什么是谱聚类?
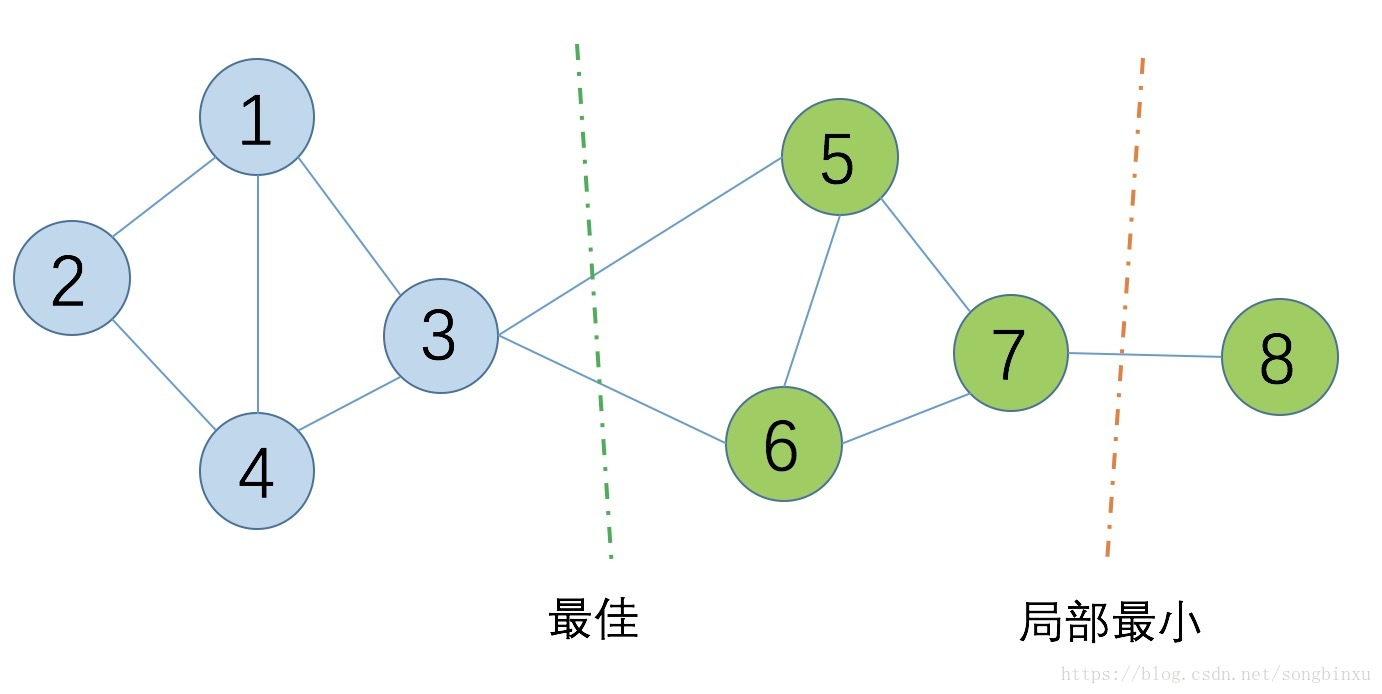
就是找到一个合适的切割点将图进行切割,核心思想就是:

