之前讲解了图注意力网络的官方tensorflow版的实现,由于自己更了解pytorch,所以打算将其改写为pytorch版本的。
对于图注意力网络还不了解的可以先去看看tensorflow版本的代码,之前讲解的地址:
非稀疏矩阵版:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/13622283.html
稀疏矩阵版:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/13623989.html
以下改写后的代码我已经上传到gihub上,地址为:
https://github.com/taishan1994/pytorch_gat
图注意力网络的官方代码使用的是tensorflow1.x版本的,地址为:
https://github.com/Diego999/pyGAT
下面开始进入正题了。
1、tensorflow1.x的一般建模过程:
- 定义好训练的数据
- 定义计算图(包含占位)
- 定义训练主函数、损失函数计算、优化器
- 定义Session,参数初始化以及实际的前向传播和反向传播计算都是在Session中
2、将tensorflow转换为pytorch代码
其他数据处理的代码都是一致的,主要是一些需要改变的地方:
2.1 数据的读取
在tensorflow中,标签是要经过onehot编码的,而在pytorch中确是不用的,在load_data中:
def load_data(dataset_str): # {'pubmed', 'citeseer', 'cora'} """Load data.""" names = ['x', 'y', 'tx', 'ty', 'allx', 'ally', 'graph'] objects = [] for i in range(len(names)): with open("data/ind.{}.{}".format(dataset_str, names[i]), 'rb') as f: if sys.version_info > (3, 0): objects.append(pkl.load(f, encoding='latin1')) else: objects.append(pkl.load(f)) x, y, tx, ty, allx, ally, graph = tuple(objects) test_idx_reorder = parse_index_file("data/ind.{}.test.index".format(dataset_str)) test_idx_range = np.sort(test_idx_reorder) if dataset_str == 'citeseer': # Fix citeseer dataset (there are some isolated nodes in the graph) # Find isolated nodes, add them as zero-vecs into the right position test_idx_range_full = range(min(test_idx_reorder), max(test_idx_reorder)+1) tx_extended = sp.lil_matrix((len(test_idx_range_full), x.shape[1])) tx_extended[test_idx_range-min(test_idx_range), :] = tx tx = tx_extended ty_extended = np.zeros((len(test_idx_range_full), y.shape[1])) ty_extended[test_idx_range-min(test_idx_range), :] = ty ty = ty_extended features = sp.vstack((allx, tx)).tolil() features[test_idx_reorder, :] = features[test_idx_range, :] adj = nx.adjacency_matrix(nx.from_dict_of_lists(graph)) labels = np.vstack((ally, ty)) labels[test_idx_reorder, :] = labels[test_idx_range, :] #pytorch的标签不需要进行one-hot编码 my_labels = np.where(labels==1)[1] idx_test = test_idx_range.tolist() idx_train = range(len(y)) idx_val = range(len(y), len(y)+500) train_my_labels_mask = sample_mask(idx_train, my_labels.shape[0]) val_my_labels_mask = sample_mask(idx_val, my_labels.shape[0]) test_my_labels_mask = sample_mask(idx_test, my_labels.shape[0]) train_my_labels = my_labels[train_my_labels_mask] val_my_labels = my_labels[val_my_labels_mask] test_my_labels = my_labels[test_my_labels_mask] train_mask = sample_mask(idx_train, labels.shape[0]) val_mask = sample_mask(idx_val, labels.shape[0]) test_mask = sample_mask(idx_test, labels.shape[0]) y_train = np.zeros(labels.shape) y_val = np.zeros(labels.shape) y_test = np.zeros(labels.shape) y_train[train_mask, :] = labels[train_mask, :] y_val[val_mask, :] = labels[val_mask, :] y_test[test_mask, :] = labels[test_mask, :] print(adj.shape) print(features.shape) data_dict = { 'adj': adj, 'features': features, 'y_train': y_train, 'y_val': y_val, 'y_test': y_test, 'train_mask': train_mask, 'val_mask': val_mask, 'test_mask': test_mask, 'train_my_labels': train_my_labels, 'val_my_labels': val_my_labels, 'test_my_labels': test_my_labels, 'my_labels': my_labels } return data_dict
