一、映射文件

1.简单的增删改(需要commit)---查
MyBatis允许增删改直接定义以下类型返回值
Integer、Long、Boolean、void
我们需要手动提交数据。
sqlSessionFactory.openSession();===>需要手动提交
sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);===>自动提交
2.获取insert-自增的主键
JDBC中Statement的方法:getGeneratedKeys();--->获取由于执行此Statement对象而创建的所有自动生成的键。
<!--自增主键的值 获取 mysql支持自增主键,自增主键值的获取,mybatis也是利用statement.getGeneratedKeys(); useGeneratedKeys="true":使用自增主键获取主键值策略 keyProperty:指定对应的主键属性,也就是mybatis获取到主键值之后,将这个值封装给JavaBean的哪个属性 --> <insert id="addEmp" parameterType="emp" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender) values(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender}) </insert>
Oracle:自增的序列
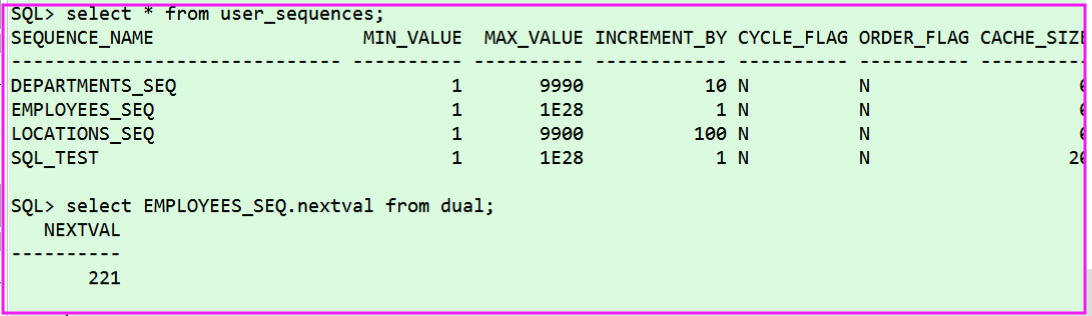
~~ before:从序列中查主键的SQL在插入SQL之前执行
<!-- Oracle不支持自增;Oracle使用序列来模拟自增; 每次插入的数据的主键是从序列中拿到的值;如何获取到这个值 --> <insert id="addEmp" databaseId="oracle" parameterType="emp"> /* keyProperty:查出的主键值封装给Javabean的哪个属性 order="BEFORE":当前SQL在插入SQL之前执行 resultType:查出数据的返回值类型 */ <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="Integer"> /*编写查询主键的SQL语句*/ select 序列名.nextval from dual </selectKey> /*插入时的主键是从序列中拿到的*/ insert into tbl_employee(id,last_name,email,gender) values (#{id},#{lastName},#{email},#{gender}) </insert>
~~after:
<!-- Oracle不支持自增;Oracle使用序列来模拟自增; 每次插入的数据的主键是从序列中拿到的值;如何获取到这个值 --> <insert id="addEmp" databaseId="oracle" parameterType="emp"> /* keyProperty:查出的主键值封装给Javabean的哪个属性 order="AFTER":当前SQL在插入SQL之后执行 resultType:查出数据的返回值类型 */ <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="Integer"> /*编写查询主键的SQL语句 获取当前的序列值 */ select 序列名.currval from dual </selectKey> insert into tbl_employee(id,last_name,email,gender) values (序列名.nextval,#{lastName},#{email},#{gender}) </insert>
3.映射文件---参数处理(单个参数&多个参数)
单个参数:MyBatis不会做特殊处理。
#{参数名}:取出参数值,参数名可以任意写。
多个参数:MyBatis会做特殊处理。
多个参数会被封装成一份Map,
key:param1...paramN,或者参数的索引也可以
value:传入的参数值
#{ }就是从Map中获取指定的key的值;
public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName(Integer id,String lastName);
<select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName" resultType="emp"> select * from tbl_employee where id = #{param1} and last_name = #{param2} </select>
命名参数:明确指定封装参数值时map的key;@Param("id")
多个参数会被封装成一个Map,
key:使用@Param注解指定的值
value:参数值
#{指定的key}:取出对应的参数值
public Employee getEmpByIdAndLastName(@Param("id") Integer id,@Param("lastName") String lastName);
<select id="getEmpByIdAndLastName" resultType="emp"> select * from tbl_employee where id = #{id} and last_name = #{lastName} </select>
4.映射文件---参数处理---POJO&TO
POJO:
如果多个参数正好是我们业务逻辑的数据模型,直接传入POJO;
#{属性名}:取出传入的POJO的属性值
Map:
如果多个参数不是业务模型中的数据,没有对应的POJO,为了方便,我们也可以传入Map;
#{key}:取出map中对应的值
public Employee getEmpByMap(Map<String,Object> map);
<select id="getEmpByMap" resultType="emp"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} and last_name=#{lastName} </select>
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class); Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("id",2); map.put("lastName","jesscia"); Employee jesscia = mapper.getEmpByMap(map); System.out.println(jesscia);
TO:
如果多个参数不是业务模型中的数据,但是经常要使用,推荐来编写一个TO(Transfer Object)数据传输对象。
例如:分页时的Page类。
5.映射文件---参数处理---参数封装扩展思考
public Employee getEmp(@param("id")Integer id,String lastName);
取值:id===>#{id/param1} last_name===>#{param2}
public Employee getEmp((Integer id,@param("e")Employee emp);
取值:id===>#{param1} last_name===>#{param2.lastName/e,lastName}
