文件程序中是以流的形式操作的。
流:数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径;
输入流:数据从数据源到程序的路径;
输出流:数据从程序到数据源的路径;
常用的文件操作和函数:
1.常用的文件操作函数和方法(打开和关闭文件)
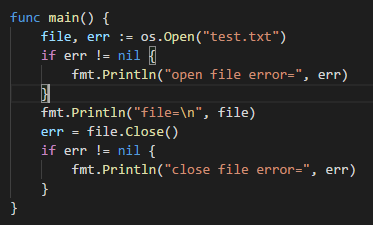
2.读取文件中的内容,并显示给终端(带缓冲区的方式),使用os.Open(),file.Close(),bufio.NewReader(),reader.ReadString()
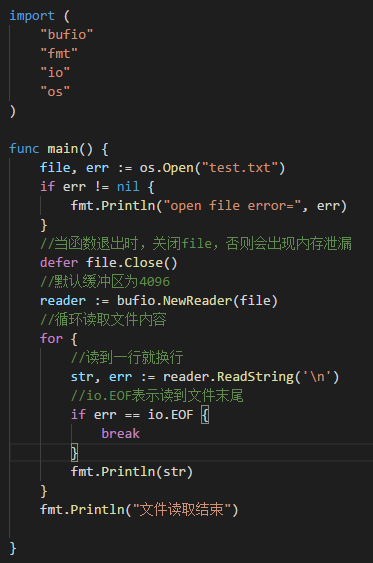
3.读取文件并显示在终端(使用Ioutil一次将整个文件读入到内存中) ,这种方式适用于文件不太大情况下,相关方法ioutil.ReadFile
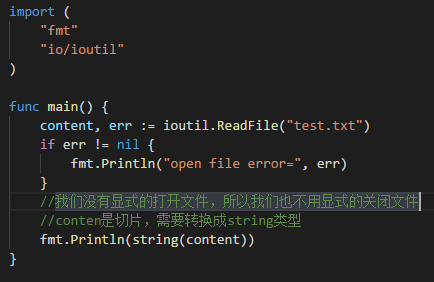
4.写文件
(1)创建一个新文件夹,并写入hello world;

(2)打开一个存在的文件,并将内容覆盖为新的;
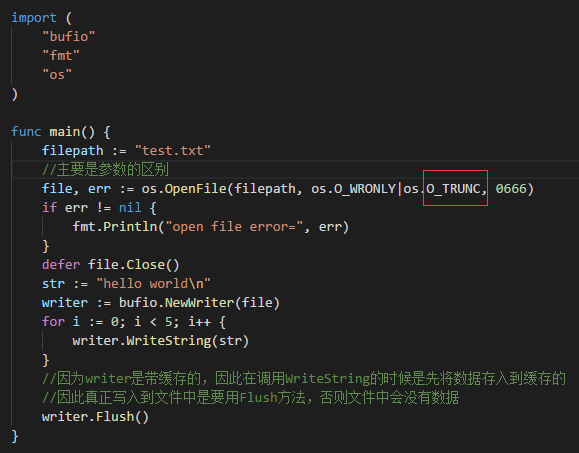
(3)打开一个存在的文件,并在末尾追加新内容;

(4)打开一个存在的文件,将原来的内容读出并显示在终端,并且追加新内容;
package main import ( "bufio" "fmt" "io" "os" ) func main() { filepath := "test.txt" //主要是参数的区别 file, err := os.OpenFile(filepath, os.O_RDWR|os.O_APPEND, 0666) if err != nil { fmt.Println("open file error= ", err) } defer file.Close() reader := bufio.NewReader(file) for { str, err := reader.ReadString(' ') if err == io.EOF { break } fmt.Println(str) } str := "hello world " writer := bufio.NewWriter(file) for i := 0; i < 5; i++ { writer.WriteString(str) } //因为writer是带缓存的,因此在调用WriteString的时候是先将数据存入到缓存的 //因此真正写入到文件中是要用Flush方法,否则文件中会没有数据 writer.Flush() }
5.读取一个文件中的内容写到另一个文件中

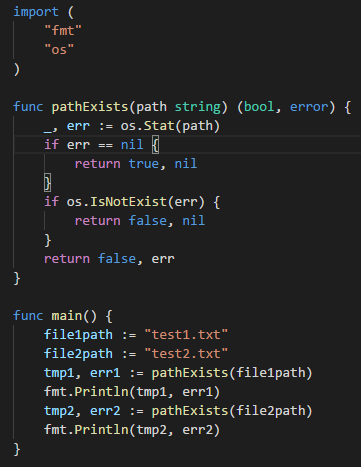
6.判断文件或目录是否存在
说明:如果文件夹存在,则返回true,nil;如果文件夹不存在,则返回false,nil;如果返回false,err,则说明是其它错误。
7.将一个目录下的图片拷贝到另一个目录下
package main import ( "bufio" "fmt" "io" "os" ) func copyFile(dstFileName string, srcFileName string) (written int64, err error) { srcfile, err := os.Open(srcFileName) if err != nil { fmt.Println("open file error=", err) } defer srcfile.Close() reader := bufio.NewReader(srcfile) dstfile, err := os.OpenFile(dstFileName, os.O_WRONLY|os.O_CREATE, 0666) if err != nil { fmt.Println("open file error=", err) } defer dstfile.Close() writer := bufio.NewWriter(dstfile) return io.Copy(writer, reader) } func main() { file1path := "D:/dlrb.jpg" file2path := "E:/dlrb.jpg" _, err := copyFile(file2path, file1path) if err == nil { fmt.Println("拷贝完成") } else { fmt.Println("拷贝失败 error=", err) } }
8.统计文件里面的不同种类字符的个数
func main() { file1path := "test1.txt" srcfile, err := os.Open(file1path) if err != nil { fmt.Println("open file error=", err) return } defer srcfile.Close() var count charCount reader := bufio.NewReader(srcfile) for { str, err := reader.ReadString(' ') if err == io.EOF { break } for _, v := range str { fmt.Println(string(v)) switch { case v >= 'a' && v <= 'z': fallthrough case v >= 'A' && v <= 'z': count.chCount++ case v == ' ' || v == ' ': count.spaceCount++ case v >= '0' && v <= '9': count.numCount++ default: count.otherCount++ } } } fmt.Printf("字符个数:%v,数字个数:%v,空格个数:%v,其它个数:%v", count.chCount, count.numCount, count.spaceCount, count.otherCount) }