[C#/.NET]Entity Framework(EF) Code First 多对多关系的实体增,删,改,查操作全程详细示例
本文我们来学习一下在Entity Framework中使用Context删除多对多关系的实体是如何来实现的。我们将以一个具体的控制台小实例来了解和学习整个实现Entity Framework 多对多关系的实体删除的操作过程。
你将学习到
-
怎样创建一个引用Entity Framework的项目;
-
怎样配置Entity Framework的数据库连接;
-
怎样去掉Entity Framework Code First 生成的表名的复数;
-
怎样通过EntityTypeConfiguartion<T>配置实体的Fluent API ;
-
怎样配置Entity Framework的实体多对多的关系映射;
-
Entity Framework数据初始化;
-
怎样使用包管理工具控制台来生成和更新数据库;
-
怎么删除Entity Framework中的多对多关系的数据。
本示例开发环境
-
操作系统:Windows 10
-
开发工具及版本:Visual Studio 2015 Update 1
-
.NET Framework版本:.NET Framework 4.6
-
程序输出方式:控制台应用程序
第一步、创建项目并引用程序包
1.1 创建项目
首先,我们创建一个控制台应用程序,取名为:EFRemoveManyToManyDemo,如下图:

1.2 引用程序包
接着打开程序包管理工具,安装必须的EntityFramework引用包,如下:

第二步、创建实体类并配置数据库连接
2.1 创建实体类
安装好Entity Framework包之后 ,我们先创建本示例需要的两个实体对应的类:User和Role(都放在Model的文件夹下),如下:
User.cs
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 4 namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Model 5 { 6 public class User 7 { 8 public User() 9 { 10 Roles = new HashSet<Role>(); 11 } 12 public int Id { get; set; } 13 public string FirstName { get; set; } 14 public string LastName { get; set; } 15 public DateTime? CreatedOn { get; set; } 16 public virtual ICollection<Role> Roles { get; set; }//多对多关系中两边都要写上ICollection 17 } 18 }
Role.cs
1 using System.Collections.Generic; 2 3 namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Model 4 { 5 public class Role 6 { 7 public Role() 8 { 9 this.Users = new HashSet<User>();!!依赖注入中的构造器注入 10 } 11 public int Id { get; set; } 12 public string Name { get; set; } 13 14 public virtual ICollection<User> Users { get; set; } 15 //多对多关系中两边都要写上ICollection 16 } 17 }
2.2 配置Fluent API
为了配置Fluent API,新建一个Mapping文件夹,再分别创建User的配置文件UserConfigurationMapping和Role的配置文件RoleConfigurationMapping,如下:
UserConfiguration.cs
using EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Model; using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration; namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Mapping { public class UserConfigurationMapping : EntityTypeConfiguration<User> { public UserConfigurationMapping() { Property(x => x.FirstName).HasMaxLength(50).IsRequired(); Property(x => x.LastName).HasMaxLength(50).IsRequired(); } } }
RoleConfigurationMapping.cs
1 using EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Model; 2 using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration; 3 4 namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Mapping 5 { 6 public class RoleConfigurationMapping : EntityTypeConfiguration<Role> 7 { 8 public RoleConfigurationMapping() 9 { 10 HasKey(x => x.Id); 11 Property(x => x.Name).HasMaxLength(50).IsRequired(); 12 HasMany(x => x.Users) 13 .WithMany(x => x.Roles) 14 .Map(m => 15 { 16 m.MapLeftKey("RoleId"); 17 m.MapRightKey("UserId"); 18 m.ToTable("LNK_User_Role"); 19 }); 20 } 21 } 22 }
2.3 创建Context类
接下来,我们再创建一个名为:ManyToManyRemoveContext的类,该类继承至DbContext类,用于管理数据库的连接上下文和数据库初始化等的一些配置和操作,如下:
using EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Mapping; using System.Data.Entity; using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration.Conventions; namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo { public class ManyToManyRemoveContext : DbContext { public ManyToManyRemoveContext() : base("ManyToManyRemoveContext") { } } }
2.4 配置连接字符串
