什么是多层感知机?
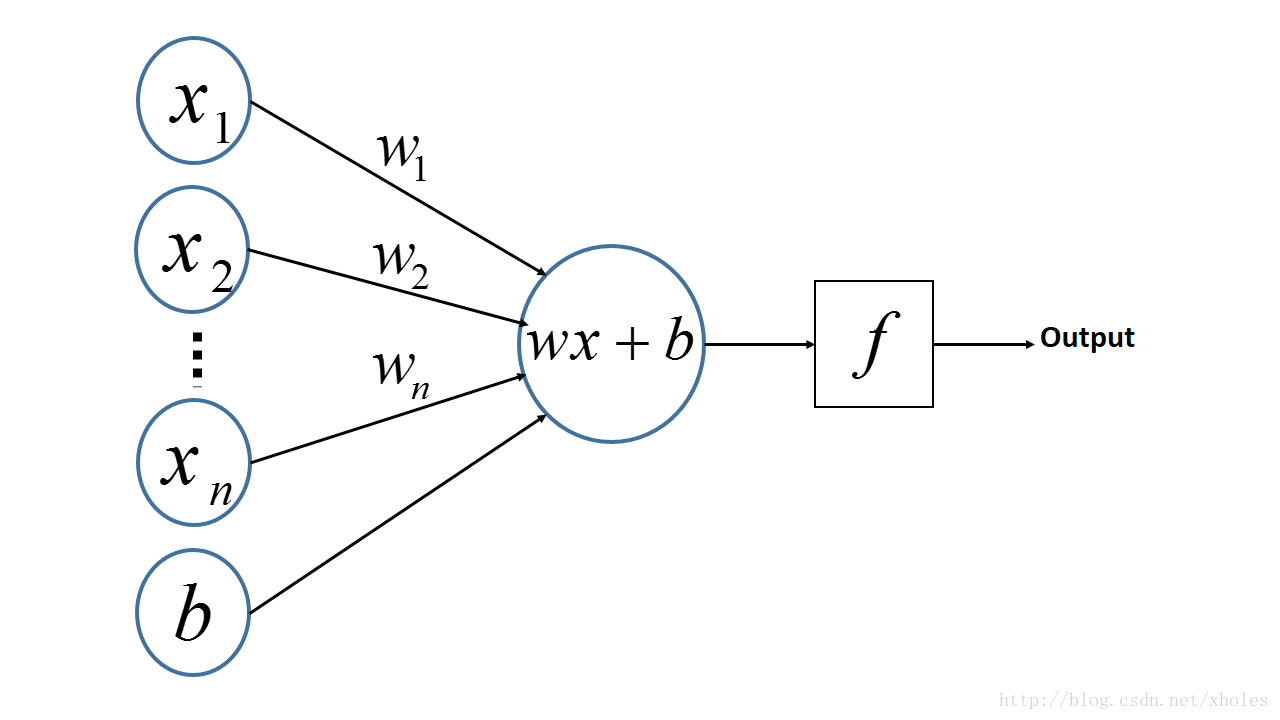
多层感知机(MLP,Multilayer Perceptron)也叫人工神经网络(ANN,Artificial Neural Network),除了输入输出层,它中间可以有多个隐层,最简单的MLP只含一个隐层,即三层的结构,如下图:

上图可以看到,多层感知机层与层之间是全连接的。多层感知机最底层是输入层,中间是隐藏层,最后是输出层。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/fg13821267836/article/details/93405572
多层感知机和感知机的区别?
我们来看下感知机是什么样的:

从上述内容更可以看出,感知机是一个线性的二分类器,但不能对非线性的数据并不能进行有效的分类。因此便有了对网络层次的加深,理论上,多层感知机可以模拟任何复杂的函数。
多层感知机的前向传播过程?
这里以输入层、一个隐含层,输出层为例:


结合之前定义的字母标记,对于第二层的三个神经元的输出则有:

将上述的式子转换为矩阵表达式:
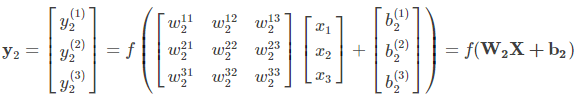
将第二层的前向传播计算过程推广到网络中的任意一层,则:
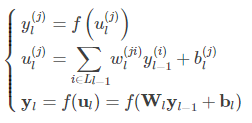 多层感知机的反向传播过程?
多层感知机的反向传播过程?