我们要使用np.where()函数,将每一个ont-hot编码中值为1的索引(也就是标签)取出来,然后在对其进行划分训练标签、验证标签和测试标签。
顺便提一下,当我们要返回的值很多的时候,可以用一个字典包装起来,最后返回该字典就行了,这符合python的编码规范。
2.2 注意力层的搭建
在tensorflow中:
conv1d = tf.layers.conv1d def attn_head(seq, out_sz, bias_mat, activation, in_drop=0.0, coef_drop=0.0, residual=False): with tf.name_scope('my_attn'): if in_drop != 0.0: seq = tf.nn.dropout(seq, 1.0 - in_drop) seq_fts = tf.layers.conv1d(seq, out_sz, 1, use_bias=False) # simplest self-attention possible f_1 = tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1) f_2 = tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1) logits = f_1 + tf.transpose(f_2, [0, 2, 1]) coefs = tf.nn.softmax(tf.nn.leaky_relu(logits) + bias_mat) if coef_drop != 0.0: coefs = tf.nn.dropout(coefs, 1.0 - coef_drop) if in_drop != 0.0: seq_fts = tf.nn.dropout(seq_fts, 1.0 - in_drop) vals = tf.matmul(coefs, seq_fts) ret = tf.contrib.layers.bias_add(vals) # residual connection if residual: if seq.shape[-1] != ret.shape[-1]: ret = ret + conv1d(seq, ret.shape[-1], 1) # activation else: ret = ret + seq return activation(ret) # activation
直接就可以使用相关api进行计算,但是在pytorch中,无论是定义自己的层还是模型,都需要先建立,然后再使用(一般是这样)。改写后的代码如下:
import torch import torch.nn as nn class Attn_head(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channel, out_sz, bias_mat, in_drop=0.0, coef_drop=0.0, activation=None, residual=False): super(Attn_head, self).__init__() self.in_channel = in_channel self.out_sz = out_sz self.bias_mat = bias_mat self.in_drop = in_drop self.coef_drop = coef_drop self.activation = activation self.residual = residual self.conv1 = nn.Conv1d(self.in_channel, self.out_sz, 1) self.conv2_1 = nn.Conv1d(self.out_sz, 1, 1) self.conv2_2 = nn.Conv1d(self.out_sz, 1, 1) self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU() self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1) #pytorch中dropout的参数p表示每个神经元一定概率失活 self.in_dropout = nn.Dropout() self.coef_dropout = nn.Dropout() self.res_conv = nn.Conv1d(self.in_channel, self.out_sz, 1) def forward(self,x): seq = x if self.in_drop != 0.0: seq = self.in_dropout(x) seq_fts = self.conv1(seq) f_1 = self.conv2_1(seq_fts) f_2 = self.conv2_2(seq_fts) logits = f_1 + torch.transpose(f_2, 2, 1) logits = self.leakyrelu(logits) coefs = self.softmax(logits + self.bias_mat) if self.coef_drop !=0.0: coefs = self.coef_dropout(coefs) if self.in_dropout !=0.0: seq_fts = self.in_dropout(seq_fts) ret = torch.matmul(coefs, torch.transpose(seq_fts, 2, 1)) ret = torch.transpose(ret, 2, 1) if self.residual: if seq.shape[1] != ret.shape[1]: ret = ret + self.res_conv(seq) else: ret = ret + seq return self.activation(ret)
要继承nn.Module类,然后在__init__中初始化相关参数以及对应的层,在forward中进行前向传播计算。
