第1 章 使用字符串

第7章 使用关联容器

下面一个交叉引用表达代码,其中包括了getword函数
 View Code
View Code
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
vector<string> getwords(const string& str)
{
vector<string> ret;
static string delim=" \\/,.;:!~*`\'\"\t\b\n#<>(){}[]]&=-+";
string word;
size_t pos,pos2;
size_t len=str.size();
pos=-1;
bool flag=true;
while(flag){
pos=str.find_first_not_of(delim,pos+1);
if(pos==string::npos)
break;
pos2=str.find_first_of(delim,pos+1);
if(pos2==string::npos)
{
pos2=len-1;
flag=false;
}
word=str.substr(pos,pos2-pos+1);
ret.push_back(word);
// cout<<word<<' ';
pos=pos2;
}
// cout<<endl;
return ret;
}
map<string, vector<int> >
xref(istream& in,
vector<string> find_words(const string&) = getwords)
{
string line;
int line_number = 0;
map<string, vector<int> > ret;
// read the next line
while (getline(in, line)) {
++line_number;
// break the input line into words
vector<string> words = find_words(line);
// remember that each word occurs on the current line
for (vector<string>::const_iterator it = words.begin();
it != words.end(); ++it)
ret[*it].push_back(line_number);
}
return ret;
}
int test1(){
string line;
while(getline(cin,line)){
getwords(line);
}
return 0;
}
int test2()
{
// call `xref' using `split' by default
map<string, vector<int> > ret = xref(cin);
// write the results
for (map<string, vector<int> >::const_iterator it = ret.begin();
it != ret.end(); ++it) {
// write the word
cout << it->first << " occurs on line(s): ";
// followed by one or more line numbers
vector<int>::const_iterator line_it = it->second.begin();
cout << *line_it; // write the first line number
++line_it;
// write the rest of the line numbers, if any
while (line_it != it->second.end()) {
cout << ", " << *line_it;
++line_it;
}
// write a new line to separate each word from the next
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
test2();
}
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
vector<string> getwords(const string& str)
{
vector<string> ret;
static string delim=" \\/,.;:!~*`\'\"\t\b\n#<>(){}[]]&=-+";
string word;
size_t pos,pos2;
size_t len=str.size();
pos=-1;
bool flag=true;
while(flag){
pos=str.find_first_not_of(delim,pos+1);
if(pos==string::npos)
break;
pos2=str.find_first_of(delim,pos+1);
if(pos2==string::npos)
{
pos2=len-1;
flag=false;
}
word=str.substr(pos,pos2-pos+1);
ret.push_back(word);
// cout<<word<<' ';
pos=pos2;
}
// cout<<endl;
return ret;
}
map<string, vector<int> >
xref(istream& in,
vector<string> find_words(const string&) = getwords)
{
string line;
int line_number = 0;
map<string, vector<int> > ret;
// read the next line
while (getline(in, line)) {
++line_number;
// break the input line into words
vector<string> words = find_words(line);
// remember that each word occurs on the current line
for (vector<string>::const_iterator it = words.begin();
it != words.end(); ++it)
ret[*it].push_back(line_number);
}
return ret;
}
int test1(){
string line;
while(getline(cin,line)){
getwords(line);
}
return 0;
}
int test2()
{
// call `xref' using `split' by default
map<string, vector<int> > ret = xref(cin);
// write the results
for (map<string, vector<int> >::const_iterator it = ret.begin();
it != ret.end(); ++it) {
// write the word
cout << it->first << " occurs on line(s): ";
// followed by one or more line numbers
vector<int>::const_iterator line_it = it->second.begin();
cout << *line_it; // write the first line number
++line_it;