可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/xholes/article/details/78461164
下面是实现代码:代码来源:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch
from __future__ import print_function, division import numpy as np import math from sklearn import datasets from mlfromscratch.utils import train_test_split, to_categorical, normalize, accuracy_score, Plot from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.activation_functions import Sigmoid, Softmax from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.loss_functions import CrossEntropy class MultilayerPerceptron(): """Multilayer Perceptron classifier. A fully-connected neural network with one hidden layer. Unrolled to display the whole forward and backward pass. Parameters: ----------- n_hidden: int: The number of processing nodes (neurons) in the hidden layer. n_iterations: float The number of training iterations the algorithm will tune the weights for. learning_rate: float The step length that will be used when updating the weights. """ def __init__(self, n_hidden, n_iterations=3000, learning_rate=0.01): self.n_hidden = n_hidden self.n_iterations = n_iterations self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.hidden_activation = Sigmoid() self.output_activation = Softmax() self.loss = CrossEntropy() def _initialize_weights(self, X, y): n_samples, n_features = X.shape _, n_outputs = y.shape # Hidden layer limit = 1 / math.sqrt(n_features) self.W = np.random.uniform(-limit, limit, (n_features, self.n_hidden)) self.w0 = np.zeros((1, self.n_hidden)) # Output layer limit = 1 / math.sqrt(self.n_hidden) self.V = np.random.uniform(-limit, limit, (self.n_hidden, n_outputs)) self.v0 = np.zeros((1, n_outputs)) def fit(self, X, y): self._initialize_weights(X, y) for i in range(self.n_iterations): # .............. # Forward Pass # .............. # HIDDEN LAYER hidden_input = X.dot(self.W) + self.w0 hidden_output = self.hidden_activation(hidden_input) # OUTPUT LAYER output_layer_input = hidden_output.dot(self.V) + self.v0 y_pred = self.output_activation(output_layer_input) # ............... # Backward Pass # ............... # OUTPUT LAYER # Grad. w.r.t input of output layer grad_wrt_out_l_input = self.loss.gradient(y, y_pred) * self.output_activation.gradient(output_layer_input) grad_v = hidden_output.T.dot(grad_wrt_out_l_input) grad_v0 = np.sum(grad_wrt_out_l_input, axis=0, keepdims=True) # HIDDEN LAYER # Grad. w.r.t input of hidden layer grad_wrt_hidden_l_input = grad_wrt_out_l_input.dot(self.V.T) * self.hidden_activation.gradient(hidden_input) grad_w = X.T.dot(grad_wrt_hidden_l_input) grad_w0 = np.sum(grad_wrt_hidden_l_input, axis=0, keepdims=True) # Update weights (by gradient descent) # Move against the gradient to minimize loss self.V -= self.learning_rate * grad_v self.v0 -= self.learning_rate * grad_v0 self.W -= self.learning_rate * grad_w self.w0 -= self.learning_rate * grad_w0 # Use the trained model to predict labels of X def predict(self, X): # Forward pass: hidden_input = X.dot(self.W) + self.w0 hidden_output = self.hidden_activation(hidden_input) output_layer_input = hidden_output.dot(self.V) + self.v0 y_pred = self.output_activation(output_layer_input) return y_pred def main(): data = datasets.load_digits() X = normalize(data.data) y = data.target # Convert the nominal y values to binary y = to_categorical(y) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.4, seed=1) # MLP clf = MultilayerPerceptron(n_hidden=16, n_iterations=1000, learning_rate=0.01) clf.fit(X_train, y_train) y_pred = np.argmax(clf.predict(X_test), axis=1) y_test = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1) accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) print ("Accuracy:", accuracy) # Reduce dimension to two using PCA and plot the results Plot().plot_in_2d(X_test, y_pred, title="Multilayer Perceptron", accuracy=accuracy, legend_labels=np.unique(y)) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
