Spring boot 多模块项目 + Swagger 让你的API可视化
前言
手写 Api 文档的几个痛点:
- 文档需要更新的时候,需要再次发送一份给前端,也就是文档更新交流不及时。
- 接口返回结果不明确
- 不能直接在线测试接口,通常需要使用工具,比如postman
- 接口文档太多,不好管理
为了前后台更好的对接,为了以后交接方便,为了不再长篇大论的手写 api 文档,那么就来用Swagger吧(不是打广告,确实强),它可以轻松的整合到 Spring 中,它既可以减少我们手写 api 文档的时间,同时又将说明文档整合到我们的代码中,这样前台看着也方便,后台工作也舒坦。
Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成、描述、调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 Web 服务。总体目标是使客户端和文件系统作为服务器以同样的速度来更新。文件的方法,参数和模型紧密集成到服务器端的代码,允许API来始终保持同步。Swagger 让部署管理和使用功能强大的API从未如此简单(其他好处网上自己搜在这里就不再多说了)。
官网地址: https://swagger.io/
本篇内容:
(1)构建多模块项目(可选单模块步骤)
(2)pom.xml 配置加载依赖
(3)Swagger 配置类(Bean)
(4)启动类配置
(5)创建工具类
(6)User 实例类
(7)定义 restful 接口(Controller 层)
为帮助快速入门上手使用,提供了简单的增删改查,使用的参数配置示例
本篇测试环境:
- SpringBoot 2.0.5.RELEASE
- Swagger 2.9.2
- JDK 1.8.191
成功截图:
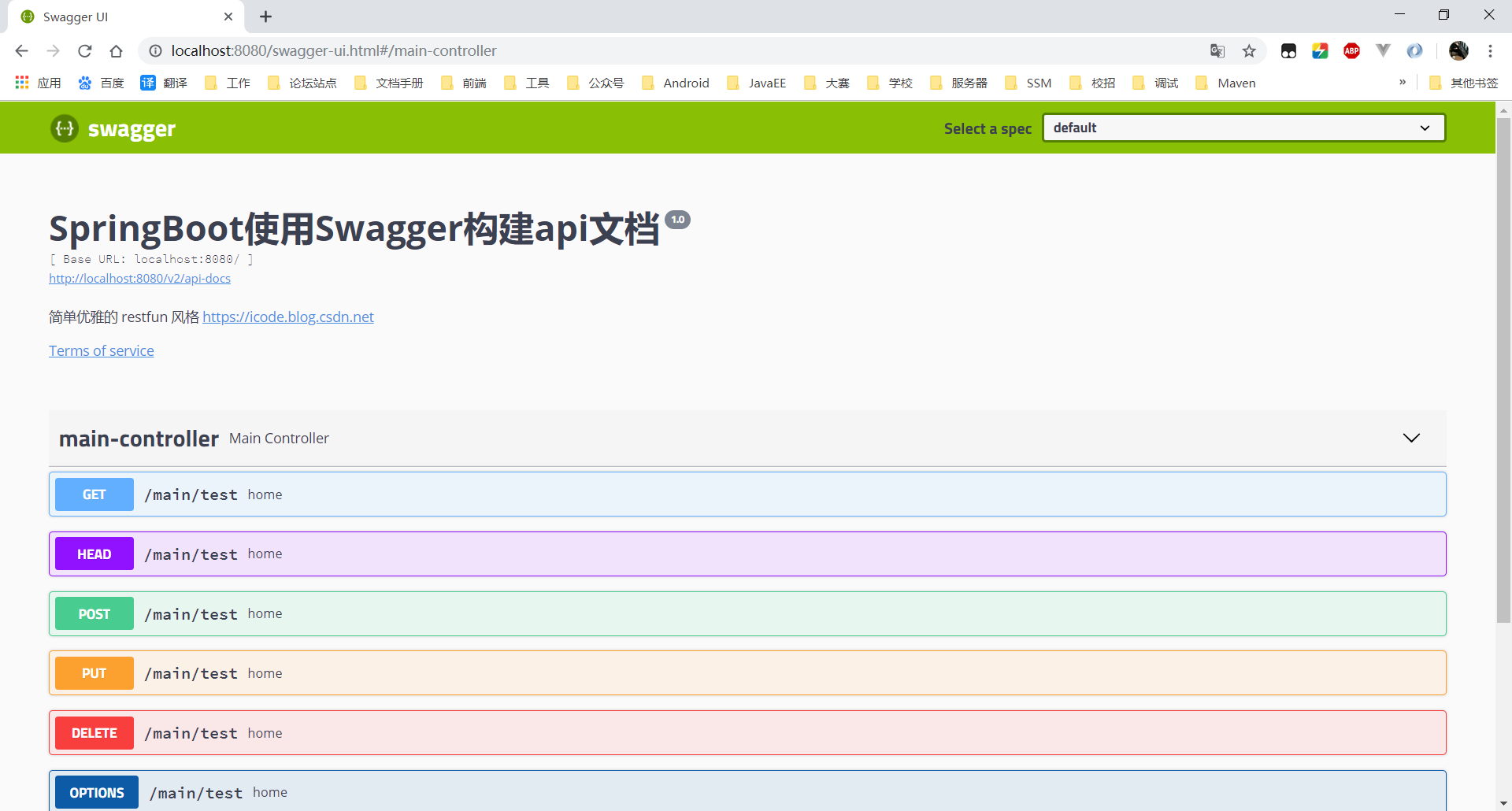
第一步:构建多模块项目(可选步骤)
如果想使用多模块,请先构建项目(建议):
如果不想使用多模块(下面模块请根据自己项目修改)
所有涉及到的文件结构:
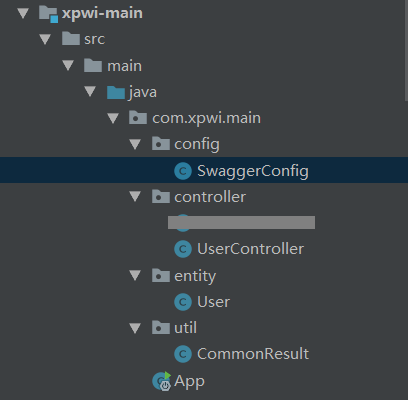
第二步:pom.xml 配置加载依赖
Spring boot 项目都会有一些依赖,为了更直观,只贴必要的部分
为你的 Spring Boot 项目再增加下面两个依赖:
pom.xml 配置:
<!--可以去下面地址查看最近版本-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
第三步:Swagger 配置类(Bean)
注意:
- basePackage 是需要自己配置的,换成自己需要扫描的包,会扫描其所有子包
- 一个就配主模块,多个就配大包,或分开配
用 @Configuration 注解该类,等价于XML中配置beans;
用 @Bean 标注方法等价于XML中配置bean
不是不可以使用 xml,提倡使用注解,是不是想起点什么?
SwaggerConfig.java 源代码:
package com.xpwi.main.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
/**
* 描述:Swagger2 Config Bean
*
* @author Xiao Pengwei
* @since 2019-03-27
*/
@Configuration
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.xpwi"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("SpringBoot使用Swagger构建api文档")
.description("简单优雅的 restfun 风格 https://icode.blog.csdn.net")
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://icode.blog.csdn.net")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
第四步:启动类配置
Application.class 加上注解 @EnableSwagger2 表示开启Swagger
package com.xpwi.main;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 描述:Spring Boot 多模块测试项目
* @author Xiao Pengwei
* @since 2019-03-25
*/
@EnableSwagger2
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
//扫描 main,test 模块中的下的所有包
//在 pom 加载子模块依赖才可以扫包
@ComponentScan({"com.xpwi.main","com.xpwi.test","com.xpwi.login"})
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//启动 Web 容器