// write the rest of the line numbers, if any
while (line_it != it->second.end()) {
cout << ", " << *line_it;
++line_it;
}
// write a new line to separate each word from the next
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
test2();
}


















代码如下:
 View Code
View Code
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <time.h>
using std::istream; using std::cin;
using std::copy; using std::cout;
using std::endl; using std::find;
using std::getline; using std::logic_error;
using std::map; using std::string;
using std::vector; using std::domain_error;
using std::rand;
typedef vector<string> Rule;
typedef vector<Rule> Rule_collection;
typedef map<string, Rule_collection> Grammar;
vector<string> getwords(const string& str)
{
vector<string> ret;
static string delim=" \\/,.;:!~*`\'\"\t\b\n#(){}[]&=-+";
string word;
size_t pos,pos2;
size_t len=str.size();
pos=-1;
bool flag=true;
while(flag){
pos=str.find_first_not_of(delim,pos+1);
if(pos==string::npos)
break;
pos2=str.find_first_of(delim,pos+1);
if(pos2==string::npos)
{
pos2=len-1;
flag=false;
}
word=str.substr(pos,pos2-pos+1);
ret.push_back(word);
cout<<word<<' ';
pos=pos2;
}
cout<<endl;
return ret;
}
// read a grammar from a given input stream
Grammar read_grammar(istream& in)
{
Grammar ret;
string line;
// read the input
while (getline(in, line)) {
// `split' the input into words
vector<string> entry = getwords(line);
if (!entry.empty())
// use the category to store the associated rule
ret[entry[0]].push_back(
Rule(entry.begin() + 1, entry.end()));
}
return ret;
}
void gen_aux(const Grammar&, const string&, vector<string>&);
int nrand(int);
vector<string> gen_sentence(const Grammar& g)
{
vector<string> ret;
gen_aux(g, "<sentence>", ret);
return ret;
}
bool bracketed(const string& s)
{
return s.size() > 1 && s[0] == '<' && s[s.size() - 1] == '>';
}
void
gen_aux(const Grammar& g, const string& word, vector<string>& ret)
{
if (!bracketed(word)) {
ret.push_back(word);
} else {
// locate the rule that corresponds to `word'
Grammar::const_iterator it = g.find(word);
if (it == g.end())
throw logic_error("empty rule");
// fetch the set of possible rules
const Rule_collection& c = it->second;
// from which we select one at random
const Rule& r = c[nrand(c.size())];
// recursively expand the selected rule
for (Rule::const_iterator i = r.begin(); i != r.end(); ++i)
gen_aux(g, *i, ret);
}
}
int main()
{
// generate the sentence
vector<string> sentence = gen_sentence(read_grammar(cin));
// write the first word, if any
vector<string>::const_iterator it = sentence.begin();
if (!sentence.empty()) {
cout << *it;
++it;
}
// write the rest of the words, each preceded by a space
while (it != sentence.end()) {
cout << " " << *it;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
// return a random integer in the range `[0,' `n)'
int nrand(int n)
{
if (n <= 0 || n > RAND_MAX)
throw domain_error("Argument to nrand is out of range");
const int bucket_size = RAND_MAX / n;
int r;
do r = rand() / bucket_size;
while (r >= n);
return r;
}
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <time.h>
using std::istream; using std::cin;
using std::copy; using std::cout;
using std::endl; using std::find;
using std::getline; using std::logic_error;
using std::map; using std::string;
using std::vector; using std::domain_error;
using std::rand;
typedef vector<string> Rule;
typedef vector<Rule> Rule_collection;