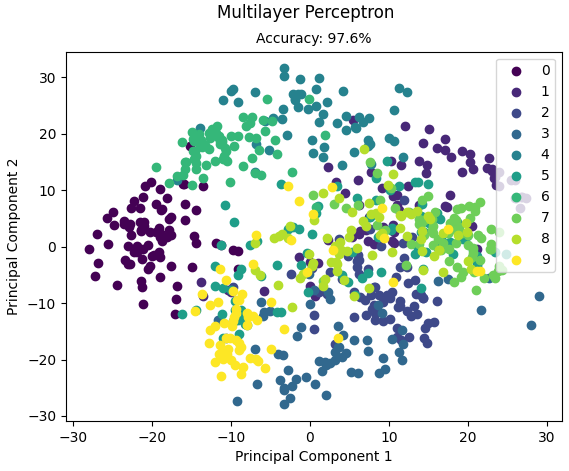
运行结果:
Accuracy: 0.967966573816156
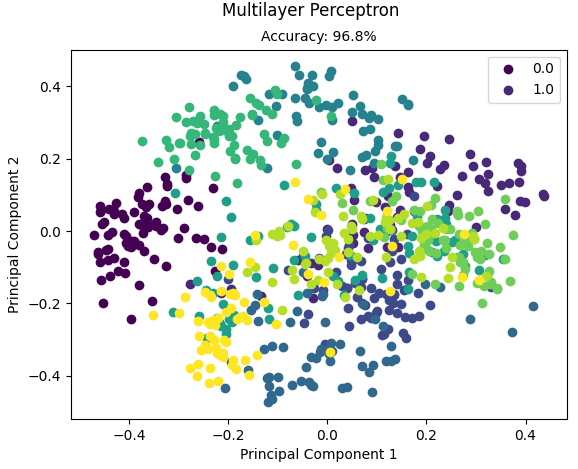
另外的一种实现是使用卷积神经网络中的全连接层实现:
from __future__ import print_function from sklearn import datasets import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import sys sys.path.append("/content/drive/My Drive/learn/ML-From-Scratch/") # Import helper functions from mlfromscratch.deep_learning import NeuralNetwork from mlfromscratch.utils import train_test_split, to_categorical, normalize, Plot from mlfromscratch.utils import get_random_subsets, shuffle_data, accuracy_score from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.optimizers import StochasticGradientDescent, Adam, RMSprop, Adagrad, Adadelta from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.loss_functions import CrossEntropy from mlfromscratch.utils.misc import bar_widgets from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation def main(): optimizer = Adam() #----- # MLP #----- data = datasets.load_digits() X = data.data y = data.target # Convert to one-hot encoding y = to_categorical(y.astype("int")) n_samples, n_features = X.shape n_hidden = 512 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.4, seed=1) clf = NeuralNetwork(optimizer=optimizer, loss=CrossEntropy, validation_data=(X_test, y_test)) clf.add(Dense(n_hidden, input_shape=(n_features,))) clf.add(Activation('leaky_relu')) clf.add(Dense(n_hidden)) clf.add(Activation('leaky_relu')) clf.add(Dropout(0.25)) clf.add(Dense(n_hidden)) clf.add(Activation('leaky_relu')) clf.add(Dropout(0.25)) clf.add(Dense(n_hidden)) clf.add(Activation('leaky_relu')) clf.add(Dropout(0.25)) clf.add(Dense(10)) clf.add(Activation('softmax')) print () clf.summary(name="MLP") train_err, val_err = clf.fit(X_train, y_train, n_epochs=50, batch_size=256) # Training and validation error plot n = len(train_err) training, = plt.plot(range(n), train_err, label="Training Error") validation, = plt.plot(range(n), val_err, label="Validation Error") plt.legend(handles=[training, validation]) plt.title("Error Plot") plt.ylabel('Error') plt.xlabel('Iterations') plt.show() _, accuracy = clf.test_on_batch(X_test, y_test) print ("Accuracy:", accuracy) # Reduce dimension to 2D using PCA and plot the results y_pred = np.argmax(clf.predict(X_test), axis=1) Plot().plot_in_2d(X_test, y_pred, title="Multilayer Perceptron", accuracy=accuracy, legend_labels=range(10)) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
运行结果:
+-----+ | MLP | +-----+ Input Shape: (64,) +------------------------+------------+--------------+ | Layer Type | Parameters | Output Shape | +------------------------+------------+--------------+ | Dense | 33280 | (512,) | | Activation (LeakyReLU) | 0 | (512,) | | Dense | 262656 | (512,) | | Activation (LeakyReLU) | 0 | (512,) | | Dropout | 0 | (512,) | | Dense | 262656 | (512,) | | Activation (LeakyReLU) | 0 | (512,) | | Dropout | 0 | (512,) | | Dense | 262656 | (512,) | | Activation (LeakyReLU) | 0 | (512,) | | Dropout | 0 | (512,) | | Dense | 5130 | (10,) | | Activation (Softmax) | 0 | (10,) | +------------------------+------------+--------------+ Total Parameters: 826378 Training: 100% [------------------------------------------------] Time: 0:00:29
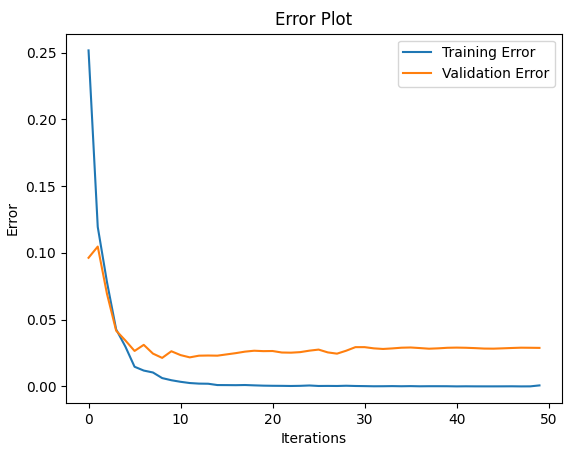
Accuracy: 0.9763231197771588