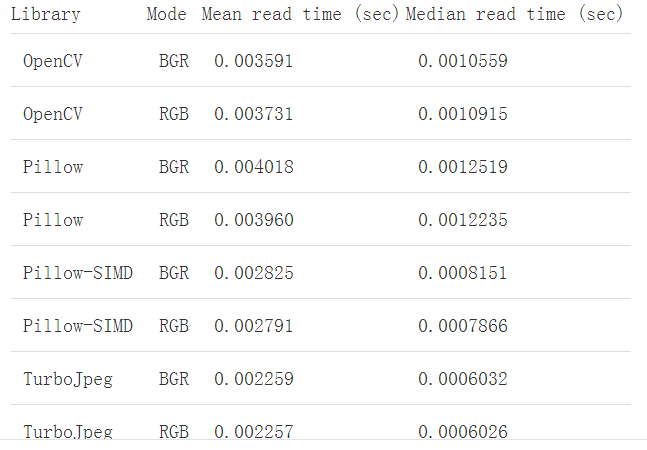
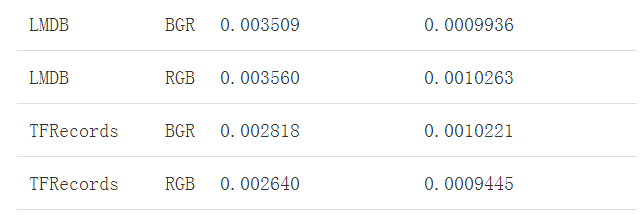
opencv和PIL都是很常见的图像处理库了,就不介绍了,主要介绍后面三个:
turbojpeg:libjpeg-turbo的python包装器,用于jpeg图像的解码和编码。
基本用法:
import cv2 from turbojpeg import TurboJPEG, TJPF_GRAY, TJSAMP_GRAY, TJFLAG_PROGRESSIVE # using default library installation jpeg = TurboJPEG() # decoding input.jpg to BGR array in_file = open('input.jpg', 'rb') bgr_array = jpeg.decode(in_file.read()) in_file.close() cv2.imshow('bgr_array', bgr_array) cv2.waitKey(0)
更多信息参考:https://www.cnpython.com/pypi/pyturbojpeg
lmdb:LMDB的全称是Lightning Memory-Mapped Database(快如闪电的内存映射数据库)。LMDB文件可以同时由多个进程打开,具有极高的数据存取速度,访问简单,不需要运行单独的数据库管理进程,只要在访问数据的代码里引用LMDB库,访问时给文件路径即可。让系统访问大量小文件的开销很大,而LMDB使用内存映射的方式访问文件,使得文件内寻址的开销非常小,使用指针运算就能实现。数据库单文件还能减少数据集复制/传输过程的开销。
基本用法:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import lmdb # 如果train文件夹下没有data.mbd或lock.mdb文件,则会生成一个空的,如果有,不会覆盖 # map_size定义最大储存容量,单位是kb,以下定义1TB容量 env = lmdb.open("./train",map_size=1099511627776) env.close()
更多信息参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41874599/article/details/86631186
tfrecords:frecords是一种二进制编码的文件格式,tensorflow专用。 能将任意数据转换为tfrecords。 更好的利用内存,更方便复制和移动,并且不需要单独的标签文件。
将图像转换为lmdb格式的数据:
import os from argparse import ArgumentParser import cv2 import lmdb import numpy as np from tools import get_images_paths def store_many_lmdb(images_list, save_path): num_images = len(images_list) # number of images in our folder file_sizes = [os.path.getsize(item) for item in images_list] # all file sizes max_size_index = np.argmax(file_sizes) # the maximum file size index # maximum database size in bytes map_size = num_images * cv2.imread(images_list[max_size_index]).nbytes * 10 env = lmdb.open(save_path, map_size=map_size) # create lmdb environment with env.begin(write=True) as txn: # start writing to environment for i, image in enumerate(images_list): with open(image, "rb") as file: data = file.read() # read image as bytes key = f"{i:08}" # get image key txn.put(key.encode("ascii"), data) # put the key-value into database env.close() # close the environment if __name__ == "__main__": parser = ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument( "--path", "-p", type=str, required=True, help="path to the images folder to collect", ) parser.add_argument( "--output", "-o", type=str, required=True, help='path to the output environment directory file i.e. "path/to/folder/env/"', ) args = parser.parse_args() if not os.path.exists(args.output): os.makedirs(args.output) images = get_images_paths(args.path) store_many_lmdb(images, args.output)
将图像转换为tfrecords格式的数据:
import os from argparse import ArgumentParser import tensorflow as tf from tools import get_images_paths def _byte_feature(value): """Convert string / byte into bytes_list.""" if isinstance(value, type(tf.constant(0))): value = value.numpy() # BytesList can't unpack string from EagerTensor. return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value])) def _int64_feature(value): """Convert bool / enum / int / uint into int64_list.""" return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])) def image_example(image_string, label): feature = { "label": _int64_feature(label), "image_raw": _byte_feature(image_string), } return tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature=feature)) def store_many_tfrecords(images_list, save_file): assert save_file.endswith( ".tfrecords", ), 'File path is wrong, it should contain "*myname*.tfrecords"' directory = os.path.dirname(save_file) if not os.path.exists(directory): os.makedirs(directory) with tf.io.TFRecordWriter(save_file) as writer: # start writer for label, filename in enumerate(images_list): # cycle by each image path image_string = open(filename, "rb").read() # read the