class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module): "Implement the PE function." def __init__(self, d_model, dropout, max_len=5000): #d_model=512,dropout=0.1, #max_len=5000代表事先准备好长度为5000的序列的位置编码,其实没必要, #一般100或者200足够了。 super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__() self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout) # Compute the positional encodings once in log space. pe = torch.zeros(max_len, d_model) #(5000,512)矩阵,保持每个位置的位置编码,一共5000个位置, #每个位置用一个512维度向量来表示其位置编码 position = torch.arange(0, max_len).unsqueeze(1) # (5000) -> (5000,1) div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, d_model, 2) * -(math.log(10000.0) / d_model)) # (0,2,…, 4998)一共准备2500个值,供sin, cos调用 pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term) # 偶数下标的位置 pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term) # 奇数下标的位置 pe = pe.unsqueeze(0) # (5000, 512) -> (1, 5000, 512) 为batch.size留出位置 self.register_buffer('pe', pe) def forward(self, x): x = x + Variable(self.pe[:, :x.size(1)], requires_grad=False) # 接受1.Embeddings的词嵌入结果x, #然后把自己的位置编码pe,封装成torch的Variable(不需要梯度),加上去。 #例如,假设x是(30,10,512)的一个tensor, #30是batch.size, 10是该batch的序列长度, 512是每个词的词嵌入向量; #则该行代码的第二项是(1, min(10, 5000), 512)=(1,10,512), #在具体相加的时候,会扩展(1,10,512)为(30,10,512), #保证一个batch中的30个序列,都使用(叠加)一样的位置编码。 return self.dropout(x) # 增加一次dropout操作 # 注意,位置编码不会更新,是写死的,所以这个class里面没有可训练的参数。
注意,位置编码不会更新,是写死的,所以这个class里面没有可训练的参数。
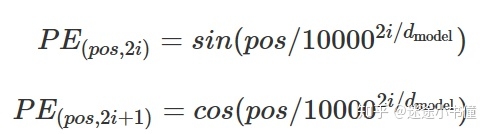
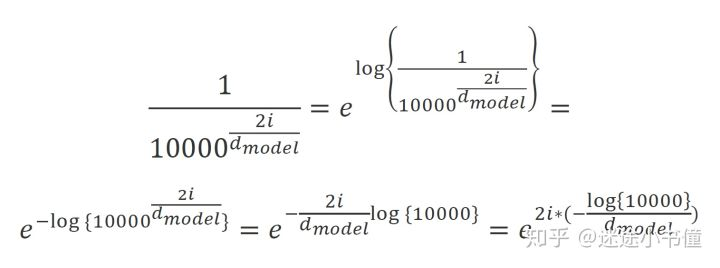
为了计算这个公式,上面的代码写的比较风骚,以2i为偶数为例子:
将字编码和位置嵌入联合使用:
nn.Sequential(Embeddings(d_model,src_vocab), PositionalEncoding(d_model,dropout)) # 例如,d_model=512, src_vocab=源语言的词表大小, #dropout=0.1即 dropout rate