2.3 搭建模型
有了注意力层之后,就可以搭建模型了,tensorflow的代码:
def inference(inputs, nb_classes, nb_nodes, training, attn_drop, ffd_drop, bias_mat, hid_units, n_heads, activation=tf.nn.elu, residual=False): attns = [] for _ in range(n_heads[0]): attns.append(layers.attn_head(inputs, bias_mat=bias_mat, out_sz=hid_units[0], activation=activation, in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=False)) h_1 = tf.concat(attns, axis=-1) for i in range(1, len(hid_units)): h_old = h_1 attns = [] for _ in range(n_heads[i]): attns.append(layers.attn_head(h_1, bias_mat=bias_mat, out_sz=hid_units[i], activation=activation, in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=residual)) h_1 = tf.concat(attns, axis=-1) out = [] for i in range(n_heads[-1]): out.append(layers.attn_head(h_1, bias_mat=bias_mat, out_sz=nb_classes, activation=lambda x: x, in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=False)) logits = tf.add_n(out) / n_heads[-1] return logits
改写之后的pytorch代码:
import numpy as np import torch.nn as nn import torch from layer import * class GAT(nn.Module): def __init__(self, nb_classes, nb_nodes, attn_drop, ffd_drop, bias_mat, hid_units, n_heads, residual=False): super(GAT, self).__init__() self.nb_classes = nb_classes self.nb_nodes = nb_nodes self.attn_drop = attn_drop self.ffd_drop = ffd_drop self.bias_mat = bias_mat self.hid_units = hid_units self.n_heads = n_heads self.residual = residual self.attn1 = Attn_head(in_channel=1433, out_sz=self.hid_units[0], bias_mat=self.bias_mat, in_drop=self.ffd_drop, coef_drop=self.attn_drop, activation=nn.ELU(), residual=self.residual) self.attn2 = Attn_head(in_channel=64, out_sz=self.nb_classes, bias_mat=self.bias_mat, in_drop=self.ffd_drop, coef_drop=self.attn_drop, activation=nn.ELU(), residual=self.residual) self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1) def forward(self, x): attns = [] for _ in range(self.n_heads[0]): attns.append(self.attn1(x)) h_1 = torch.cat(attns, dim=1) out = self.attn2(h_1) logits = torch.transpose(out.view(self.nb_classes,-1), 1, 0) logits = self.softmax(logits) return logits
和tensorflow代码不同的是,这里我们仅仅定义了两层注意力。还需要注意的是,我们在__init__中定义相关层的时候,对于输入和输出的维度我们是要预先知道的,并填充进去,如果在forward中实际的值与预先定义的维度不同,那么就会报错。
2.4 进行训练、验证和测试
首先还是来看一下tensorflow是怎么定义的:
with tf.Graph().as_default(): with tf.name_scope('input'): ftr_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, nb_nodes, ft_size)) bias_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, nb_nodes, nb_nodes)) lbl_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=(batch_size, nb_nodes, nb_classes)) msk_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=(batch_size, nb_nodes)) attn_drop = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=()) ffd_drop = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=()) is_train = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool, shape=()) logits = model.inference(ftr_in, nb_classes, nb_nodes, is_train, attn_drop, ffd_drop, bias_mat=bias_in, hid_units=hid_units, n_heads=n_heads, residual=residual, activation=nonlinearity) log_resh = tf.reshape(logits, [-1, nb_classes]) lab_resh = tf.reshape(lbl_in, [-1, nb_classes]) msk_resh = tf.reshape(msk_in, [-1]) loss = model.masked_softmax_cross_entropy(log_resh, lab_resh, msk_resh) accuracy = model.masked_accuracy(log_resh, lab_resh, msk_resh) train_op = model.training(loss, lr, l2_coef) saver = tf.train.Saver() init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer()) vlss_mn = np.inf vacc_mx = 0.0 curr_step = 0 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) train_loss_avg = 0 train_acc_avg = 0 val_loss_avg = 0 val_acc_avg = 0 for epoch in range(nb_epochs): print("epoch: ",epoch) tr_step = 0 tr_size = features.shape[0] while tr_step * batch_size < tr_size: _, loss_value_tr, acc_tr = sess.run([train_op, loss, accuracy], feed_dict={ ftr_in: features[tr_step*batch_size:(tr_step+1)*batch_size], bias_in: biases[tr_step*batch_size:(tr_step+1)*batch_size], lbl_in: y_train[tr_step*batch_size:(tr_step+1)*batch_size], msk_in: train_mask[tr_step*batch_size:(tr_step+1)*batch_size], is_train: True, attn_drop: 0.6, ffd_drop: 0.6}) train_loss_avg += loss_value_tr train_acc_avg += acc_tr tr_step += 1 vl_step = 0 vl_size = features.shape[0] while vl_step * batch_size < vl_size: loss_value_vl, acc_vl = sess.run([loss, accuracy], feed_dict={ ftr_in: features[vl_step*batch_size:(vl_step+1)*batch_size], bias_in: biases[vl_step*batch_size:(vl_step+1)*batch_size], lbl_in: y_val[vl_step*batch_size:(vl_step+1)*batch_size], msk_in: val_mask[vl_step*batch_size:(vl_step+1)*batch_size], is_train: False, attn_drop: 0.0, ffd_drop: 0.0}) val_loss_avg += loss_value_vl val_acc_avg += acc_vl vl_step += 1 print('Training: loss = %.5f, acc = %.5f | Val: loss = %.5f, acc = %.5f' % (train_loss_avg/tr_step, train_acc_avg/tr_step, val_loss_avg/vl_step, val_acc_avg/vl_step)) if val_acc_avg/vl_step >= vacc_mx or val_loss_avg/vl_step <= vlss_mn: if val_acc_avg/vl_step >= vacc_mx and val_loss_avg/vl_step <= vlss_mn: vacc_early_model = val_acc_avg/vl_step vlss_early_model = val_loss_avg/vl_step saver.save(sess, checkpt_file) vacc_mx = np.max((val_acc_avg/vl_step, vacc_mx)) vlss_mn = np.min((val_loss_avg/vl_step, vlss_mn)) curr_step = 0 else: curr_step += 1 if curr_step == patience: print('Early stop! Min loss: ', vlss_mn, ', Max accuracy: ', vacc_mx) print('Early stop model validation loss: ', vlss_early_model, ', accuracy: ', vacc_early_model) break train_loss_avg = 0 train_acc_avg = 0 val_loss_avg = 0 val_acc_avg = 0 saver.restore(sess, checkpt_file) ts_size = features.shape[0] ts_step = 0 ts_loss = 0.0 ts_acc = 0.0 while ts_step * batch_size < ts_size: loss_value_ts, acc_ts = sess.run([loss, accuracy], feed_dict={ ftr_in: features[ts_step*batch_size:(ts_step+1)*batch_size], bias_in: biases[ts_step*batch_size:(ts_step+1)*batch_size], lbl_in: y_test[ts_step*batch_size:(ts_step+1)*batch_size], msk_in: test_mask[ts_step*batch_size:(ts_step+1)*batch_size], is_train: False, attn_drop: 0.0, ffd_drop: 0.0}) ts_loss += loss_value_ts ts_acc += acc_ts ts_step += 1 print('Test loss:', ts_loss/ts_step, '; Test accuracy:', ts_acc/ts_step) sess.close()
