1 Pom文件
1.1 spring-boot-starter-parent
表示当前pom文件从spring-boot-starter-parent继承下来,在spring-boot-starter-parent中提供了很多默认配置,可以简化我们的开发。
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
- Java版本和编码方式
<properties>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<resource.delimiter>@</resource.delimiter>
<maven.compiler.source>${java.version}</maven.compiler.source>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.target>${java.version}</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
- 依赖管理spring-boot-dependencies
<properties>
<activemq.version>5.15.9</activemq.version>
<antlr2.version>2.7.7</antlr2.version>
<appengine-sdk.version>1.9.73</appengine-sdk.version>
<artemis.version>2.6.4</artemis.version>
...
</properties>
这样比如使用starter-web的时候就不需要指定版本号
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
- 使用自己的parent项目
这时候将依赖管理的问题放到dependencyManagement中。
官网说明文档见:13.2.2 Using Spring Boot without the Parent POM
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
1.2 打包管理
使用mvn package打包的plugin。
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
1.3 Starters
官网见:13.5 Starters
Starters are a set of convenient dependency descriptors that you can include in your application. You get a one-stop shop for all the Spring and related technologies that you need without having to hunt through sample code and copy-paste loads of dependency descriptors. For example, if you want to get started using Spring and JPA for database access, include the spring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependency in your project.
- 官方starter命名
spring-boot-starter-*
- 自定义starter命名
thirdpartyproject-spring-boot-starter
- spring-boot-web-starter
查看其diagram,可以排除某个依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
2 XXXApplication
2.1 @SpringBootApplication
官网见:18. Using the @SpringBootApplication Annotation
等同于@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan和@Configuration
2.2 SpringApplication.run
官网见:23. SpringApplication
3 配置文件
3.1 初步感受
server.port=9090
3.2 yml文件
application.yml
3.3 给属性注入值
- 实体类Person和IDCard
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
private String[] hobbies;
private IDCard idCard;
...
}
public class IDCard {
private int id;
private String number;
}
- yml注入写法
person:
name: Jack
age: 17
birthday: 1997/06/01
hobbies: [code,sing,share]
idCard:
id: 1
number: 111
- Person类增加注解
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person")
- 测试
@Autowired
private Person person;
如果Person类上报错,在Pom文件中加入如下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</dependency>
4 处理动静态资源
4.1 动态资源
官网见:90.2 Reload Templates without Restarting the Container
- templates
resources目录下有一个templates文件夹,可以将动态资源放到其中
- 引入thymeleaf
<!--thymeleaf的jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
- templates下新建test.html文件
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
</head>
<body>
<span style="color:red; font-size:30pt" th:text="${str}"></span>
</body>
- controller中return test
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/gupao")
public class GupaoController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model){
String str="hello spring boot";
//想要动态的显示在网页当中
model.addAttribute("str",str);
//接下来的页面是能够动态显示传过来的数据
return "test";
}
}
4.2 静态资源
- static文件夹
在resources目录下有一个static文件夹,可以将静态资源放到其中,浏览器可以直接访问。
- 静态资源其他存放文件夹
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/"
"classpath:/resources/"
"classpath:/static/"
"classpath:/public/"
- WebMvcAutoConfiguration源码分析
WebMvcAutoConfiguration--->WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter.addResourceHandlers(xxx)--->
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()
return this.staticLocations;
private String[] staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = {
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
- 自定义静态资源文件夹
观察
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties {
配置application.properties
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/gupao/
5 整合MyBatis
5.1 需求
通过Spring Boot Web项目api接口的方式,整合MyBatis实现crud的操作。
5.2 创建Spring Boot Web项目
重温一下web项目创建的过程。
5.3 引入项目中需要的starter依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
5.4 创建数据库表
db_gupao_springboot--->t_user
5.5 创建domain/User对象
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String number;
...
