Java实验报告
班级 计科二班 学号 20188450 姓名 李代传
完成时间 2019.10.8
评分等级
实验四 类的继承
- 实验目的
- 理解抽象类与接口的使用;
- 了解包的作用,掌握包的设计方法。
- 实验要求
- 掌握使用抽象类的方法。
- 掌握使用系统接口的技术和创建自定义接口的方法。
- 了解 Java 系统包的结构。
- 掌握创建自定义包的方法。
- 实验内容
(一)抽象类的使用
1. 设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
2.编程技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
(二)使用接口技术
1定义接口Shape,其中包括一个方法size(),设计"直线"、"圆"、类实现Shape接口。分别创建一个"直线"、"圆"对象,将各类图形的大小输出。
- 编程技巧
(1) 接口中定义的方法在实现接口的具体类中要重写实现;
(2) 利用接口类型的变量可引用实现该接口的类创建的对象。
- 实验过程(请自己调整格式)
实验代码1



package 抽象类简单实现;
public abstract class Shape {
public abstract double area();
}
package 抽象类简单实现;
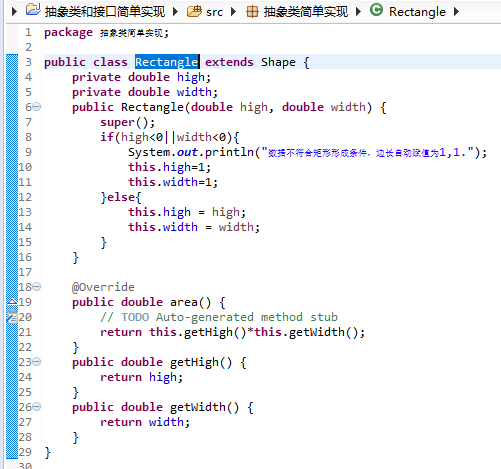
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private double high;
private double width;
public Rectangle(double high, double width) {
super();
if(high<0||width<0){
System.out.println("数据不符合矩形形成条件,边长自动赋值为1,1.");
this.high=1;
this.width=1;
}else{
this.high = high;
this.width = width;
}
}
@Override
public double area() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.getHigh()*this.getWidth();
}
public double getHigh() {
return high;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
}
package 抽象类简单实现;
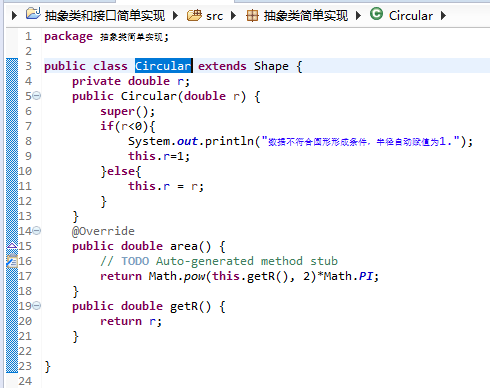
public class Circular extends Shape {
private double r;
public Circular(double r) {
super();
if(r<0){
System.out.println("数据不符合圆形形成条件,半径自动赋值为1.");
this.r=1;
}else{
this.r = r;
}
}
@Override
public double area() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return Math.pow(this.getR(), 2)*Math.PI;
}
public double getR() {
return r;
}
}
package 抽象类简单实现;
public class Triangle extends Shape {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public Triangle(double a, double b, double c) {
super();
if(a<0||b<0||c<0||a+b<=c||a+c<=b||b+c<=a){
System.out.println("不满足三角形形成条件,边长自动赋值为3,4,5。");
this.a=3;
this.b=4;
this.c=5;
}else{
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
}
@Override
public double area() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double p=(this.getA()+this.getB()+this.getC())/2;
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
}
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
}
package 抽象类简单实现;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Shape[] shapes=new Shape[3];
Shape triangle=new Triangle(10,3,20);
shapes[0]=triangle;
Shape rectangle=new Rectangle(10,20);
shapes[1]= rectangle;
Shape circular=new Circular(10);
shapes[2]=circular;
for(Shape shape:shapes){
System.out.print(shape.toString());
System.out.println("的面积为:"+shape.area());
}
}
}
实验结果1

实验代码2


package 接口简单实现;
public interface Shape {
void size();
}
package 接口简单实现;
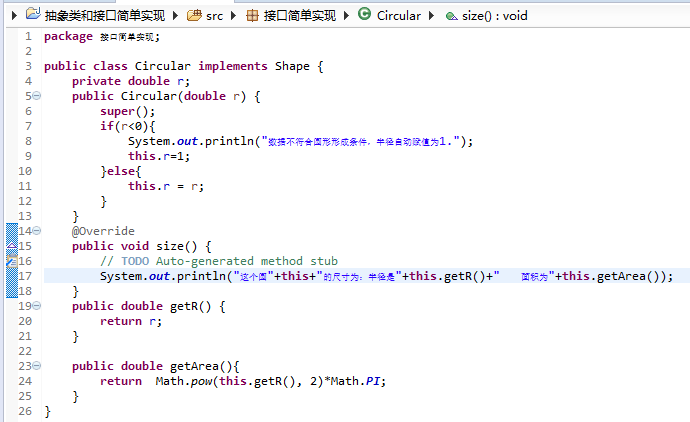
public class Circular implements Shape {
private double r;
public Circular(double r) {
super();
if(r<0){
System.out.println("数据不符合圆形形成条件,半径自动赋值为1.");
this.r=1;
}else{
this.r = r;
}
}
@Override
public void size() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("这个圆"+this+"的尺寸为:半径是"+this.getR()+" 面积为"+this.getArea());
}
public double getR() {
return r;
}
public double getArea(){
return Math.pow(this.getR(), 2)*Math.PI;
}
}
package 接口简单实现;
public class StraightLine implements Shape {
private double length;
public StraightLine(double length) {
super();
if(length<0){
System.out.println("数据不符合直线形成条件,长度自动赋值为1");
this.length=1;
}else{
this.length = length;
}
}
@Override
public void size() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("这条直线"+this+"长度为"+this.getLength());
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
}
package 接口简单实现;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Shape[] shapes=new Shape[2];
Shape circular=new Circular(10);
shapes[0]=circular;
Shape straightLine=new StraightLine(30);
shapes[1]=straightLine;
for(Shape shape:shapes){
System.out.print("图形的size为:");
shape.size();
System.out.println();
}
}
}
实验结果2

- 结论
加深了我对于各类方法的认识,以及对于数据各方面的考虑。其实我想加的话,还可以用InputMismatchException来控制得到数据只能为数字或者能转化成数字的字符串。但我不用,嘻嘻。
六 :课程总结
老师讲的很好,并且讲的很细节,就比如那个java对象池,里面保存的匿名字符串对象,我就忽略了。
抽象父类:模板作用;
接口:标准作用。
能用接口的尽量优先使用接口。
Object类的原始.equals()方法比较的是地址,如果子类需要自行使用的话,需要覆写后使用。同理,原始的.toString()方法是打印类名并@十六进制地址,如果需要自行使用的话,应该先覆写后使用。