就是建立图、然后在Session中执行。
这里需要注意的是,features的维度是(2708,1433),无论是tensorflow还是pytorch,都需要对其扩充一个维度:(1,2708,1433),其余数据也同样。在计算损失的时候,网络输出的值的维度注意是:(2708,7),就没有了之前的那个维度了。在pytorch中,输入的形状和tensorflow也不大一样,它的输入是:(1,1433,2708),第二位是特征的维度,第三位才是节点的数目,这是和tensorflow主要的区别之一。
接下来看下pytorch中是怎么做的:
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import numpy as np from utils import * from model import * np.random.seed(1) torch.manual_seed(1) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(1) torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") data = load_data("cora") adj = data['adj'] features = data['features'] y_train = data['y_train'] y_val = data['y_val'] y_test = data['y_test'] train_mask = data['train_mask'] val_mask = data['val_mask'] test_mask = data['test_mask'] train_my_labels = data['train_my_labels'] val_my_labels = data['val_my_labels'] test_my_labels = data['test_my_labels'] my_labels = data['my_labels'] features, spars = preprocess_features(features) #节点数目 nb_nodes = features.shape[0] #特征维度 ft_sizes = features.shape[1] #类别数目 nb_classes = my_labels.shape[0] #将邻接矩阵的稀疏形式转换为原始矩阵 adj = adj.todense() #新增加一个维度 adj = adj[np.newaxis] features = features[np.newaxis] y_train = y_train[np.newaxis] y_val = y_val[np.newaxis] y_test = y_test[np.newaxis] #train_mask = train_mask[np.newaxis] #val_mask = val_mask[np.newaxis] #test_mask = test_mask[np.newaxis] biases = torch.from_numpy(adj_to_bias(adj, [nb_nodes], nhood=1)).float().to(device) features = torch.from_numpy(features) #pytorch输入的特征:[batch, features,nodes],第二位是特征维度 #而tensorflow的输入是:[batch, nodes, features] features = torch.transpose(features,2,1).to(device) #定义相关变量 hid_units=[8] n_heads=[8, 1] epochs = 5000 lr = 0.01 #定义模型 gat = GAT(nb_classes=nb_classes, nb_nodes=nb_nodes, attn_drop=0.0, ffd_drop=0.0, bias_mat=biases, hid_units=hid_units, n_heads=n_heads, residual=False).to(device) criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = optim.Adam(params=gat.parameters(),lr=lr,betas=(0.9, 0.99)) #y_train = torch.from_numpy(np.where(y_train==1)[2]) #y_val = torch.from_numpy(np.where(y_val==1)[2]) #y_test = torch.from_numpy(np.where(y_test==1)[2]) train_my_labels = torch.from_numpy(train_my_labels).long().to(device) val_my_labels = torch.from_numpy(val_my_labels).long().to(device) test_my_labels = torch.from_numpy(test_my_labels).long().to(device) train_mask = np.where(train_mask == 1)[0] val_mask = np.where(val_mask == 1)[0] test_mask = np.where(test_mask == 1)[0] train_mask = torch.from_numpy(train_mask).to(device) val_mask = torch.from_numpy(val_mask).to(device) test_mask = torch.from_numpy(test_mask).to(device) print("训练节点个数:", len(train_my_labels)) print("验证节点个数:", len(val_my_labels)) print("测试节点个数:", len(test_my_labels)) def train(): gat.train() correct = 0 optimizer.zero_grad() outputs = gat(features) train_mask_outputs = torch.index_select(outputs, 0, train_mask) #print("train_mask_outputs.shape:",train_mask_outputs.shape) #print("train_my_labels.shape[0]:",train_my_labels.shape[0]) _, preds =torch.max(train_mask_outputs.data, 1) loss = criterion(train_mask_outputs, train_my_labels) loss.backward() optimizer.step() correct += torch.sum(preds == train_my_labels).to(torch.float32) acc = correct / train_my_labels.shape[0] return loss,acc def val(): gat.eval() with torch.no_grad(): correct = 0 outputs = gat(features) val_mask_outputs = torch.index_select(outputs, 0, val_mask) #print("val_mask_outputs.shape:",val_mask_outputs.shape) #print("val_my_labels.shape[0]:",val_my_labels.shape[0]) _, preds =torch.max(val_mask_outputs.data, 1) loss = criterion(val_mask_outputs, val_my_labels) correct += torch.sum(preds == val_my_labels).to(torch.float32) acc = correct / val_my_labels.shape[0] return loss,acc def test(): gat.eval() with torch.no_grad(): correct = 0 outputs = gat(features) test_mask_outputs = torch.index_select(outputs, 0, test_mask) #print("test_mask_outputs.shape:",test_mask_outputs.shape) #print("val_my_labels.shape[0]:",val_my_labels.shape[0]) _, preds =torch.max(test_mask_outputs.data, 1) loss = criterion(test_mask_outputs, test_my_labels) correct += torch.sum(preds == test_my_labels).to(torch.float32) acc = correct / test_my_labels.shape[0] print("TestLoss:{:.4f},TestAcc:{:.4f}".format(loss,acc)) return loss,acc,test_mask_outputs.cpu().numpy(),test_my_labels.cpu().numpy() from sklearn.manifold import TSNE import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def main(): train_loss_history = [] val_loss_history = [] train_acc_history = [] val_acc_history = [] for epoch in range(1,epochs+1): train_loss,train_acc = train() val_loss,val_acc = val() print("epoch:{:03d},TrainLoss:{:.4f},TrainAcc:{:.4f},ValLoss:{:.4f},ValAcc:{:.4f}" .format(epoch,train_loss,train_acc,val_loss,val_acc)) train_loss_history.append(train_loss) train_acc_history.append(train_acc) val_loss_history.append(val_loss) val_acc_history.append(val_acc) num_epochs = range(1, epochs + 1) plt.plot(num_epochs, train_loss_history, 'b--') plt.plot(num_epochs, val_loss_history, 'r-') plt.title('Training and validation Loss ') plt.xlabel("Epochs") plt.ylabel("Loss") plt.legend(["train_loss", 'val_loss']) plt.savefig("loss.png") plt.close() plt.plot(num_epochs, train_acc_history, 'b--') plt.plot(num_epochs, val_acc_history, 'r-') plt.title('Training and validation Acc ') plt.xlabel("Epochs") plt.ylabel("Acc") plt.legend(['train_acc','val_acc']) plt.savefig("acc.png") plt.close() _, _, test_data, test_labels = test() tsne = TSNE(perplexity=30, n_components=2, init='pca', n_iter=5000) # TSNE降维,降到2 low_dim_embs = tsne.fit_transform(test_data) plt.title('tsne result') plt.scatter(low_dim_embs[:,0], low_dim_embs[:,1], marker='o', c=test_labels) plt.savefig("tsne.png") plt.close() main()