使得切割的边的权重和最小,对于无向图而言就是切割的边数最少,如上所示。但是,切割的时候可能会存在局部最优,有以下两种方法:
(1)RatioCut:核心是要求划分出来的子图的节点数尽可能的大
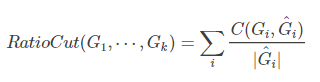
分母变为子图的节点的个数 。
(2)NCut:考虑每个子图的边的权重和
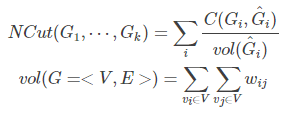
分母变为子图各边的权重和。
具体之后求解可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/songbinxu/article/details/80838865
谱聚类的整体流程?
- 计算距离矩阵(例如欧氏距离)
- 利用KNN计算邻接矩阵 A
- 由 A 计算度矩阵 D 和拉普拉斯矩阵 L
- 标准化 L→$D^{−1/2}LD^{−1/2}$
- 对矩阵 $D^{−1/2}LD^{−1/2}$进行特征值分解,得到特征向量 $H_{nn}$
- 将 $H_{nn}$ 当成样本送入 Kmeans 聚类
- 获得聚类结果 C=(C1,C2,⋯,Ck)
python实现:
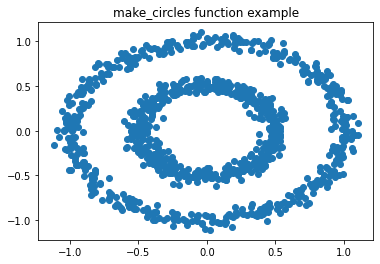
(1)首先是数据的生成:
from sklearn import datasets
x1, y1 = datasets.make_circles(n_samples=1000, factor=0.5, noise=0.05)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline plt.title('make_circles function example') plt.scatter(x1[:, 0], x1[:, 1], marker='o') plt.show()
x1的形状是(1000,2)
(2)接下来,我们要计算两两样本之间的距离:
import numpy as np
def euclidDistance(x1, x2, sqrt_flag=False): res = np.sum((x1-x2)**2) if sqrt_flag: res = np.sqrt(res) return res
将这些距离用矩阵的形式保存:
def calEuclidDistanceMatrix(X): X = np.array(X) S = np.zeros((len(X), len(X))) for i in range(len(X)): for j in range(i+1, len(X)): S[i][j] = 1.0 * euclidDistance(X[i], X[j]) S[j][i] = S[i][j] return S
S = calEuclidDistanceMatrix(x1)
array([[0.00000000e+00, 1.13270081e+00, 2.62565479e+00, ..., 2.99144277e+00, 1.88193070e+00, 1.12840739e+00], [1.13270081e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 2.72601994e+00, ..., 2.95125426e+00, 5.11864947e-01, 6.05388856e-05], [2.62565479e+00, 2.72601994e+00, 0.00000000e+00, ..., 1.30747922e-02, 1.18180915e+00, 2.74692378e+00], ..., [2.99144277e+00, 2.95125426e+00, 1.30747922e-02, ..., 0.00000000e+00, 1.26037239e+00, 2.97382982e+00], [1.88193070e+00, 5.11864947e-01, 1.18180915e+00, ..., 1.26037239e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 5.22992113e-01], [1.12840739e+00, 6.05388856e-05, 2.74692378e+00, ..., 2.97382982e+00, 5.22992113e-01, 0.00000000e+00]])
(3)使用KNN计算跟每个样本最接近的k个样本点,然后计算出邻接矩阵:
def myKNN(S, k, sigma=1.0): N = len(S) #定义邻接矩阵 A = np.zeros((N,N)) for i in range(N): #对每个样本进行编号 dist_with_index = zip(S[i], range(N)) #对距离进行排序 dist_with_index = sorted(dist_with_index, key=lambda x:x[0]) #取得距离该样本前k个最小距离的编号 neighbours_id = [dist_with_index[m][1] for m in range(k+1)] # xi's k nearest neighbours #构建邻接矩阵 for j in neighbours_id: # xj is xi's neighbour A[i][j] = np.exp(-S[i][j]/2/sigma/sigma) A[j][i] = A[i][j] # mutually return A
A = myKNN(S,3)
array([[1. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. , 0. ], [0. , 1. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. , 0.99996973], [0. , 0. , 1. , ..., 0. , 0. , 0. ], ..., [0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 1. , 0. , 0. ], [0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 1. , 0. ], [0. , 0.99996973, 0. , ..., 0. , 0. , 1. ]])
(4)计算标准化的拉普拉斯矩阵
def calLaplacianMatrix(adjacentMatrix): # compute the Degree Matrix: D=sum(A) degreeMatrix = np.sum(adjacentMatrix, axis=1) # compute the Laplacian Matrix: L=D-A laplacianMatrix = np.diag(degreeMatrix) - adjacentMatrix # normailze # D^(-1/2) L D^(-1/2) sqrtDegreeMatrix = np.diag(1.0 / (degreeMatrix ** (0.5))) return np.dot(np.dot(sqrtDegreeMatrix, laplacianMatrix), sqrtDegreeMatrix)
L_sys = calLaplacianMatrix(A)
array([[ 0.66601736, 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. , 0. ], [ 0. , 0.74997723, 0. , ..., 0. , 0. , -0.28868642], [ 0. , 0. , 0.74983185, ..., 0. , 0. , 0. ], ..., [ 0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0.66662382, 0. , 0. ], [ 0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0.74953329, 0. ], [ 0. , -0.28868642, 0. , ..., 0. , 0. , 0.66665079]])
(5)特征值分解
lam, V = np.linalg.eig(L_sys) # H'shape is n*n lam = zip(lam, range(len(lam))) lam = sorted(lam, key=lambda x:x[0]) H = np.vstack([V[:,i] for (v, i) in lam[:1000]]).T H = np.asarray(H).astype(float)
(6)使用谱聚类进行聚类
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans def spKmeans(H): sp_kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2).fit(H) return sp_kmeans.labels_
labels = spKmeans(H) plt.title('spectral cluster result') plt.scatter(x1[:, 0], x1[:, 1], marker='o',c=labels) plt.show()

(7) 对比使用kmeans聚类
pure_kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2).fit(x1) plt.title('pure kmeans cluster result') plt.scatter(x1[:, 0], x1[:, 1], marker='o',c=pure_kmeans.labels_) plt.show()

参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/13180579.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/chenmo1/p/11681669.html