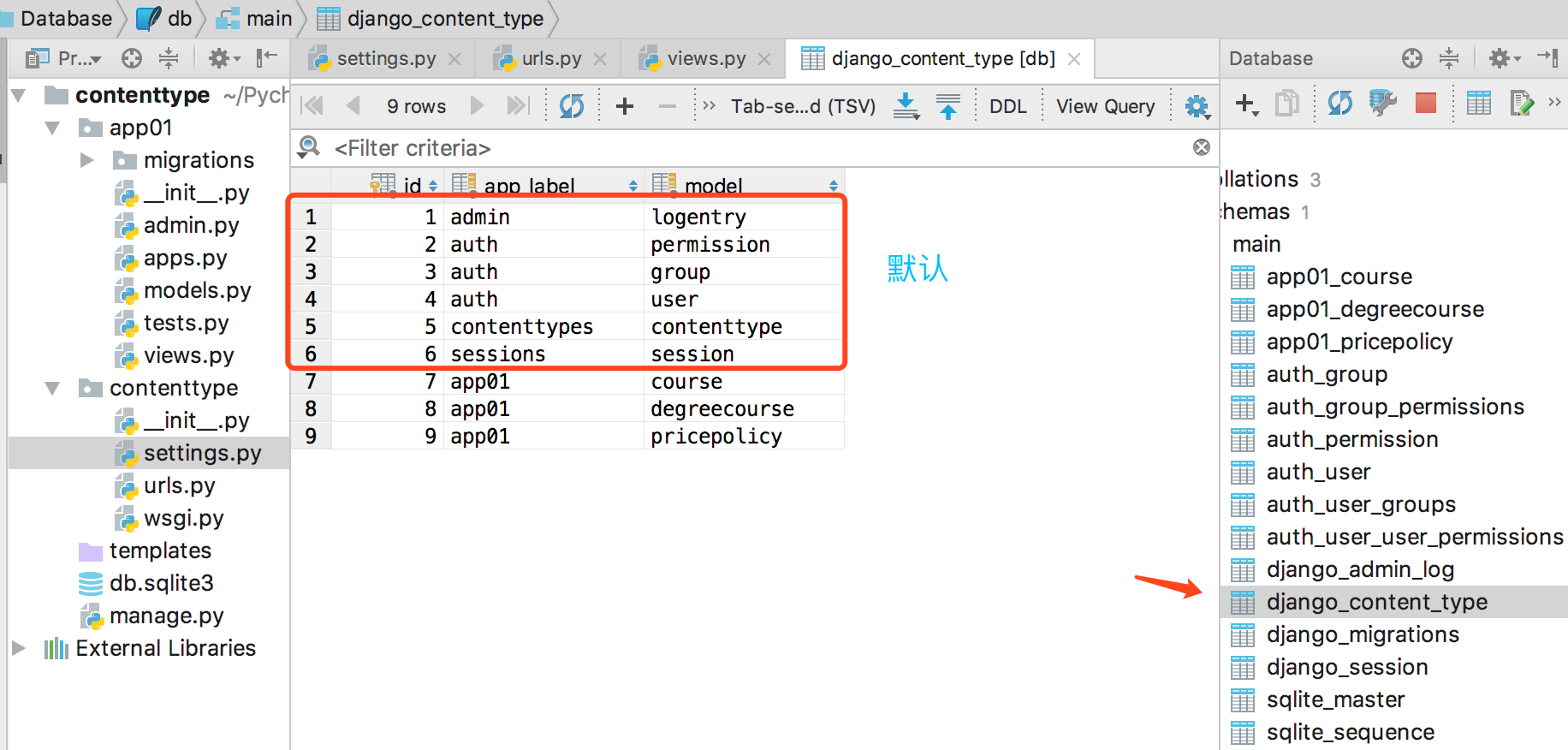
django_content_type记录了当前的Django项目中所有model所属的app(即app_label属性)以及model的名字(即model属性)。
django_content_type并不只是记录属性这么简单.了contenttypes是对model的一次封装,因此可以通过contenttypes动态的访问model类型,而不需要每次import具体的model类型。
1、ContentType实例提供的接口
- ContentType.model_class()
获取当前ContentType类型所代表的模型类
- ContentType.get_object_for_this_type()
使用当前ContentType类型所代表的模型类做一次get查询
2、ContentType管理器(manager)提供的j接口
- ContentType.objects.get_for_id()
- 通过id寻找ContentType类型,这个跟传统的get方法的区别就是它跟get_for_model共享一个缓存,因此更为推荐。
- ContentType.objects.get_for_model()
- 通过model或者model的实例来寻找ContentType类型
三、Django ContentTypes框架使用场景
1、设计模型(创建表结构)
假设我们创建如下模型,里面包含学位课程、专题课程、价格策略。
价格策略既可以是专题课程的价格策略,也可以是学位课程的价格策略。需要在pricepolicy对象里添加非常多的ForeignKey。示例如下所示:
class Food(models.Model): """ id title 1 面包 2 牛奶 """ title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 不会生成字段 只用于反向查询 coupons = GenericRelation(to="Coupon") class Fruit(models.Model): """ id title 1 苹果 2 香蕉 """ title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 如果有40张表,则每一个都要建立外键关系 class Coupon(models.Model): """ id title food_id fruit_id 1 面包九五折 1 null 2 香蕉满10元减5元 null 2 """ title = models.CharField(max_length=32) food = models.ForeignKey(to="Food") fruit = models.ForeignKey(to="Fruit")
这样做很傻,会造成代码重复和字段浪费。有一种优化的方案是:用两个字段去定位对象不用去创建多个外键关系。
# 方法二:用两个字段去定位对象不用去创建多个外键关系 class Coupon(models.Model): """ id title table_id object_id(对应表对应对象的ID) 1 面包九五折 1 1 2 香蕉满10元减5元 2 2 """ title = models.CharField(max_length=32) table = models.ForeignKey(to="Table") # 与table表建立外键关系 object_id = models.IntegerField() # 由object_id定位到表中的某一个对象,但没有建立外键关系 class Table(models.Model): """ id app_name table_name 1 demo food 2 demo fruit """ app_name = models.CharField(max_length=32) table_name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
最好的方式是,只有当你需要对某个对象或模型进行评论时,才创建pricepolicy与那个模型的关系。示例如下所示:
# 方法三:基于ContentTypes创建表结构 class Coupon(models.Model): title = models.CharField(max_length=32) # 优惠券名称 # 第一步:与ContentType表绑定外键关系 content_type = models.ForeignKey(to=ContentType, on_delete=None) # 第二步:建立对象id object_id = models.IntegerField() # 第三步:content_type和object_id绑定外键关系 content_object = GenericForeignKey("content_type", "object_id")
学位课程、专题课程、价格策略基于django contenttypes创建表结构如下所示:
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey, GenericRelation
class DegreeCourse(models.Model):
"""学位课程"""
name = models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True)
course_img = models.CharField(max_length=255, verbose_name="缩略图")
brief = models.TextField(verbose_name="学位课程简介", )
class Course(models.Model):
"""专题课程"""
name = models.CharField(max_length=128, unique=True)
course_img = models.CharField(max_length=255)
# 不会在数据库生成列,只用于帮助你进行查询
policy_list = GenericRelation("PricePolicy")
class PricePolicy(models.Model):
"""价格策略表"""
content_type = models.ForeignKey(ContentType, on_delete=models.CASCADE) # 关联course or degree_course
object_id = models.PositiveIntegerField() # 正整数PositiveInteger
# GenericForeignKey不会在数据库生成列,只用于帮助你进行添加和查询
content_object = GenericForeignKey('content_type', 'object_id') # 将两个字段放在这个对象中
# 周期
valid_period_choices = (
(1, '1天'),
(3, '3天'),
(7, '1周'), (14, '2周'),
(30, '1个月'),
(60, '2个月'),
(90, '3个月'),
(180, '6个月'), (210, '12个月'),
(540, '18个月'), (720, '24个月'),
)
# 价格
valid_period = models.SmallIntegerField(choices=valid_period_choices)
price = models.FloatField()
(1)GenericForeignKey
Django ContentType提供了一种GenericForeignKey的类型,通过这种类型可以指定content_object。
GenericForeignKey不会在数据库生成列,只用于帮助你进行添加和查询。
(2)GenericRelation
GenericRelation不会在数据库生成列,只用于帮助你进行查询。
(3)pricepolicy里有三个重要字段
-
content_type: 内容类型,代表了模型的名字(比如Course,DegreeCourse)
-
object_id: 传入对象的id
-
content_object: 传入的实例化对象,其包含两个属性content_type和object_id。
2、视图操作
(1)在价格策略表(pricepolicy)中添加数据
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse from app01 import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType def test(request):
# 方法一: models.PricePolicy.objects.create( valid_period=7, price=6.6, content_type=ContentType.objects.get(model="course"), object_id=1 ) # 方法二: models.PricePolicy.objects.create( valid_period=14, price=9.9, content_object=models.Course.objects.get(id=1) # 'content_type', 'object_id' ) return HttpResponse("...")