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
System.out.println("[启动成功]"+new Date());
}
}
第五步:创建工具类
用于返回通用数据格式的工具类
CommonResult.java 源代码:
package com.xpwi.main.util;
/**
* 描述:通用返回类型
* @author Xiao Pengwei
* @since 2019-03-27
*/
public class CommonResult {
private String status;
private Object result;
private Object message;
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public Object getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(Object result) {
this.result = result;
}
public Object getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(Object message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
第六步:User 实例类
User 模拟对应数据库字段的实体类
User.java 源代码:
package com.xpwi.main.entity;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 描述:User 实体类
* @author Xiao Pengwei
* @since 2019-03-27
*/
public class User {
private String id;
private String username;
private int age;
private Date ctm;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getCtm() {
return ctm;
}
public void setCtm(Date ctm) {
this.ctm = ctm;
}
}
第七步:!定义 restful 接口(Controller 层)
最重要的一步,也是开发中最常用的一步
创建 UserController.java 源代码:
package com.xpwi.main.controller;
import com.xpwi.main.entity.User;
import com.xpwi.main.util.CommonResult;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import springfox.documentation.annotations.ApiIgnore;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 描述:Controller 类
* @author Xiao Pengwei
* @since 2019-03-27
*/
@RestController
@Api(value = "用户测试模块")
public class UserController {
// 创建线程安全的Map
static Map<String, User> users = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, User>());
/**
* 根据ID查询用户
* @param id
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation(value="获取用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来获取用户详细信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "String", paramType = "path")
@RequestMapping(value = "user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<CommonResult> getUserById (@PathVariable(value = "id") String id){
CommonResult commonResult = new CommonResult();
try {
User user = users.get(id);
commonResult.setResult(user);
commonResult.setStatus("ok");
} catch (Exception e) {
commonResult.setResult(e.getClass().getName() + ":" + e.getMessage());