##特别注意:如果是Collection(List、Set)类型或者是数组,也会特殊处理。也是把传入的List或者数组封装在map中。
key:Collection(collection),如果是List还可以使用这个key(list)
public Employee getEmpById(List<Integer> ids);
取值:取出第一个id值: #{list[0]}
===============可以结合MyBatis源码,看怎样处理参数。=============
6.映射文件===参数处理===#与$取值区别
#{ }:可以获取map中的值或者POJO对象属性的值;
${ }:可以获取map中的值或者POJO对象属性的值;
select * from tbl_employee where id=${id} and last_name=#{lastName}
Preparing: select * from tbl_employee where id=2 and last_name=?
区别:
#{ }:是以预编译的形式,将参数设置到sql语句中;PreparedStatement;防止sql注入
${ }:取出的值直接拼接在sql语句中,会有安全问题;
大多数情况下,我们取参数的值都应该去使用#{ };
原生JDBC不支持占位符的地方我们就可以使用${ }进行取值;
比如分表、排序。。。:按照年份分表拆分
select * from ${year}_salary where xxx;
select * from tbl_employee order by ${f_name};按照什么排序
7.映射文件===参数处理===#取值时指定参数相关规则
#{ }:更丰富的用法;
规定参数的一些规则:
javaType、jdbcType、mode(存储过程)、numericScale、
resultMap、typeHandler、jdbcTypeName、expression(未来准备支持的功能)
jdbcType通常需要在某种特定的条件下被设置:
在我们数据为null的时候,有些数据库可能不能识别mybatis对null的处理。比如Oracle(报错);
JdbcType OTHER:无效的类型;因为mybatis对所有的null都映射的是原生Jdbc的OTHER类型,Oracle不能正确处理;
MyBatis里有JdbcType枚举类,与数据库中的各种类型进行映射。
例如:#{email, JdbcType=NULL},在Oracle环境下,如果email为NUll,怎会出现JdbcType OTHER错误,把JdbcType改为NULL就行。即#{email,JdbcType=NULL}。
由于全局配置中:jdbcTypeForNull=OTHER;Oracle不支持;两种解决方法:
1、#{email, jdbcType=NULL};
2、jdbcTypeForFull=NULL
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/> 在全局配置文件中设置
7.映射文件===select返回List

resultType: 如果返回是一个集合,要写集合中元素的类型。
public List<Employee> getEmpsByLastNameLike(String lastName);
<select id="getEmpsByLastNameLike" resultType="emp"> select * from tbl_employee where last_name like #{lastName} </select>
List<Employee> list = mapper.getEmpsByLastNameLike("%s%");
System.out.println("list:"+list);
8.映射文件===select记录封装Map
返回一条记录的map;key就是列名,值就是对应的值
//返回一条记录的map;key就是列名,值就是对应的值 public Map<String,Object> getEmpByIdReturnMap(Integer id);
<select id="getEmpByIdReturnMap" resultType="map"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} </select>
//单条记录的key值是列名 Map<String, Object> map = mapper.getEmpByIdReturnMap(2); String lastName = (String) map.get("last_name");
返回多条记录封装到map中:===注解@MapKey的使用:告诉MyBatis封装的时候使用哪个属性作为map的key
//多条记录封装一个Map:Map<Integer,Employee>:键是这条记录的主键,值是记录封装后的Javabean //告诉Mybatis封装这个Map的时候使用哪个属性作为map的key。 @MapKey("id") public Map<Integer,Employee> getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap(String lastName);
<select id="getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap" resultType="emp"> select * from tbl_employee where last_name like #{lastName} </select>
Map<Integer, Employee> map = mapper.getEmpByLastNameLikeReturnMap("%s%");
9.映射文件===select_resultMap===自定义结果映射规则
自动映射:

自定义resultMap,高级映射:
<!--自定义某个Javabean的封装规则 type:自定义规则的java类型 id:唯一id,方便引用 --> <resultMap id="MyEmp" type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> <!--指定主键列的封装规则 id:定义主键会底层有优化; column:指定哪一列 property:指定对应的Javabean属性 --> <id column="id" property="id"/> <!--定义普通列封装规则 --> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <!--其他不指定的列会自动封装:我们只要写resultMap就把全部的映射规则全写上--> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> </resultMap> <!--resultMap:自定义结果集映射规则;--> <select id="getEmpById" resultMap="MyEmp"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} </select>
10.映射文件===select_resultMap===关联查询_环境搭建
数据库准备:
/*创建部门表*/
CREATE TABLE tbl_dept(
id int(11) PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
dept_name VARCHAR(255)
)
/*向表Employee中插入一列*/
ALTER TABLE tbl_employee ADD COLUMN d_id INT(11);
/*添加约束,外键关联*/
ALTER TABLE tbl_employee ADD CONSTRAINT fk_emp_dept
FOREIGN KEY(d_id) REFERENCES tbl_dept(id)
/*查*/
SELECT e.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.email email,e.d_id d_id,
d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name
FROM tbl_employee e,tbl_dept d
WHERE e.d_id=d.id AND e.id=2
在Employee类中增加所属部门(另一个类)信息。
public Employee getEmpAndDept(Integer id);
<!-- 场景一: 查询Employee的同时查询员工对应的部门 Employee====Department 一个员工有与之对应的部门信息; --> <!-- 联合查询:级联属性封装结果集 --> <resultMap id="MyDifEmp" type="emp"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="did" property="dept.id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="dept.departmentName"/> </resultMap> <select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="MyDifEmp"> SELECT e.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.email email,e.d_id d_id, d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name FROM tbl_employee e,tbl_dept d WHERE e.d_id=d.id AND e.id=#{id} </select>
Employee empAndDept = mapper.getEmpAndDept(2);
System.out.println(empAndDept);
System.out.println(empAndDept.getDept());
11.映射文件===select_resultMap关联查询association定义关联对象封装规则
<!--使用association定义关联的单个对象的封装规则--> <resultMap id="MyDifEmp2" type="emp"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <!--association:可以指定联合的Javabean对象 property:指定哪个属性是联合的对象 javaType:指定属性的java类型[不能省略] --> <association property="dept" javaType="department"> <id column="did" property="id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/> </association> </resultMap> <select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="MyDifEmp2"> SELECT e.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.email email,e.d_id d_id, d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name FROM tbl_employee e,tbl_dept d WHERE e.d_id=d.id AND e.id=#{id} </select>
12.映射文件===select_resultMap关联查询association分步查询
public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id);
<resultMap id="MyEmpByStep" type="emp"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <!--association:定义关联对象的封装规则 select:表明当前属性是调用select指定的方法查出的结果 column:指定将哪一列的值传给这个方法 流程:使用select指定的方法(传入column指定的这列参数的值)查出对象,并封装给property指定的属性 --> <association property="dept" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById" column="d_id"> </association> </resultMap> <!--使用association进行分步查询 1、先按照员工id查询员工信息 2、根据查询员工信息中的d_id值去部门表查询部门信息 --> <select id="getEmpByIdStep" resultMap="MyEmpByStep"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} </select>
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper"> <select id="getDeptById" resultType="department"> select id,dept_name departmentName from tbl_dept where id=#{id} </select> </mapper>
Employee empByIdStep = mapper.getEmpByIdStep(2);
System.out.println(empByIdStep);
System.out.println(empByIdStep.getDept());
结果:控制台上会出现两次数据库查询
