接上一节。
本节实现如何通过基于xml文件的方式,而不是基于注解的方式来配置事务。
1.将相应文件中的注解全部去掉
2.为这三个属性加上getters和setters方法。
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; private BookShopDao bookShopDao; private BookShopService bookShopService;
3.将目录调整为如下结构:
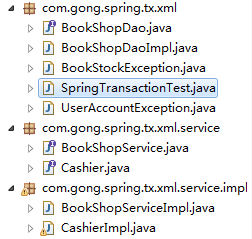
4.在applicationContext-tx.xml文件中进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 导入资源文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <!-- 配置 C3P0 数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property> <property name="initialPoolSize" value="${jdbc.initPoolSize}"></property> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="${jdbc.maxPoolSize}"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置 Spirng 的 JdbcTemplate --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <bean id="bookShopDao" class="com.gong.spring.tx.xml.BookShopDaoImpl"> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property> </bean> <bean id="bookShopService" class="com.gong.spring.tx.xml.service.impl.BookShopServiceImpl"> <property name="bookShopDao" ref="bookShopDao"></property> </bean> <bean id="cashier" class="com.gong.spring.tx.xml.service.impl.CashierImpl"> <property name="bookShopService" ref="bookShopService"></property> </bean> <!-- 1.配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 2.配置事务属性 --> <tx:advice id="txAdice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="purchase" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW"/> <tx:method name="*"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 3.配置事务切入点 ,并将切入点和事务属性关联起来 --> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.gong.spring.tx.xml.service.*.*(..))" id="txPointCut"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdice" pointcut-ref="txPointCut"/> </aop:config> </beans>
基于xml文件配置的方式配置事务有三个步骤:
(1)配置事务管理器
(2)配置事务属性
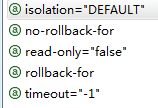
(3)配置事务切入点,将切入点和事务属性关联起来。
expression="execution(* com.gong.spring.tx.xml.service.*.*(..))是将service下的所有实现类的所有方法都加入到切入点。然后切入点和事务属性关联起来,
最后的结果与基于注解的配置方式是一致的。