大体上还是很简单明了的,这里还是的注意一个问题。在pytorch中,我们首使用网络对整个图进行计算,但是我们只更新根据mask所得的节点的参数,如果直接是使用outputs[train_mask],这样是不行的,pytroch的张量是不支持根据布尔值来进行分割的,如果我们将里面的True和False转换为1和0,虽然不会报错,但是就根本没有作用,因此在一开始,我们就要找到哪些节点是需要被训练的,取得其索引值,然后使用torch.index_select()进行切割。
最后绘制了损失函数和准确率随epoch的变化情况以及降维之后测试数据的分布情况。
3、结果
官方实现:
Dataset: cora ----- Opt. hyperparams ----- lr: 0.005 l2_coef: 0.0005 ----- Archi. hyperparams ----- nb. layers: 1 nb. units per layer: [8] nb. attention heads: [8, 1] residual: False nonlinearity: <function elu at 0x7f1b7507af28> model: <class 'models.gat.GAT'> (2708, 2708) (2708, 1433) epoch: 1 Training: loss = 1.94574, acc = 0.14286 | Val: loss = 1.93655, acc = 0.13600 epoch: 2 Training: loss = 1.94598, acc = 0.15714 | Val: loss = 1.93377, acc = 0.14800 epoch: 3 Training: loss = 1.94945, acc = 0.14286 | Val: loss = 1.93257, acc = 0.19600 epoch: 4 Training: loss = 1.93438, acc = 0.24286 | Val: loss = 1.93172, acc = 0.22800 epoch: 5 Training: loss = 1.93199, acc = 0.17143 | Val: loss = 1.93013, acc = 0.36400 。。。。。。 epoch: 674 Training: loss = 1.23833, acc = 0.49286 | Val: loss = 1.01357, acc = 0.81200 Early stop! Min loss: 1.010906457901001 , Max accuracy: 0.8219999074935913 Early stop model validation loss: 1.3742048740386963 , accuracy: 0.8219999074935913 Test loss: 1.3630210161209106 ; Test accuracy: 0.8219999074935913
自己的pytorch实现:
(2708, 2708) (2708, 1433) 训练节点个数: 140 验证节点个数: 500 测试节点个数: 1000 epoch:001,TrainLoss:7.9040,TrainAcc:0.0000,ValLoss:7.9040,ValAcc:0.0000 epoch:002,TrainLoss:7.9040,TrainAcc:0.0000,ValLoss:7.9039,ValAcc:0.1920 epoch:003,TrainLoss:7.9039,TrainAcc:0.0714,ValLoss:7.9039,ValAcc:0.1600 epoch:004,TrainLoss:7.9038,TrainAcc:0.1000,ValLoss:7.9039,ValAcc:0.1020 。。。。。。 epoch:2396,TrainLoss:7.0191,TrainAcc:0.8929,ValLoss:7.4967,ValAcc:0.7440 epoch:2397,TrainLoss:7.0400,TrainAcc:0.8786,ValLoss:7.4969,ValAcc:0.7580 epoch:2398,TrainLoss:7.0188,TrainAcc:0.8929,ValLoss:7.4974,ValAcc:0.7580 epoch:2399,TrainLoss:7.0045,TrainAcc:0.9071,ValLoss:7.4983,ValAcc:0.7620 epoch:2400,TrainLoss:7.0402,TrainAcc:0.8714,ValLoss:7.4994,ValAcc:0.7620 TestLoss:7.4805,TestAcc:0.7700
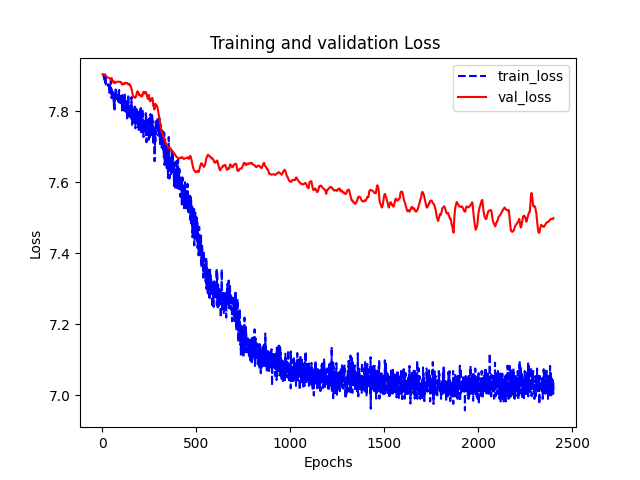
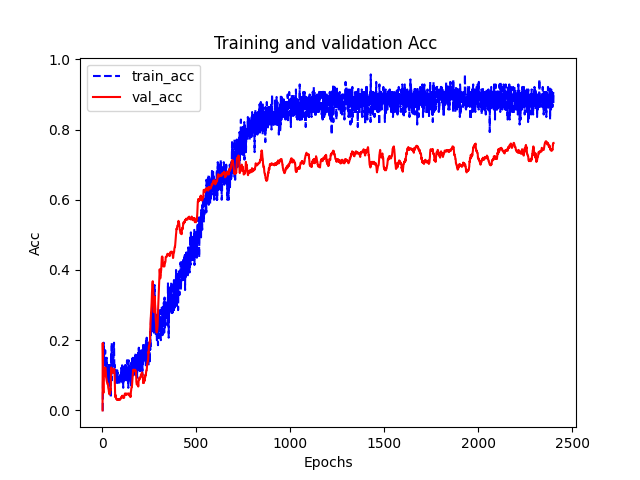
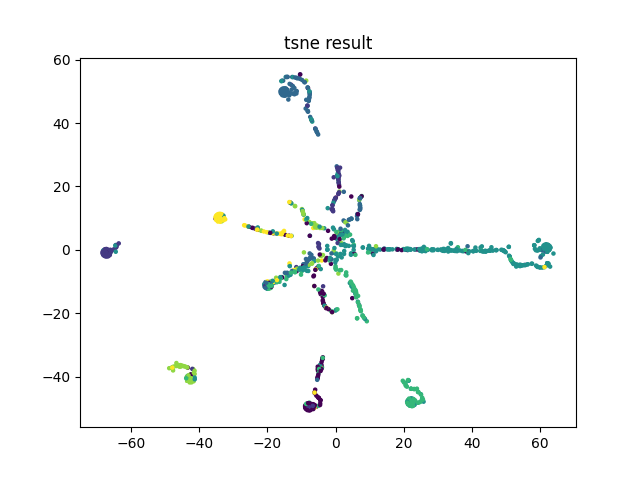
可能实现的和原始tensorflow版本的还有一些差别,自己实现的只有0.77。还有点奇怪的地方是loss比官方的大好多。。。
4、总结
关于tensorflow代码转pytorch需要注意的一些地方:
(1)输入的数据不同,比如特征,tensorflow是(1,2708,1433),pytorch的是(1,1433,2708)。
(2)标签的编码方式不同,tensorflow是onehot编码,比如[[0,0,1],[1,0,0],[0,1,0]],pytorch就是原始的类[2,0,1]。
(3)构建模型的方式不同,tensorflow直接使用,pytorch要继承nn.Module,然后在__init__建立层,在forward中进行计算。
(4)训练验证测试的不同,tensorflow要先构建计算图,然后在Session中执行计算,也就是静态图,pytorch是动态图,没有显示的定义计算图。
(5)相关的接口也不同,这是自然而然的,毕竟都有着自己的设计理念,比如tf.concat()对应torch.cat(),即使名字相同的两个类,使用的方法也可能是不同的。
总而言之,动手是最重要的。
如果哪里有问题,还请指出。