commonResult.setStatus("error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(commonResult);
}
/**
* 查询用户列表
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation(value="获取用户列表", notes="获取用户列表")
@RequestMapping(value = "users", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<CommonResult> getUserList (){
CommonResult commonResult = new CommonResult();
try {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>(users.values());
commonResult.setResult(userList);
commonResult.setStatus("ok");
} catch (Exception e) {
commonResult.setResult(e.getClass().getName() + ":" + e.getMessage());
commonResult.setStatus("error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(commonResult);
}
/**
* 添加用户
* @param user
* @return
*/
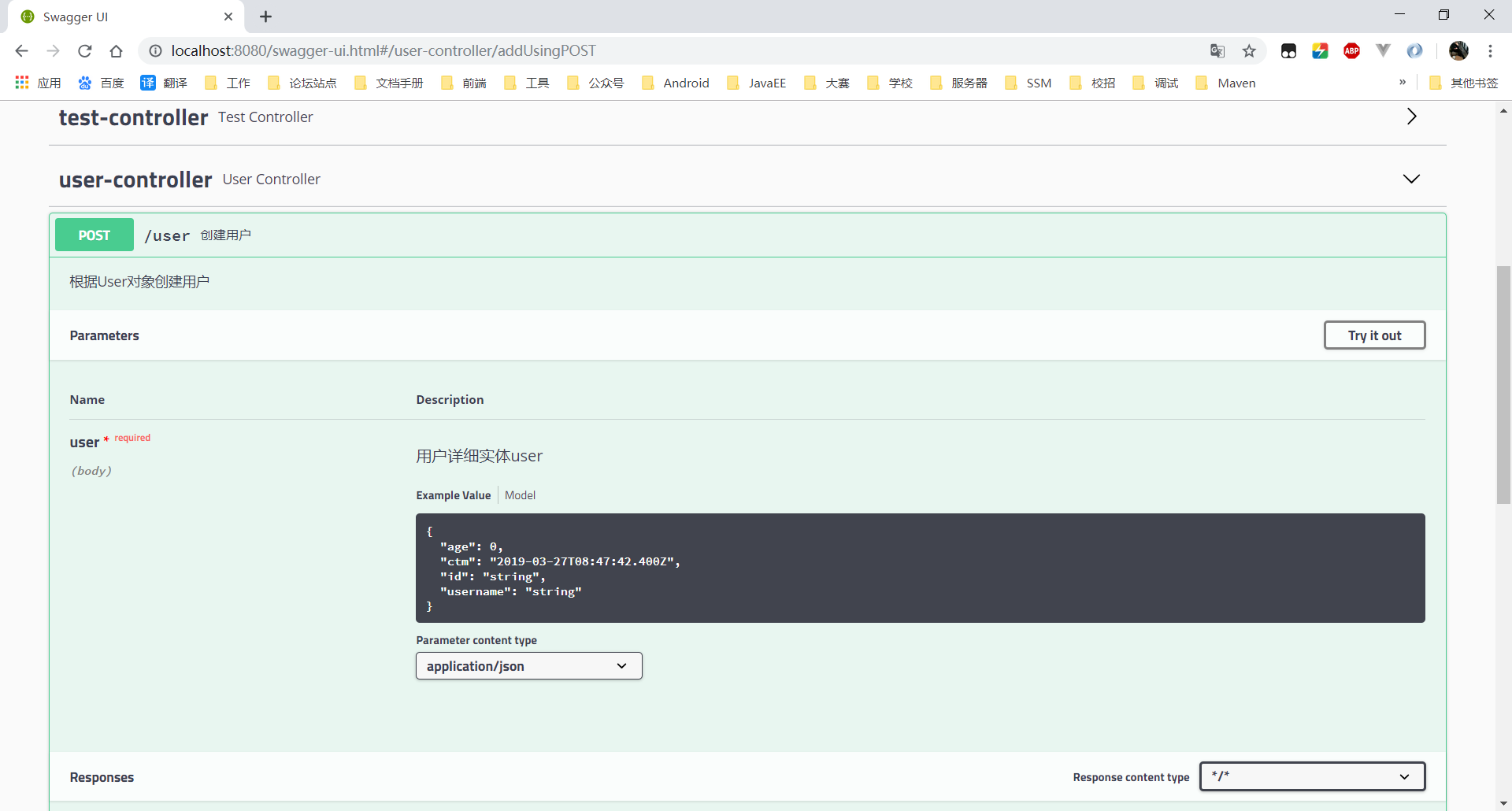
@ApiOperation(value="创建用户", notes="根据User对象创建用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
@RequestMapping(value = "user", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<CommonResult> add (@RequestBody User user){
CommonResult commonResult = new CommonResult();
try {
users.put(user.getId(), user);
commonResult.setResult(user.getId());
commonResult.setStatus("ok");
} catch (Exception e) {
commonResult.setResult(e.getClass().getName() + ":" + e.getMessage());
commonResult.setStatus("error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(commonResult);
}
/**
* 根据id删除用户
* @param id
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation(value="删除用户", notes="根据url的id来指定删除用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "String", paramType = "path")
@RequestMapping(value = "user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public ResponseEntity<CommonResult> delete (@PathVariable(value = "id") String id){
CommonResult commonResult = new CommonResult();
try {
users.remove(id);
commonResult.setResult(id);
commonResult.setStatus("ok");
} catch (Exception e) {
commonResult.setResult(e.getClass().getName() + ":" + e.getMessage());
commonResult.setStatus("error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(commonResult);
}
/**
* 根据id修改用户信息
* @param user
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation(value="更新信息", notes="根据url的id来指定更新用户信息")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "String",paramType = "path"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