访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/ 后,查看价格策略表保存的数据:
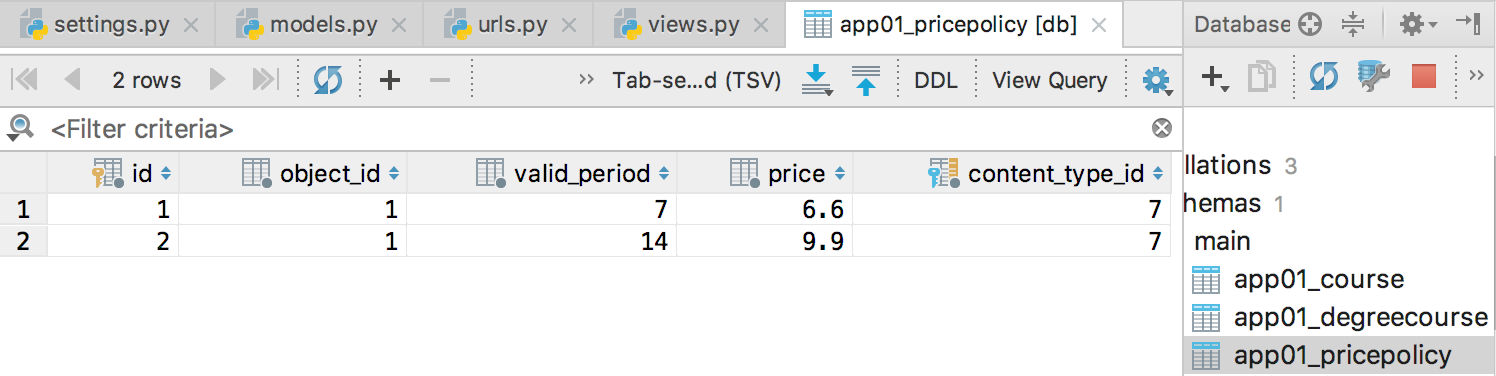
(2)根据某个价格策略对象,找到其对应的表和数据
这里以查看管理课程名称为例:
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
from app01 import models
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
def test(request):
price = models.PricePolicy.objects.get(id=2)
print(price.content_object.name) # 21天入门python 即自动帮忙找到对应的对象
return HttpResponse("...")
(3)找到某个课程关联的所有价格策略
注意这里需要利用到GenericRelation。
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
from app01 import models
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
def test(request):
obj = models.Course.objects.get(id=1)
print(obj.policy_list.all()) # <QuerySet [<PricePolicy: PricePolicy object (1)>, <PricePolicy: PricePolicy object (2)>]>
return HttpResponse("...")
查询结果是一个QuerySet对象,如果想让查询结果更加清楚:
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
from app01 import models
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
def test(request):
obj = models.Course.objects.get(id=1)
for item in obj.policy_list.all():
print(item.id, item.valid_period, item.price)
"""
1 7 6.6
2 14 9.9
"""
return HttpResponse("...")
四、总结ContentType
如果一张表与N张表动态地要创建Foreign Key关系,如果创建 Foreign key 将生成很多列,这样很多都是空的,造成严重浪费空间。只要是一张表要和多张表建立外键关系的情况,都可以考虑使用django的ContentType组件来帮助实现,以简化表结构的设计。
ContentType组件的作用:可以通过两个字段(GenericForeignKey, GenericRelation),在保证列数不变的情况下,让一张表和N张表做Foreign Key关系。