再在App.config配置文件中添加本地的数据库连接字符串,大致如下(具体的请根据你的实际数据连接参数来):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <configSections> <!-- For more information on Entity Framework configuration, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=237468 --> <section name="entityFramework" type="System.Data.Entity.Internal.ConfigFile.EntityFrameworkSection, EntityFramework, Version=6.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" requirePermission="false" /> </configSections> <startup> <supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.6" /> </startup> <connectionStrings> <add name="ManyToManyRemoveContext" connectionString="server=你的数据库服务器地址;database=ManyToManyRemoveDemo;uid=你的数据库登录名;pwd=密码" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient"/> </connectionStrings> <entityFramework> <defaultConnectionFactory type="System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.LocalDbConnectionFactory, EntityFramework"> <parameters> <parameter value="mssqllocaldb" /> </parameters> </defaultConnectionFactory> <providers> <provider invariantName="System.Data.SqlClient" type="System.Data.Entity.SqlServer.SqlProviderServices, EntityFramework.SqlServer" /> </providers> </entityFramework> </configuration>
2.5 重写Context
为了将我们刚才写的Fluent API应用到对应的实体上,所以我们需要重写(override)DbContext的OnModelCreating方法,如下:
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder); modelBuilder.Conventions.Remove<PluralizingTableNameConvention>(); modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new UserConfigurationMapping()); modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new RoleConfigurationMapping()); }
其中
modelBuilder.Conventions.Remove<PluralizingTableNameConvention>();
是将Entity Framework Code First在实体类生成对应表时去掉表名的复数用的。简单地说就是,默认情况下,Entity Framework Code First在由实体类生成对应表时的表名是复数形式的,比如本例的User和Role类,如果没有这句配置,在生成表名的时候将会是Users和Roles这两个表名,反之,则是User和Role这两个表名。
好了,下面贴出完整的ManyToManyRemoveContext.cs文件的代码:
1 using EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Mapping; 2 using EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Model; 3 using System.Data.Entity; 4 using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration.Conventions; 5 6 namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo 7 { 8 public class ManyToManyRemoveContext : DbContext 9 { 10 public ManyToManyRemoveContext() : base("ManyToManyRemoveContext") 11 { 12 13 } 14 15 protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) 16 { 17 base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder); 18 modelBuilder.Conventions.Remove<PluralizingTableNameConvention>(); 19 20 modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new UserConfigurationMapping()); 21 modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new RoleConfigurationMapping()); 22 } 23 24 public DbSet<User> Users { get; set; } 25 public DbSet<Role> Roles { get; set; } 26 } 27 }
本文写到这里,关于Entity Framework的引用,实体类的声明和Fluent API配置以及与数据库连接等操作都已完成了。接下来我们要做的是利用Entity Framework所实体生成到配置好的数据库中。
第三步、应用Migration生成数据库
在接下来的过程中,我们会用到包管理控制台(Package Manager Console)和三个命令:
3.1 Enable-Migrations
命令使用方式如下图:

运行以上命令后,Entity Framework会自动在我们的项目中创建一个名为Migrations的文件夹,同时生成一个Configuartion.cs的配置文件。这时的项目结构大致是这样的:
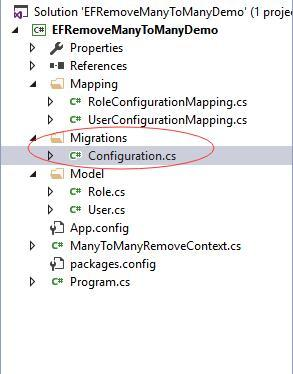
生成好Configuration.cs的文件我们再作数据的初始化,如下:
namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Migrations { using Model; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Data.Entity.Migrations; using System.Linq; internal sealed class Configuration : DbMigrationsConfiguration<ManyToManyRemoveContext> { public Configuration() { AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = false; } protected override void Seed(ManyToManyRemoveContext context) { var roles = new List<Role> { new Role{ Id=1,Name="超级管理员" }, new Role{ Id=2,Name="管理员" }, new Role{ Id=3,Name="一般用户" } }; var users = new List<User> { new User {Id=1,FirstName="Kobe",LastName="Bryant",CreatedOn=DateTime.Now,Roles=roles }, new User {Id=2,FirstName="Chris",LastName="Paul",CreatedOn=DateTime.Now,Roles=roles.Where(x=>x.Id==2).ToList() }, new User {Id=3,FirstName="Jerimy",LastName="Lin",CreatedOn=DateTime.Now,Roles=roles.Take(2).ToList() } }; } } }
完成第一个命令和数据初始化配置后,我们进行第二个命令。
3.2 Add-Migration Init -Verbose
执行此命令后,会在Migrations的文件夹中自动生成一个形如:时间戳_Init.cs的数据迁移文件,如本例生成的是201512040507219_Init.cs这样一个文件名,其中Init是我们指定的本次数据迁移的版本名称,文件中的内容如下:
1 namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Migrations 2 { 3 using System; 4 using System.Data.Entity.Migrations; 5 6 public partial class Init : DbMigration 7 { 8 public override void Up() 9 { 10 CreateTable( 11 "dbo.Role", 12 c => new 13 { 14 Id = c.Int(nullable: false, identity: true), 15 Name = c.String(nullable: false, maxLength: 50), 16 }) 17 .PrimaryKey(t => t.Id); 18 19 CreateTable( 20 "dbo.User", 21 c => new 22 { 23 Id = c.Int(nullable: false, identity: true), 24 FirstName = c.String(nullable: false, maxLength: 50), 25 LastName = c.String(nullable: false, maxLength: 50), 26 CreatedOn = c.DateTime(), 27 }) 28 .PrimaryKey(t => t.Id); 29 30 CreateTable( 31 "dbo.LNK_User_Role", 32 c => new 33 { 34 RoleId = c.Int(nullable: false), 35 UserId = c.Int(nullable: false), 36 }) 37 .PrimaryKey(t => new { t.RoleId, t.UserId }) 38 .ForeignKey("dbo.Role", t => t.RoleId, cascadeDelete: true) 39 .ForeignKey("dbo.User", t => t.UserId, cascadeDelete: true) 40 .Index(t => t.RoleId) 41 .Index(t => t.UserId); 42 43 } 44 45 public override void Down() 46 { 47 DropForeignKey("dbo.LNK_User_Role", "UserId", "dbo.User"); 48 DropForeignKey("dbo.LNK_User_Role", "RoleId", "dbo.Role"); 49 DropIndex("dbo.LNK_User_Role", new[] { "UserId" }); 50 DropIndex("dbo.LNK_User_Role", new[] { "RoleId" }); 51 DropTable("dbo.LNK_User_Role"); 52 DropTable("dbo.User"); 53 DropTable("dbo.Role"); 54 } 55 } 56 }
我们可以通过这个文件中的内容看到,有Up()和Down()这两个方法,Up()方法要执行的其实就是本次数据迁移要对数据进行的操作,而Down()方法则是在以后我们如果要退回到此版本应该执行的操作。
经过以上两个命令,如你迫不及待地要去数据库管理工具中查看有一个名叫:ManyToManyRemoveDemo的数据库是否已生成,那么很遗憾地告诉你,还没有。这时,我们还得执行最后一个命令来生成数据库和实体对应的表。
3.3 Update-Database -Verbose
执行以上命令,我们这时再打开数据库管理工具。没错ManyToManyRemoveDemo就在那里。再查看表是否成功生成呢,再检查一下表中是否有我们初始化的数据呢,没错,这些都是可以有的。怎么样,惊喜吧,欢呼吧,我们做到了!!!

但还没完,请先回复平静,这还只是一个开始。Entity Framework还可以做得更多,我们需要学习的也还有很多,编程的道路从来就不是一步到位的,得有个过程。一步一步往下看吧。
第四步、增、删、改、查操作
4.1 查询数据示例
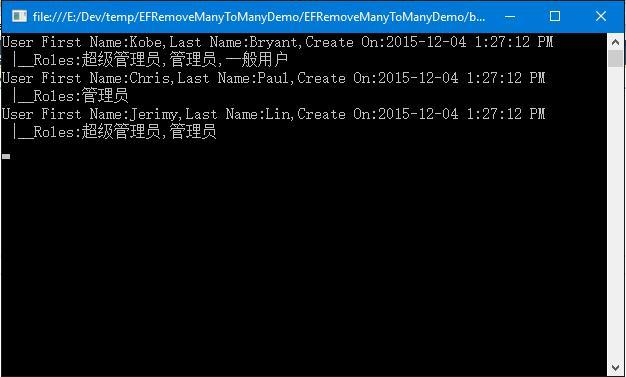
打开我们项目的Program.cs文件。首先,我们来查询(Query)一下数据库中的数据,如下:
1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 { 3 Query(); 4 ReadKey(); 5 } 6 7 static void Query() 8 { 9 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 10 { 11 var users = cxt.Users.ToList(); 12 users.ForEach(x => 13 { 14 WriteLine("User First Name:{0},Last Name:{1},Create On:{2} |__Roles:{3}", x.FirstName, x.LastName, x.CreatedOn, string.Join(",", x.Roles.Select(r => r.Name))); 15 }); 16 } 17 }
运行结果如图:
4.2 更新数据示例
再来更新一条数据库中的数据怎么样,如下:
1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 { 3 Update(); 4 Query(); 5 ReadKey(); 6 } 7 8 static void Query() 9 { 10 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 11 { 12 var users = cxt.Users.ToList(); 13 users.ForEach(x => 14 { 15 WriteLine("User First Name:{0},Last Name:{1},Create On:{2} |__Roles:{3}", x.FirstName, x.LastName, x.CreatedOn, string.Join(",", x.Roles.Select(r => r.Name))); 16 }); 17 } 18 } 19 20 static void Update() 21 { 22 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 23 { 24 var user = cxt.Users.FirstOrDefault(x=>x.Id==3); 25 user.FirstName = "ShuHao"; 26 cxt.SaveChanges(); 27 } 28 }
运行结果如我们所料,如图:

4.3 删除数据示例
Id为3的User的FirstName已经从数据库更新了。同样的,我们要完成删除操作也比较简,如下:
1 static void Remove() 2 { 3 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 4 { 5 var user = cxt.Users.FirstOrDefault(x=>x.Id==2); 6 cxt.Users.Remove(user); 7 cxt.SaveChanges(); 8 } 9 }
4.4 新增数据示例
就不再贴图了。最后是添加操作,向User表添加一个用户并分配一个Id为1的角色,代码如下:
1 static void Add() 2 { 3 List<Role> roles; 4 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 5 { 6 roles = cxt.Roles.ToList(); 7 cxt.Users.Add(new User 8 { 9 Id = 4, 10 FirstName = "Console", 11 LastName = "App", 12 CreatedOn = DateTime.Now, 13 Roles = roles.Where(x => x.Id == 1).ToList() 14 }); 15 } 16 }
4.5 删除多对多数据的示例
好了,以上是对User(用户实体)进行简单的增、删、改、查的操作,那么我们要实现多对多的删除操作呢?也就是删除用户的同时删除其对应的角色,实现的代码如下:
1 static void RemoveManyToMany() 2 { 3 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 4 { 5 var user = cxt.Users.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == 1); 6 var roles = new List<Role>(); 7 roles.AddRange(user.Roles.Select(x => x)); 8 foreach (var role in roles) 9 { 10 user.Roles.Remove(role); 11 } 12 cxt.Users.Remove(user); 13 cxt.SaveChanges(); 14 } 15 }
运行结果如图:

完整示例代码及下载地址
好了,最后把Program.cs这个测试文件贴上来,供参考:
1 using EFRemoveManyToManyDemo.Model; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using static System.Console; 6 7 namespace EFRemoveManyToManyDemo 8 { 9 public class Program 10 { 11 static void Main(string[] args) 12 { 13 //Update(); 14 WriteLine("Before many to many removed"); 15 Query(); 16 RemoveManyToMany(); 17 WriteLine("After many to many removed"); 18 Query(); 19 ReadKey(); 20 } 21 22 static void Query() 23 { 24 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 25 { 26 var users = cxt.Users.ToList(); 27 users.ForEach(x => 28 { 29 WriteLine("User First Name:{0},Last Name:{1},Create On:{2} |__Roles:{3}", x.FirstName, x.LastName, x.CreatedOn, string.Join(",", x.Roles.Select(r => r.Name))); 30 }); 31 } 32 } 33 34 static void Add() 35 { 36 List<Role> roles; 37 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 38 { 39 roles = cxt.Roles.ToList(); 40 cxt.Users.Add(new User 41 { 42 Id = 4, 43 FirstName = "Console", 44 LastName = "App", 45 CreatedOn = DateTime.Now, 46 Roles = roles.Where(x => x.Id == 1).ToList() 47 }); 48 } 49 } 50 51 static void Update() 52 { 53 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 54 { 55 var user = cxt.Users.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == 3); 56 user.FirstName = "ShuHao"; 57 cxt.SaveChanges(); 58 } 59 } 60 61 static void Remove() 62 { 63 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 64 { 65 var user = cxt.Users.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == 2); 66 cxt.Users.Remove(user); 67 cxt.SaveChanges(); 68 } 69 } 70 71 static void RemoveManyToMany() 72 { 73 using (var cxt = new ManyToManyRemoveContext()) 74 { 75 var user = cxt.Users.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == 1); 76 var roles = new List<Role>(); 77 roles.AddRange(user.Roles.Select(x => x)); 78 foreach (var role in roles) 79 { 80 user.Roles.Remove(role); 81 } 82 cxt.Users.Remove(user); 83 cxt.SaveChanges(); 84 } 85 } 86 } 87 }