})
@RequestMapping(value = "user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ResponseEntity<CommonResult> update (@PathVariable("id") String id, @RequestBody User user){
CommonResult commonResult = new CommonResult();
try {
User user1 = users.get(id);
user1.setUsername(user.getUsername());
user1.setAge(user.getAge());
users.put(id, user1);
commonResult.setResult(user1);
commonResult.setStatus("ok");
} catch (Exception e) {
commonResult.setResult(e.getClass().getName() + ":" + e.getMessage());
commonResult.setStatus("error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ResponseEntity.ok(commonResult);
}
@ApiIgnore//使用该注解忽略这个API
@RequestMapping(value = "/hi", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String jsonTest() {
return " hi you!";
}
}
第八步:启动 Spring Boot,打开浏览器
只需访问:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
swagger-ui.html 是默认的,不用担心自己没有创建这个文件,这个就是那个 UI 咯
第九步:常用注解
swagger 提供的常用的注解有:
- @Api:用在类上,说明该类的作用
- @ApiOperation:用在方法上,说明方法的作用,标注在具体请求上,value 和 notes 的作用差不多,都是对请求进行说明;tags 则是对请求进行分类的,比如你有好几个 controller,分别属于不同的功能模块,那这里我们就可以使用 tags 来区分了。
- @ApiImplicitParams:用在方法上包含一组参数说明
- @ApiImplicitParam:用在 @ApiImplicitParams 注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面。
- @ApiResponses:用于表示一组响应
- @ApiResponse:用在 @ApiResponses 中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
- @ApiModel:描述一个 Model 的信息(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用
@RequestBody 这样的场景,请求参数无法使用 @ApiImplicitParam 注解进行描述的时候)表明这是一个被 swagger 框架管理的 model,用于class上 - @ApiModelProperty: 这里顾名思义,描述一个 model 的属性,就是标注在被标注了 @ApiModel 的class的属性上,这里的 value 是对字段的描述,example 是取值例子,注意这里的 example很有用,对于前后端开发工程师理解文档起到了关键的作用,因为会在 api 文档页面上显示出这些取值来;这个注解还有一些字段取值,可以自己研究,举例说一个:position,表明字段在 model 中的顺序。
第十步:使用
一般 swagger 需要一下api的权限,需要在对应的模块进行排除:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-resources/configuration/ui
http://localhost:8080/swagger-resources
http://localhost:8080/api-docs
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
http://localhost:8080/swagger-resources/configuration/security
如果项目上线并且需要关闭 swagger 接口,可以通过配置权限,或者再 SwaggerConfig 里面
return new Docket 的时候加多一个.enable(false)
技术朋友群
- 一键加群
- QQ群:621657432