typedef map<string, Rule_collection> Grammar;
vector<string> getwords(const string& str)
{
vector<string> ret;
static string delim=" \\/,.;:!~*`\'\"\t\b\n#(){}[]&=-+";
string word;
size_t pos,pos2;
size_t len=str.size();
pos=-1;
bool flag=true;
while(flag){
pos=str.find_first_not_of(delim,pos+1);
if(pos==string::npos)
break;
pos2=str.find_first_of(delim,pos+1);
if(pos2==string::npos)
{
pos2=len-1;
flag=false;
}
word=str.substr(pos,pos2-pos+1);
ret.push_back(word);
cout<<word<<' ';
pos=pos2;
}
cout<<endl;
return ret;
}
// read a grammar from a given input stream
Grammar read_grammar(istream& in)
{
Grammar ret;
string line;
// read the input
while (getline(in, line)) {
// `split' the input into words
vector<string> entry = getwords(line);
if (!entry.empty())
// use the category to store the associated rule
ret[entry[0]].push_back(
Rule(entry.begin() + 1, entry.end()));
}
return ret;
}
void gen_aux(const Grammar&, const string&, vector<string>&);
int nrand(int);
vector<string> gen_sentence(const Grammar& g)
{
vector<string> ret;
gen_aux(g, "<sentence>", ret);
return ret;
}
bool bracketed(const string& s)
{
return s.size() > 1 && s[0] == '<' && s[s.size() - 1] == '>';
}
void
gen_aux(const Grammar& g, const string& word, vector<string>& ret)
{
if (!bracketed(word)) {
ret.push_back(word);
} else {
// locate the rule that corresponds to `word'
Grammar::const_iterator it = g.find(word);
if (it == g.end())
throw logic_error("empty rule");
// fetch the set of possible rules
const Rule_collection& c = it->second;
// from which we select one at random
const Rule& r = c[nrand(c.size())];
// recursively expand the selected rule
for (Rule::const_iterator i = r.begin(); i != r.end(); ++i)
gen_aux(g, *i, ret);
}
}
int main()
{
// generate the sentence
vector<string> sentence = gen_sentence(read_grammar(cin));
// write the first word, if any
vector<string>::const_iterator it = sentence.begin();
if (!sentence.empty()) {
cout << *it;
++it;
}
// write the rest of the words, each preceded by a space
while (it != sentence.end()) {
cout << " " << *it;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
// return a random integer in the range `[0,' `n)'
int nrand(int n)
{
if (n <= 0 || n > RAND_MAX)
throw domain_error("Argument to nrand is out of range");
const int bucket_size = RAND_MAX / n;
int r;
do r = rand() / bucket_size;
while (r >= n);
return r;
}
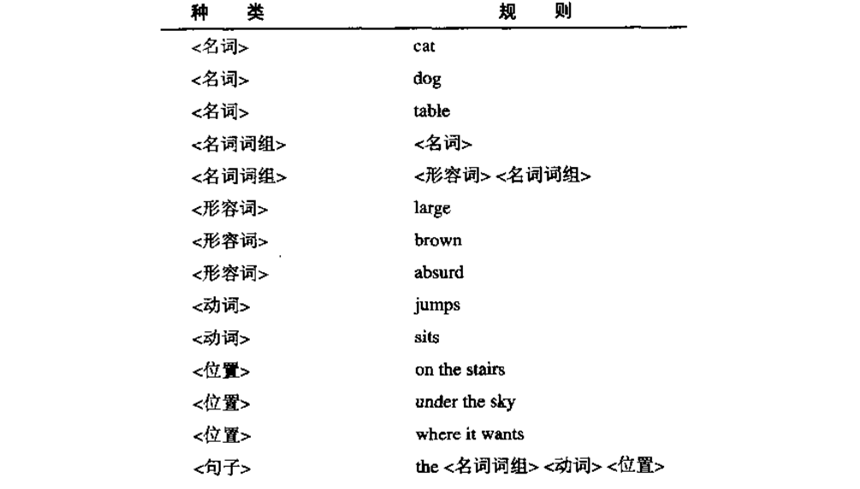
输入如下:
<noun> cat
<noun> dog
<noun> table
<noun_phrase> <adjective> <noun_phrase>
<noun_phrase> <noun>
<adjective> large
<adjective> brown
<adjective> absurd
<verb> jumps
<verb> sits
<location> on the stairs
<location> under the sky
<location> wherever it wants
<sentence> the <noun_phrase> <verb> <location>
<noun> dog
<noun> table
<noun_phrase> <adjective> <noun_phrase>
<noun_phrase> <noun>
<adjective> large
<adjective> brown
<adjective> absurd
<verb> jumps
<verb> sits
<location> on the stairs
<location> under the sky
<location> wherever it wants
<sentence> the <noun_phrase> <verb> <location>
第14章 句柄


代码如下:
Handle.h
 View Code
View Code
#ifndef GUARD_Handle_h
#define GUARD_Handle_h
template <class T> class Handle {
public:
Handle(): p(0) { }
Handle(const Handle& s): p(0) { if (s.p) p = s.p->clone(); }
Handle& operator=(const Handle&);
~Handle() { delete p; }
Handle(T* t): p(t) { }
operator bool() const { return p; }
T& operator*() const;
T* operator->() const;
private:
T* p;
};
#include <stdexcept>
using std::runtime_error;
template <class T>
Handle<T>& Handle<T>::operator=(const Handle& rhs)
{
if (&rhs != this) {
delete p;
p = rhs.p ? rhs.p->clone() : 0;
}
return *this;
}
template <class T>
T& Handle<T>::operator*() const
{
if (p)
return *p;
throw runtime_error("unbound Handle");
}
template <class T>
T* Handle<T>::operator->() const
{
if (p)
return p;
throw runtime_error("unbound Handle");
}
#endif
#define GUARD_Handle_h
template <class T> class Handle {
public:
Handle(): p(0) { }
Handle(const Handle& s): p(0) { if (s.p) p = s.p->clone(); }
Handle& operator=(const Handle&);
~Handle() { delete p; }
Handle(T* t): p(t) { }
operator bool() const { return p; }
T& operator*() const;
T* operator->() const;
private:
T* p;
};
#include <stdexcept>
using std::runtime_error;
template <class T>
Handle<T>& Handle<T>::operator=(const Handle& rhs)
{
if (&rhs != this) {
delete p;
p = rhs.p ? rhs.p->clone() : 0;
}
return *this;
}
template <class T>
T& Handle<T>::operator*() const
{
if (p)
return *p;
throw runtime_error("unbound Handle");
}
template <class T>
T* Handle<T>::operator->() const
{
if (p)
return p;
throw runtime_error("unbound Handle");
}
#endif


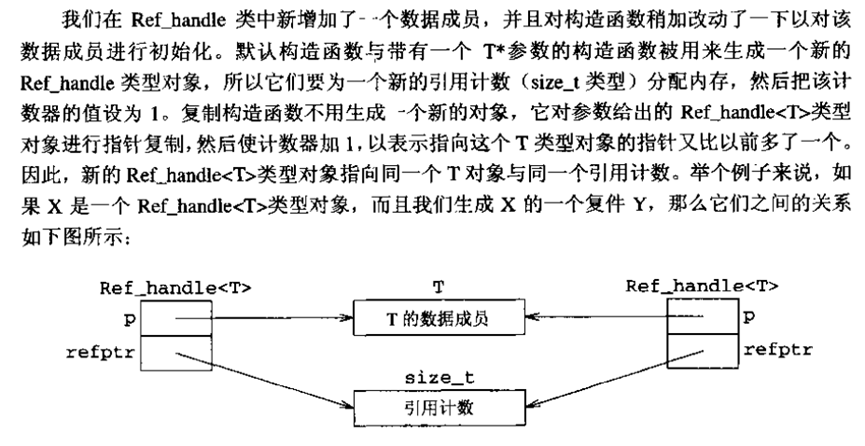
代码如下:
Ref_handle.h
 View Code
View Code
#ifndef Ref_handle_h
#define Ref_handle_h
#include <cstddef>
#include <stdexcept>
template <class T> class Ref_handle {
public:
// manage reference count as well as pointer
Ref_handle(): p(0), refptr(new size_t(1)) { }
Ref_handle(T* t): p(t), refptr(new size_t(1)) { }
Ref_handle(const Ref_handle& h): p(h.p), refptr(h.refptr) {
++*refptr;
}
Ref_handle& operator=(const Ref_handle&);
~Ref_handle();
// as before
operator bool() const { return p; }
T& operator*() const {
if (p)
return *p;
throw std::runtime_error("unbound Ref_handle");
}
T* operator->() const {
if (p)
return p;
throw std::runtime_error("unbound Ref_handle");
}
private:
T* p;
std::size_t* refptr; // added
};
template <class T>
Ref_handle<T>& Ref_handle<T>::operator=(const Ref_handle& rhs)
{
++*rhs.refptr;
// free the left-hand side, destroying pointers if appropriate
if (--*refptr == 0) {
delete refptr;
delete p;
}
// copy in values from the right-hand side
refptr = rhs.refptr;
p = rhs.p;
return *this;
}
template <class T> Ref_handle<T>::~Ref_handle()
{
if (--*refptr == 0) {
delete refptr;
delete p;
}
}
#endif
#define Ref_handle_h
#include <cstddef>
#include <stdexcept>
template <class T> class Ref_handle {
public:
// manage reference count as well as pointer
Ref_handle(): p(0), refptr(new size_t(1)) { }
Ref_handle(T* t): p(t), refptr(new size_t(1)) { }
Ref_handle(const Ref_handle& h): p(h.p), refptr(h.refptr) {
++*refptr;
}
Ref_handle& operator=(const Ref_handle&);
~Ref_handle();
// as before
operator bool() const { return p; }
T& operator*() const {
if (p)
return *p;
throw std::runtime_error("unbound Ref_handle");
}
T* operator->() const {
if (p)
return p;
throw std::runtime_error("unbound Ref_handle");
}
private:
T* p;
std::size_t* refptr; // added
};
template <class T>
Ref_handle<T>& Ref_handle<T>::operator=(const Ref_handle& rhs)
{
++*rhs.refptr;
// free the left-hand side, destroying pointers if appropriate
if (--*refptr == 0) {
delete refptr;
delete p;
}
// copy in values from the right-hand side
refptr = rhs.refptr;
p = rhs.p;
return *this;
}
template <class T> Ref_handle<T>::~Ref_handle()
{
if (--*refptr == 0) {
delete refptr;
delete p;
}
}
#endif