}
5.6 开发dao层
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
User find(String username);
List<User> list();
int insert(User user);
int delete(int id);
int update(User user);
}
5.7 开发service层
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
public UserMapper userMapper;
public User findByUsername(String username){
return userMapper.find(username);
}
public List<User> listUser(){
return userMapper.list();
}
public int insertUser(User user){
return userMapper.insert(user);
}
public int updateUser(User user){
return userMapper.update(user);
}
public int delete(int id){
return userMapper.delete(id);
}
}
5.8 开发controller层
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/user",method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/listone")
@ResponseBody
public User listOne(String username){
return userService.findByUsername(username);
}
@RequestMapping("/listall")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> listAll(){
return userService.listUser();
}
@RequestMapping(value="/add",method= RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String add(User user){
int result=userService.insertUser(user);
if(result>=1) {
return "添加成功";
}else{
return "添加失败";
}
}
@RequestMapping(value="/update",method= RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String update(User user){
int result=userService.updateUser(user);
if(result>=1) {
return "修改成功";
}else{
return "修改失败";
}
}
@RequestMapping(value="/delete",method= RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(int id){
int result=userService.delete(id);
if(result>=1) {
return "删除成功";
}else{
return "删除失败";
}
}
}
5.9 resources目录下创建mapper文件夹---UserMapper.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC
"-//mybatis.org//DTD com.example.Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.csdn.springbootmybatis.dao.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="result" type="com.gupao.springbootmybatis.domain.User">
<result property="username" column="username"/>
<result property="password" column="password"/>
<result property="number" column="number"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="find" resultMap="result">
SELECT * FROM t_user where username=#{username}
</select>
<select id="list" resultMap="result">
SELECT * FROM t_user
</select>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.gupao.springbootmybatis.domain.User"
keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
INSERT INTO t_user
(
id,username,password,number
)
VALUES (
#{id},
#{username, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{password, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{number}
)
</insert>
<delete id="delete" parameterType="int">
delete from t_user where id=#{id}
</delete>
<update id="update" parameterType="com.gupao.springbootmybatis.domain.User">
update t_user set user.username=#{username},user.password=#{password},user.number=#{number} where user.id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
5.10 application.properties文件配置
#数据源
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/boot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#mybatis托管mapper文件
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
5.11 启动项目测试
- 查询
http://localhost:8888/user/listone?username=Jack
- 全部查询
http://localhost:8888/user/listall
- 增加
http://localhost:8888/user/add?id=3&username=AAA&password=111111&number=300
- 更新
http://localhost:8888/user/update?id=3&username=BBB
- 删除
http://localhost:8888/user/delete?id=3
6 项目打包
- jar包
mvn -Dmaven.test.skip -U clean install
java -jar xxx.jar
- war包
<groupId>com.csdn</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-demo2</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
7 Spring Boot in less than 10 minutes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhkwLtDIMHI&feature=youtu.be
BUILD ANYTHING WITH SPRING BOOT
Spring Boot is the starting point for building all Spring-based applications. Spring Boot is designed to get you up and running as quickly as possible, with minimal upfront configuration of Spring.
| - | Get started in seconds using Spring Initializr |
| - | Build anything: REST API, WebSocket, web, streaming, tasks, and more |
| - | Simplified security |
| - | Rich support for SQL and NoSQL |
| - | Embedded runtime support: Tomcat, Jetty, and Undertow |
| - | Developer productivity tools such as LiveReload and Auto Restart |
| - | Curated dependencies that just work |
| - | Production-ready features such as tracing, metrics, and health status |
| - | Works in your favorite IDE: Spring Tool Suite, IntelliJ IDEA, and NetBeans |
7.1 IDEA创建工程
group:com.example
artifact:bootiful
dependencies:Reactive Web,Reactive MongoDB,Lombok,Actuator,Security
7.2 DATA DRIVE
Spring Data integrates seamlessly with SQL and NoSQL persistence stores. Spring Data supports reactive data access,too!
@Component
class DataWriter implements ApplicationRunner {
private final CustomerRepository customerRepository;
DataWriter(CustomerRepository customerRepository) {
this.customerRepository = customerRepository;
}
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
Flux.just("Jack", "Rechal", "Richard", "Jobs")
.flatMap(name -> customerRepository.save(new Customer(null, name)))
.subscribe(System.out::println);
}
}
interface CustomerRepository extends ReactiveMongoRepository<Customer, String> {
}
@Document
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
class Customer {
private String id,name;
public Customer(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
7.3 REST
On the web,nobody knows you're a reactive microservice.
@SpringBootApplication
public class BootifulApplication {
@Bean
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routes(CustomerRepository cr){
return RouterFunctions.route(GET("/customers"),serverRequest -> ok().body(cr.findAll(),Customer.class));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BootifulApplication.class, args);
}
}
7.4 OBSERVABILITY
How's your app's health?Who better to articulate that then the application itself?
Spring Boot featurese strong opinions,loosely held.
It's easy to change any of them with properties or pluggable implementations
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=*
@Bean
HealthIndicator healthIndicator(){
return () -> Health.status("I <3 Production").build();
}
访问:curl http://localhost:8080/actuator/health | jq
7.5 SECURITY
Effortlessly plugin authentication and authorization in a traditional or reactive application with Spring Security
@Bean
MapReactiveUserDetailsService users(){
return new MapReactiveUserDetailsService(User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("user").password("pw").roles("USER").build());
}
访问:curl -vu user:pw http://localhost:8080/customers | jq
7.6 TO PRODUCTION
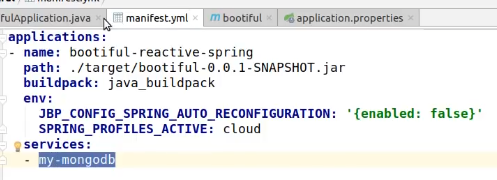
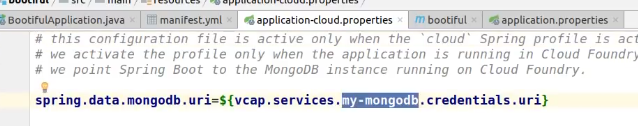
Let's provision a MongoDB instance,configure our application's route and MongoDB binding,and then push our application to production with Cloud Foundry.
命令切换到bootiful根目录下
cf services
定位到my-mongodb文件夹
- 复制对应文件,修改和观察


大家可以扫描下方二维码关注下我的微信公众号,公众号内没有福利,只会定期生产技术性文章!