image as bytes string tf_example = image_example( image_string, label, ) # save the data as tf.Example object writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString()) # and write it into database if __name__ == "__main__": parser = ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument( "--path", "-p", type=str, required=True, help="path to the images folder to collect", ) parser.add_argument( "--output", "-o", type=str, required=True, help='path to the output tfrecords file i.e. "path/to/folder/myname.tfrecords"', ) args = parser.parse_args() image_paths = get_images_paths(args.path) store_many_tfrecords(image_paths, args.output)
使用不同的方式读取图像,同时默认是以BGR的格式读取:
import os from abc import abstractmethod from timeit import default_timer as timer import cv2 import lmdb import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from PIL import Image from turbojpeg import TurboJPEG os.environ["TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL"] = "3" class ImageLoader: extensions: tuple = (".png", ".jpg", ".jpeg", ".tiff", ".bmp", ".gif", ".tfrecords") def __init__(self, path: str, mode: str = "BGR"): self.path = path self.mode = mode self.dataset = self.parse_input(self.path) self.sample_idx = 0 def parse_input(self, path): # single image or tfrecords file if os.path.isfile(path): assert path.lower().endswith( self.extensions, ), f"Unsupportable extension, please, use one of {self.extensions}" return [path] if os.path.isdir(path): # lmdb environment if any([file.endswith(".mdb") for file in os.listdir(path)]): return path else: # folder with images paths = [os.path.join(path, image) for image in os.listdir(path)] return paths def __iter__(self): self.sample_idx = 0 return self def __len__(self): return len(self.dataset) @abstractmethod def __next__(self): pass class CV2Loader(ImageLoader): def __next__(self): start = timer() path = self.dataset[self.sample_idx] # get image path by index from the dataset image = cv2.imread(path) # read the image full_time = timer() - start if self.mode == "RGB": start = timer() image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # change color mode full_time += timer() - start self.sample_idx += 1 return image, full_time class PILLoader(ImageLoader): def __next__(self): start = timer() path = self.dataset[self.sample_idx] # get image path by index from the dataset image = np.asarray(Image.open(path)) # read the image as numpy array full_time = timer() - start if self.mode == "BGR": start = timer() image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) # change color mode full_time += timer() - start self.sample_idx += 1 return image, full_time class TurboJpegLoader(ImageLoader): def __init__(self, path, **kwargs): super(TurboJpegLoader, self).__init__(path, **kwargs) self.jpeg_reader = TurboJPEG() # create TurboJPEG object for image reading def __next__(self): start = timer() file = open(self.dataset[self.sample_idx], "rb") # open the input file as bytes full_time = timer() - start if self.mode == "RGB": mode = 0 elif self.mode == "BGR": mode = 1 start = timer() image = self.jpeg_reader.decode(file.read(), mode) # decode raw image full_time += timer() - start self.sample_idx += 1 return image, full_time class LmdbLoader(ImageLoader): def __init__(self, path, **kwargs): super(LmdbLoader, self).