一、继承
1、题目
运行 TestInherits.java 示例,观察输出,注意总结父类与子类之间构造方法的调用关系修改Parent构造方法的代码,显式调用GrandParent的另一个构造函数,注意这句调用代码是否是第一句,影响重大!
TestInherits.java:
class Grandparent { public Grandparent(){ System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent2 extends Grandparent{ public Parent2(){ super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child2 extends Parent2 { public Child2() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { public static void main(String args[]) { Child2 c = new Child2(); } }
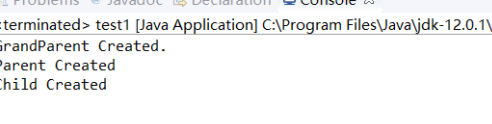
3、结论:
1、子类的构造方法在执行之前,必须先调用父类的构造方法
2、通过 super 调用父类构造方法,super必须是子类构造
public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); parent.myValue++; parent.printValue(); ((Child)parent).myValue++; parent.printValue(); } } class Parent{ public int myValue=100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
方法中编写的第一个语句
3、super本身就是调用父类的构造方法,而且可以执行父类被隐藏的成员变量和被覆盖的父类成员方法
4、思索:为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
5、解答:不能,子类拥有父类的成员变量和成员方法,如果不调用父类的构造方法,则从父类继承而来的成员变
量和成员方法不能进行初始化。而不能反过来调用原因是,因为父类不能知道子类有什么成员变量和成员方法
并且这样做子类不能在父类帮助下完成继承来的成员变量的初始化,导致成员变量无法初始化,程序就会报错,
无法执行。
二,多态
1,在实践中理解把握复杂的知识-1
ParentChildTest.java

2. 你如何解释会得到这样的输出?
前两行正常,
第三行,当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,
第四行,parent=child;仅仅是将parent中有的值用child的值代替,所以parent.myValue++;parent只有一个自己的myValue值,而输出的是child的myValue。
第五行,强制类型转换,++作用在child的myValue,输出的也是child的myValue
3. 计算机是不会出错的,之所以得 到这样的运行结果也是有原因的, 那么从这些运行结果中,你能总 结出Java的哪些语法特性?
总结:
1,当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
2,这个特性实际上就是面向对象“多态”特性的具体表现。
3,如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。
4,如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的!