DEBUG 11-16 21:04:50,898 ==> Preparing: select * from tbl_employee where id=? (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145) DEBUG 11-16 21:04:50,923 ==> Parameters: 2(Integer) (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145) DEBUG 11-16 21:04:50,949 ====> Preparing: select id,dept_name departmentName from tbl_dept where id=? (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145) DEBUG 11-16 21:04:50,953 ====> Parameters: 1(Integer) (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145) DEBUG 11-16 21:04:50,957 <==== Total: 1 (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145) DEBUG 11-16 21:04:50,958 <== Total: 1 (BaseJdbcLogger.java:145) Employee{id=2, lastName='jesscia', email='jesscia@qq.com', gender='0', dept=Department{id=1, departmentName='开发部'}} Department{id=1, departmentName='开发部'}
13.映射文件===select_resultMap关联查询association分步查询&延时加载
分步查询:1.可以组合已有的方法来完成复杂功能,2.可以使用延迟加载
在分步查询的基础之上:延时加载
<!--可以使用延迟加载 Employee==>Dept; 我们每次查询Employee对象时,都将一起查询出来。 部门信息在我们使用的时候再去查询。 分步查询的基础之上加上两个配置, -->
在全局配置文件中设置:
<settings> <!--显示的指定每个我们需要更改的配置的值,即使他是默认的。防止版本更新带来的问题--> <!--打开延时加载的开关--> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!--将积极加载改为消极加载及按需加载--> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> </settings>
然后就可以按需加载了。
14.映射文件===select_resultMap关联查询collection定义关联集合封装规则
场景二:查询部门的时候将部门对应的所有员工信息也查询出来
public Department getDeptByIdPlus(Integer id)throws Exception;
嵌套结果集的方式:
<!--collection:嵌套结果集的方式--> <resultMap id="MyDept" type="department"> <id column="did" property="id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/> <!--collection:定义关联集合类型的属性的封装规则 ofType:指定集合里面元素的类型 --> <collection property="emps" ofType="emp"> <id column="eid" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="getDeptByIdPlus" resultMap="MyDept"> SELECT d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name, e.id eid,e.last_name last_name,e.email email,e.gender gender FROM tbl_dept d LEFT JOIN tbl_employee e ON d.id=e.d_id WHERE d.id=#{id} </select>
15.映射文件===select_resultMap关联查询collection分步查询&延时加载
public Department getDeptByIdStep(Integer id);
<!--==========分步查询===========--> <resultMap id="MyDept2" type="department"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/> <collection property="emps" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.EmployeeMapperPlus.getEmpsByDid" column="id"> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="getDeptByIdStep" resultMap="MyDept2"> select id,dept_name departmentName from tbl_dept where id=#{id} </select>
public List<Employee> getEmpsByDid(Integer did);
<select id="getEmpsByDid" resultType="emp"> select * from tbl_employee where d_id=#{did} </select>
小扩展:在association和collection中的column属性
作用:分步查询中的要传递的参数值
当多列的值传递过去:将多列的值封装成map传递;
column="{key1=column1, key2=column2}"
======================================
fetchType=“lazy”:表示使用延迟加载;
-lazy:延迟
-eager:立即
16.映射文件===select_resultMap的discriminator鉴别器
mybatis可以使用discriminator判断某列的值,然后根据某列的值改变封装行为。
封装Employee:
如果查询出的是女生:就把部门信息查询出来,否则不查询;
如果是男生,把last_name这一列的值赋值给email;
<resultMap id="MyEmpDis" type="emp"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <!--column:指定判断的列名 javaType:列值对应的java类型 --> <discriminator javaType="string" column="gender"> <!--女生 resultType:指定封装的结果类型--> <case value="0" resultType="emp"> <association property="dept" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById" column="d_id"> </association> </case> <!--男生--> <case value="1" resultType="emp"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <result column="last_name" property="email"/> </case> </discriminator> </resultMap>
<select id="getEmpByIdStep" resultMap="MyEmpDis"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} </select>