__init__(path, **kwargs) self.path = path self._dataset_size = 0 self.dataset = self.open_database() # we need to open the database to read images from it def open_database(self): lmdb_env = lmdb.open(self.path) # open the environment by path lmdb_txn = lmdb_env.begin() # start reading lmdb_cursor = lmdb_txn.cursor() # create cursor to iterate through the database self._dataset_size = lmdb_env.stat()[ "entries" ] # get number of items in full dataset return lmdb_cursor def __iter__(self): self.dataset.first() # return the cursor to the first database element return self def __next__(self): start = timer() raw_image = self.dataset.value() # get raw image image = np.frombuffer(raw_image, dtype=np.uint8) # convert it to numpy image = cv2.imdecode(image, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # decode image full_time = timer() - start if self.mode == "RGB": start = timer() image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) full_time += timer() - start start = timer() self.dataset.next() # step to the next element in database full_time += timer() - start return image, full_time def __len__(self): return self._dataset_size # get dataset length class TFRecordsLoader(ImageLoader): def __init__(self, path, **kwargs): super(TFRecordsLoader, self).__init__(path, **kwargs) self._dataset = self.open_database() def open_database(self): def _parse_image_function(example_proto): return tf.io.parse_single_example(example_proto, image_feature_description) # dataset structure description image_feature_description = { "label": tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), "image_raw": tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), } raw_image_dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(self.path) # open dataset by path parsed_image_dataset = raw_image_dataset.map( _parse_image_function, ) # parse dataset using structure description return parsed_image_dataset def __iter__(self): self.dataset = self._dataset.as_numpy_iterator() return self def __next__(self): start = timer() value = next(self.dataset)[ "image_raw" ] # step to the next element in database and get new image image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(value).numpy() # decode raw image full_time = timer() - start if self.mode == "BGR": start = timer() image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) full_time += timer() - start return image, full_time def __len__(self): return self._dataset.reduce( np.int64(0), lambda x, _: x + 1, ).numpy() # get dataset length methods = { "cv2": CV2Loader, "pil": PILLoader, "turbojpeg": TurboJpegLoader, "lmdb": LmdbLoader, "tfrecords": TFRecordsLoader, }
显示图像:
from argparse import ArgumentParser import cv2 from loader import ( CV2Loader, LmdbLoader, PILLoader, TFRecordsLoader, TurboJpegLoader, methods, ) def show_image(method, image): cv2.imshow(f"{method} image", image) k = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF if k == 27: # check ESC pressing return True else: return False def show_images(loader): num_images = len(loader) loader = iter(loader) for idx in range(num_images): image, time = next(loader) print_info(image, time) stop = show_image(type(loader).__name__, image) if stop: cv2.destroyAllWindows() return def print_info(image, time): print( f"Image with {image.shape[0]}x{image.shape[1]} size has been loading for {time} seconds", ) def demo(method, path): loader = methods[method](path) # get the image loader show_images(loader) if __name__ == "__main__": parser = ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument( "--path", "-p", type=str, help="path to image, folder of images, lmdb environment path or tfrecords database path", ) parser.add_argument( "--method", required=True, choices=["cv2", "pil", "turbojpeg", "lmdb", "tfrecords"], help="Image loading methods to use in benchmark", ) args = parser.parse_args() demo(args.method, args.path)
更多细节请参考:
https://github.com/spmallick/learnopencv/tree/master/Efficient-image-loading
https://www.learnopencv.com/efficient-image-loading/
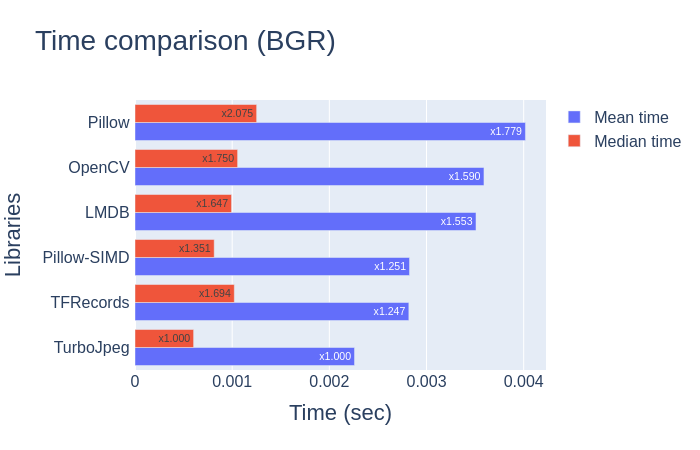
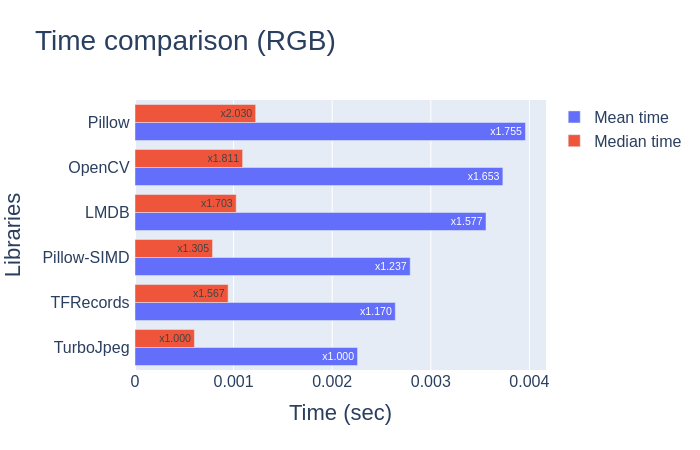
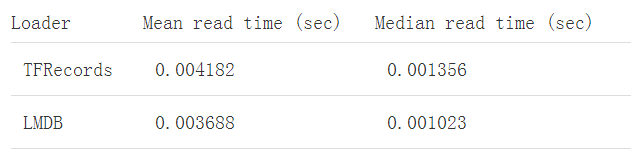
这里就只看结果了: