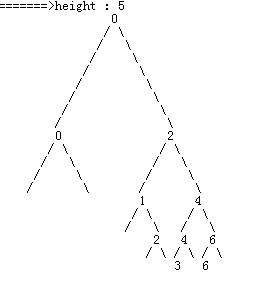
本文阐述使用Java如何打印二叉树,打印结果如下
1. 实现思路
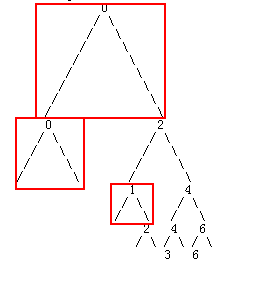
如图所示,以每个节点作为一个打印单元,每个节点包括数值和两边的分叉,而两边分叉的位置是由数值决定,所以每个节点的打印第一步需要找到数值的坐标点
1.1 找数值的坐标点
图中可以看到,除了根节点以外,其他节点数值均位于父节点的左分叉或右分叉的末端,也就是说,只要确认根节点的坐标,而两边的分叉的长度是固定的(后面会提到如何确定分叉的长度),就能确定整个树所有节点的坐标。而根节点的横向坐标很直观的看到就是位于整个树中间点,而竖向坐标位于坐标1。所以下面一步需要确认整个数的宽度。
1.2 树的宽度确定
树的宽度肯定是由树的高度来决定,如下图所示
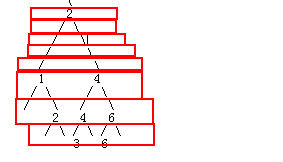
先将树进行分行,由于数值与上方斜线位于一列,所以不独立生成一行,而树的高度跟行数的映射关系如下
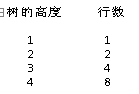
从中发现的规律是,行数 = 2(高度 - 1)
而行数与宽度的映射关系如下:
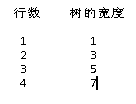
从中发现的规律是,宽度 = 2 * (行数) - 1
这样就能最终确定树的宽度与树的高度的关系,进而确认树的宽度值,而树的高度计算有很多现成方法,贴一下参考代码如下
public int height(){ if(root == null){ return 0 ; } return heightInner(root) ; } private int heightInner(TreeNode node){ if(node == null) return 0 ; TreeNode leftNode = node.getLeftNode() ; TreeNode rightNode = node.getRightNode() ; if(leftNode == null && rightNode == null){ return 1 ; } int leftHeight = heightInner(leftNode) ; int rightHeight = heightInner(rightNode) ; return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1 ; }
1.3 分叉长度的确定
数值的坐标确认了,剩下的是两边分叉,分叉的对于数值的相对位置是确定的,未知的是分叉的长度,下面介绍一下如何确定分叉长度
还有通过找规律的方式,如下图:
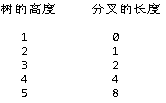
规律其实显而易见:
分叉的长度 =
if(高度 == 1){
0
}else{
2(树的高度 - 2)
}
这样分叉的长度也是可以根据高度来确定
1.4 如何打印
经过以上分析,我们就确认整个树的每个数值以及斜线的坐标位置,但是我们知道Java控制的输出是一行一行进行打印,每一行都可能多个节点的不同部分,我的做法是新建一个Map,Map的key就是行数,value则记录每一行需要打印的内容,由于控制台的打印是从左往右,所以对树前序遍历,根据之前分析的每个打印元素的坐标,用map的value记录需要打印的内容。
2. 贴上关键实现代码
public void printTree(){ if(root == null){ System.out.println("Tree is empty"); } int height = height() ; System.out.println("=======>height : " + height); int maxFloorNum = 1 ; for (int i = 1; i < height; i++) { maxFloorNum = maxFloorNum * 2 ; } int maxWidth = 2 * (maxFloorNum - 1) + 1 ; int col = (maxWidth - 1) / 2 + 1 ; Map<Integer,StringBuilder> lineRecord = new HashMap<>() ; printTreeFloor(root,1,col,height,lineRecord) ; Iterator<Integer> iterator = lineRecord.keySet().iterator() ; List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>() ; while (iterator.hasNext()) { list.add(iterator.next()) ; } Collections.sort(list); for (Integer line:list) { StringBuilder sb = lineRecord.get(line) ; System.out.println(sb); } } private void printTreeFloor(TreeNode node,int row,int col,int height,Map<Integer,StringBuilder> lineRecord){ if(node == null) return ; StringBuilder line = ensureLineInRecord(lineRecord,row) ; //打印空格 int existCol = line.length() ; for(int j = 0;j < col - existCol;j++){ line.append(" "); } line.append(node.getValue()); row++; line = ensureLineInRecord(lineRecord,row) ; int wingsWidth = 1 ; if(height == 1) wingsWidth = 0 ; for(int i = 1 ;i < height - 1 ; i++){ wingsWidth = wingsWidth * 2 ; } //打印分割线 for (int i = 1; i <= wingsWidth; i++) { //左边空格 existCol = line.length() ; for(int j = 0;j < col - i - existCol;j++){ line.append(" "); } line.append("/"); for(int j = 0;j < (i - 1) * 2 + 1;j++){ line.append(" "); } line.append("\"); row++; line = ensureLineInRecord(lineRecord,row) ; } printTreeFloor(node.getLeftNode(),row,col - wingsWidth,height - 1,lineRecord); printTreeFloor(node.getRightNode(),row,col + wingsWidth,height - 1,lineRecord); } private StringBuilder ensureLineInRecord(Map<Integer,StringBuilder> lineRecord,int row){ if(!lineRecord.containsKey(row)){ StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder() ; lineRecord.put(row, b) ; } return lineRecord.get(row) ; }
3. 总结
3.1 本文中分析的这种做法不支持数值的长度大于1
3.2 感觉做法还是有点复杂,不知道是不是我想多了,谁要有更好的做法,可以留言告知 o(∩_∩)o